Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
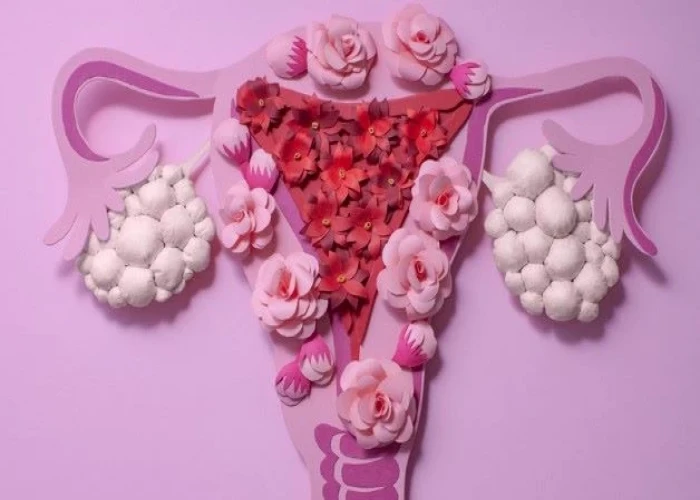
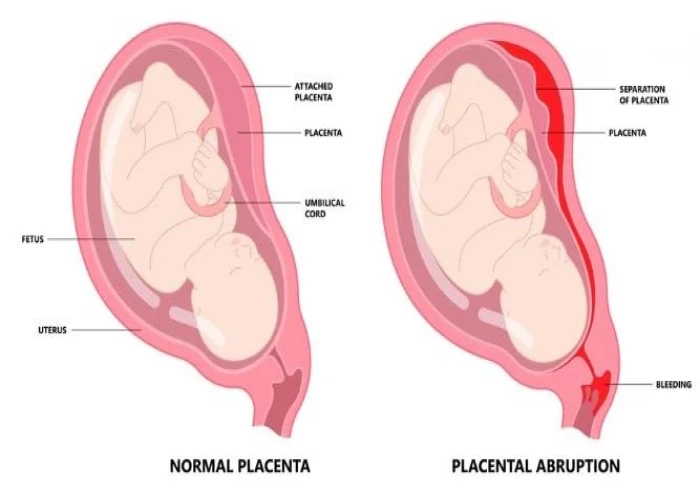
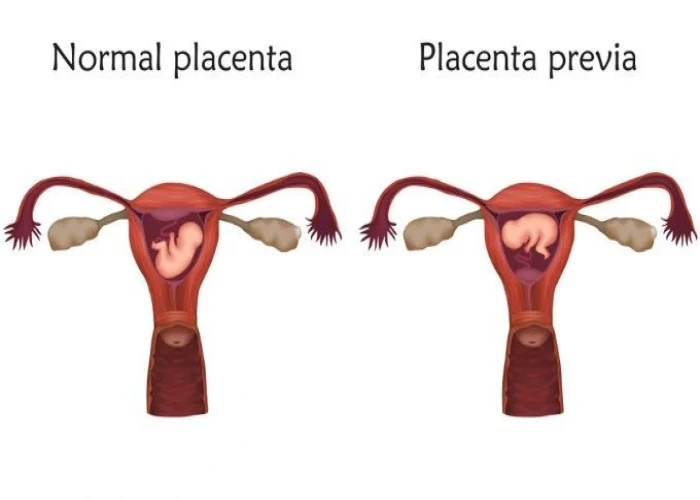
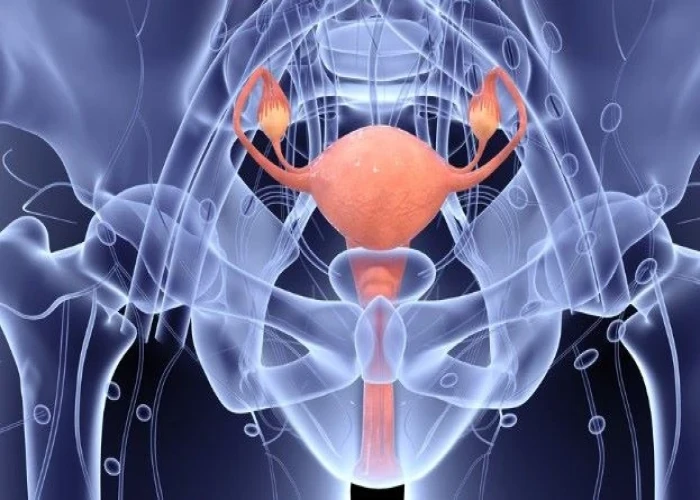
Vagina - Diseases
The vagina is an elastic, muscular canal that extends from the vulva (external genitalia) to the cervix of the uterus. It is an important part of the female reproductive system and serves as the birth canal during childbirth. It also allows for menstrual flow to exit the body.
The walls of the vagina are lined with mucous membranes and folds of tissue called rugae, which allow the vagina to stretch and accommodate sexual intercourse, childbirth, and menstrual flow. The vagina has a natural lubrication mechanism that helps to reduce friction during sexual intercourse.
The vagina is also home to a complex ecosystem of microorganisms, collectively called the vaginal microbiome. These microorganisms help to maintain a healthy environment in the vagina and protect against infections.
Various medical conditions can affect the vagina, including vaginal infections, vaginal dryness, and vaginal atrophy (thinning and inflammation of the vaginal walls). Treatment for these conditions can range from medication to lifestyle changes to surgery, depending on the severity of the condition and the woman's individual circumstances.

