Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Diarrhea - Homeopathic remedies
Diarrhea is a common condition that is characterized by frequent loose or watery stools. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral or bacterial infections, food poisoning, inflammatory bowel disease, lactose intolerance, and certain medications.
Symptoms of diarrhea may include abdominal pain, cramping, nausea, vomiting, and dehydration. In most cases, diarrhea can be treated at home by staying hydrated with water, clear broths, or electrolyte-rich drinks and by avoiding solid foods until the diarrhea subsides. Over-the-counter medications such as loperamide may also be used to help manage symptoms.
If diarrhea persists for more than a few days or is accompanied by severe symptoms such as high fever, blood in the stool, or severe dehydration, it is important to seek medical attention. In these cases, treatment may involve prescription medications, IV fluids, and additional testing to determine the underlying cause of the diarrhea.
Preventing diarrhea involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and thoroughly, especially after using the bathroom or handling food, and avoiding food or water that may be contaminated.
Urinary incontinence

Warts
Plague

Bed-sores
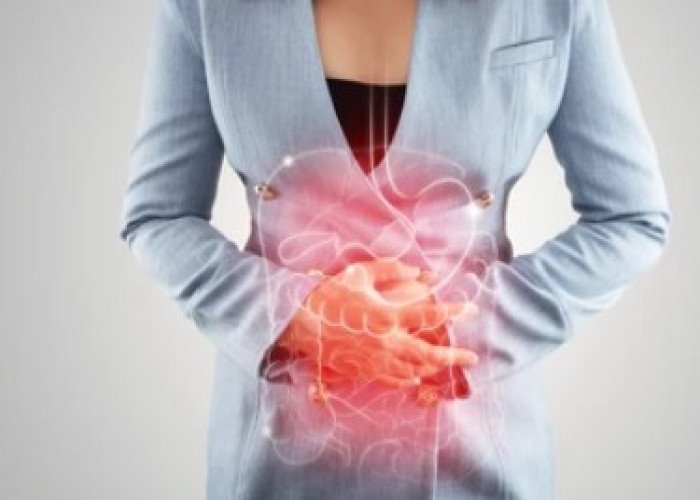

Indigestion

Menstrual cramps
Anemia

Acne
Diarrhea, ডায়রিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.