Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Bronchitis - Homeopathic remedies
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition that occurs when the bronchial tubes in the lungs become inflamed, often due to an infection or irritation. It can be acute, lasting for a few weeks, or chronic, lasting for several months or longer.
Symptoms of bronchitis include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and production of mucus or phlegm. In acute cases, symptoms may last for a few weeks and typically improve with rest and self-care measures. In chronic cases, symptoms may persist or recur for several months or longer, leading to ongoing respiratory problems and decreased quality of life.
Treatment for bronchitis may involve a combination of home remedies and medical treatments. Home remedies may include getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, using a humidifier or steam inhalation to ease breathing, and avoiding irritants such as smoke or pollution. Over-the-counter medications such as cough suppressants or pain relievers may also help manage symptoms.
In cases of bacterial bronchitis, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection. In chronic cases, bronchodilators or corticosteroids may be used to help improve breathing and reduce inflammation.
Preventing bronchitis involves taking steps to reduce the risk of respiratory infections, such as washing hands regularly, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and getting vaccinated against the flu and pneumonia. It is also important to avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, as well as other irritants such as air pollution or chemical fumes, which can increase the risk of bronchitis and other respiratory conditions.
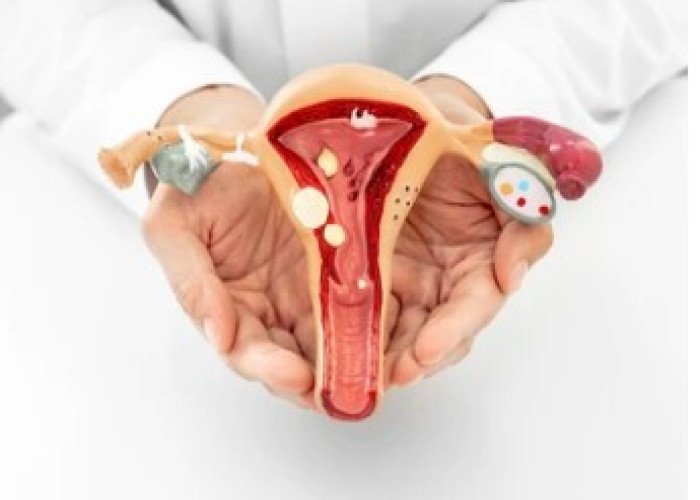
Gangrene of uterus

Snoring
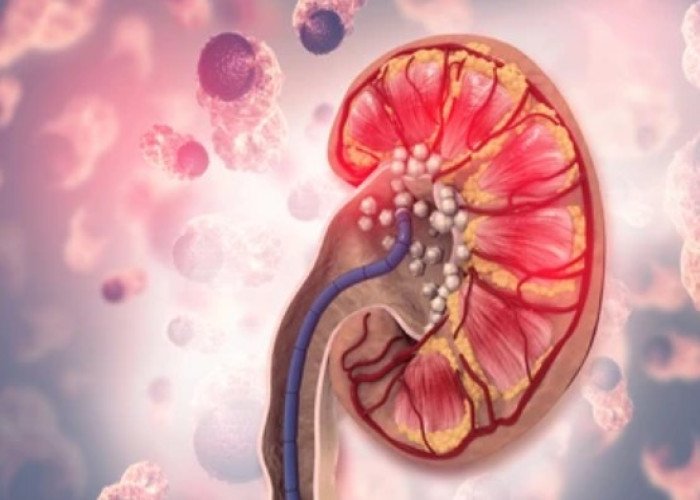
Urinary stones
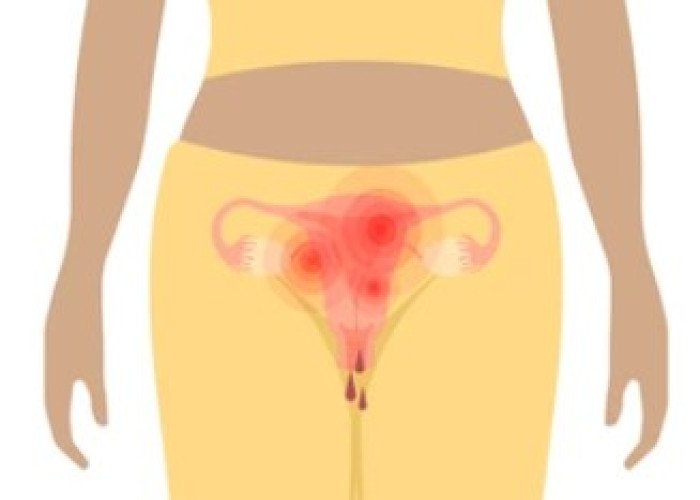
Bleeding from uterus

Hot sensitive
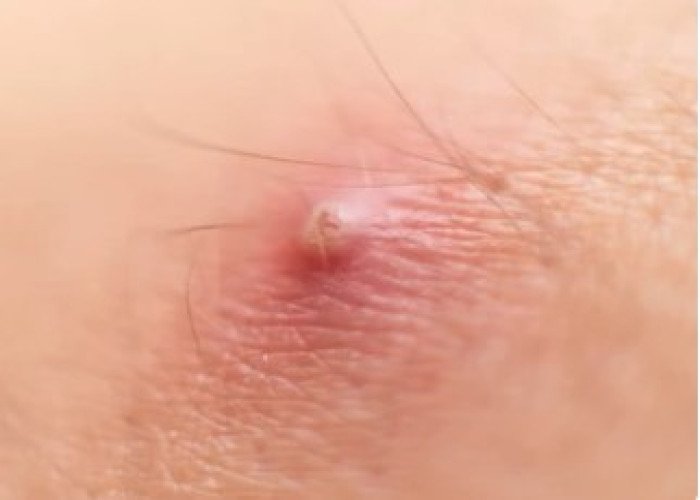
Malignant boil
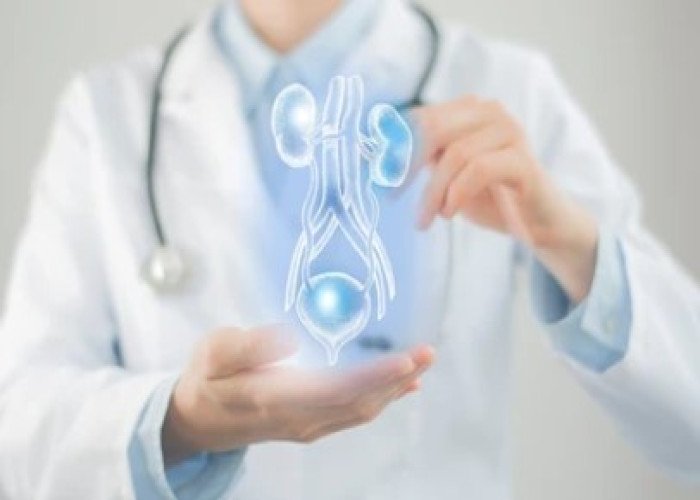
Urinary incontinence

Back pain
Bronchitis, ব্রঙ্কাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.