Small intestine
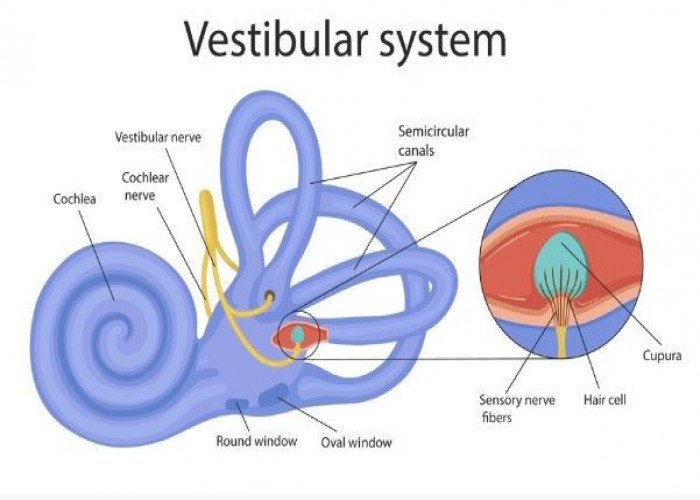
Vestibule of the Inner ear
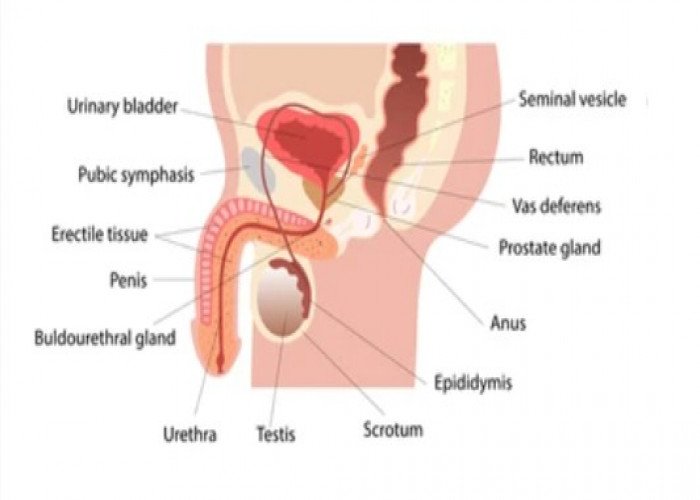
Penis

Retina Eye

Nails

Gallbladder

Abdomen
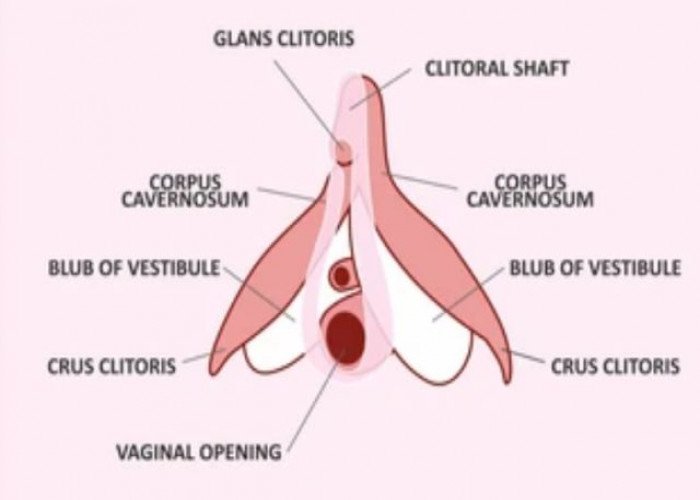
Clitoris
Vagina, যোনি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.