Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Cold - Homeopathic remedies
A cold is a common viral infection that affects the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, throat, and sinuses. Cold symptoms usually start within a few days of exposure to the virus and may include:
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Sneezing
- Congestion
- Mild body aches
- Mild headache
- Low-grade fever
Cold viruses are easily transmitted from person to person through close contact or touching contaminated surfaces. The best way to prevent colds is to practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently with soap and water, avoiding close contact with sick people, and covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze.
Treatment for a cold typically involves rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and using over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms such as pain, fever, and congestion. Antibiotics are not effective against cold viruses, as they only work against bacterial infections. Most people recover from a cold within a week or two, although some may experience lingering symptoms for longer.
If your cold symptoms are severe or do not improve after a few days, it is important to seek medical attention to rule out other underlying conditions and receive appropriate treatment. Additionally, if you have a weakened immune system, such as from an underlying medical condition or medication, you may be at higher risk for complications from a cold and should seek medical attention promptly.

Rheumatism

Filariasis

Sensuality
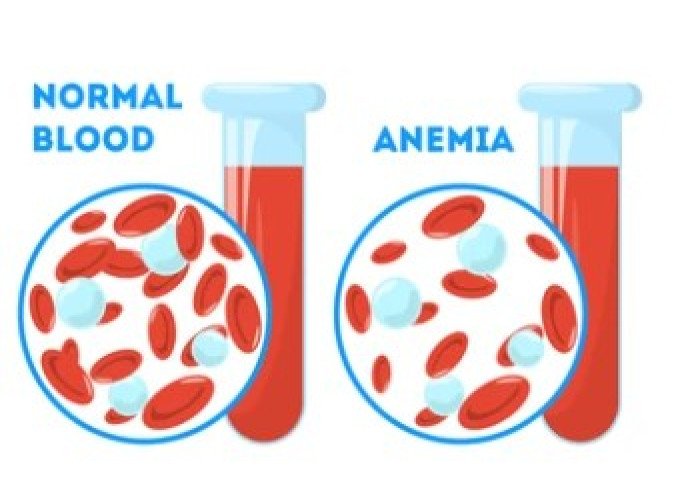
Hemoglobin deficiency
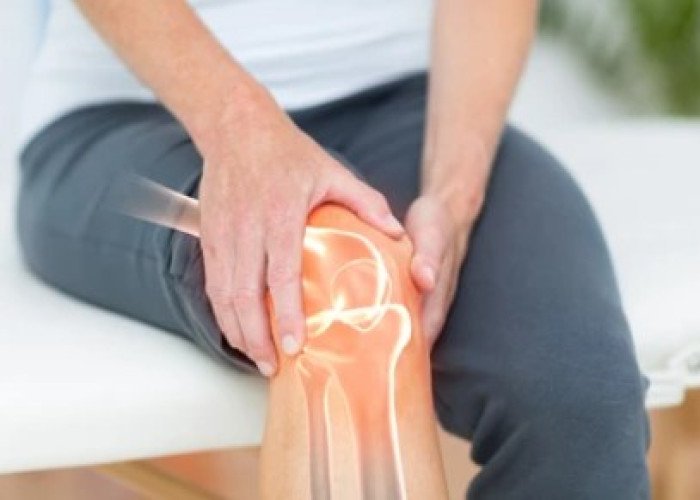
Knee arthritis

Ghost dream

Sadness

Heart attack
Cold, সর্দি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.