Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Menorrhagia (Heavy menstrual bleeding)
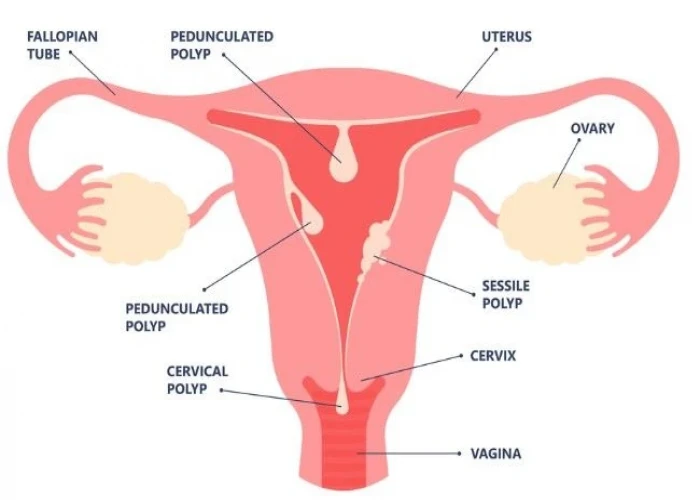
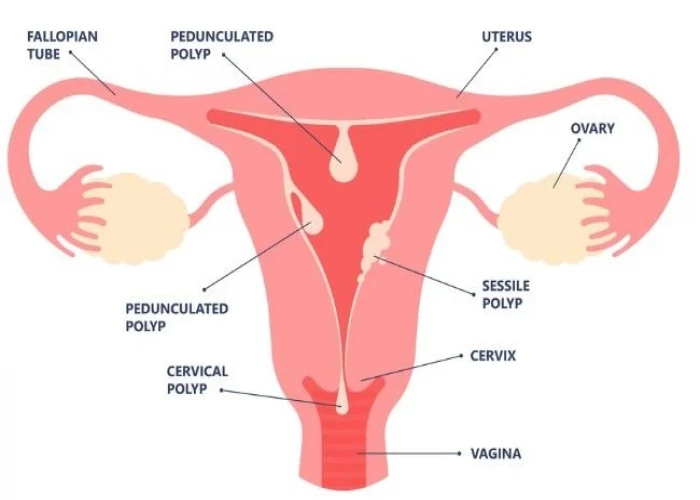
Menorrhagia is the medical term for heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding that can interfere with a woman's daily activities. It is a common problem affecting many women at some point in their lives. The amount of blood loss during a menstrual period can vary widely from woman to woman, but menorrhagia is diagnosed when a woman loses more than 80 ml of blood per cycle.
Symptoms of menorrhagia may include:
- Menstrual periods lasting longer than seven days
- Heavy bleeding that requires changing tampons or pads every one to two hours or more frequently
- Blood clots larger than a quarter
- Anemia (low red blood cell count), which can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath
The causes of menorrhagia can vary and may include:
- Hormonal imbalances, such as anovulation or thyroid disorders
- Uterine fibroids or polyps
- Endometriosis
- Adenomyosis
- Blood clotting disorders
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Certain medications, such as blood thinners or hormonal contraceptives
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
Treatment options for menorrhagia depend on the underlying cause and severity of the bleeding. They may include:
- Hormonal medications, such as oral contraceptives or progesterone therapy
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce bleeding and pain
- Tranexamic acid, a medication that helps reduce heavy menstrual bleeding
- Surgical procedures, such as endometrial ablation or hysterectomy, for severe or refractory cases
It's important for women to talk to their healthcare provider if they experience heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, as it can cause anemia and other health problems if left untreated. Women should also continue to receive regular gynecologic care, including pelvic exams and cervical cancer screening, as they age.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Heavy menstrual period or bleeding
- Menstrual periods more than a week
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Needing to use double sanitary protection to control menstrual flow
- Needing to wake up to change sanitary protection during the night
- Passing blood clots larger than a quarter
- Restricting daily activities due to heavy menstrual flow
- Symptoms of anemia, such as tiredness, fatigue or shortness of breath
- Throbbing or cramping pain in the lower abdomen that can be intense
Disease Causes
Menorrhagia (heavy menstrual bleeding)
In some cases, the cause of heavy menstrual bleeding is unknown, but a number of conditions may cause menorrhagia. Common causes include:
- Hormone imbalance. In a normal menstrual cycle, a balance between the hormones estrogen and progesterone regulates the buildup of the lining of the uterus (endometrium), which is shed during menstruation. If a hormone imbalance occurs, the endometrium develops in excess and eventually sheds by way of heavy menstrual bleeding.
- A number of conditions can cause hormone imbalances, including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), obesity, insulin resistance and thyroid problems.
- Dysfunction of the ovaries. If your ovaries don't release an egg (ovulate) during a menstrual cycle (anovulation), your body doesn't produce the hormone progesterone, as it would during a normal menstrual cycle. This leads to hormone imbalance and may result in menorrhagia.
- Uterine fibroids. These noncancerous (benign) tumors of the uterus appear during your childbearing years. Uterine fibroids may cause heavier than normal or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
- Polyps. Small, benign growths on the lining of the uterus (uterine polyps) may cause heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
- Adenomyosis. This condition occurs when glands from the endometrium become embedded in the uterine muscle, often causing heavy bleeding and painful periods.
- Intrauterine device (IUD). Menorrhagia is a well-known side effect of using a nonhormonal intrauterine device for birth control. Your doctor will help you plan for alternative management options.
- Pregnancy complications. A single, heavy, late period may be due to a miscarriage. Another cause of heavy bleeding during pregnancy includes an unusual location of the placenta, such as a low-lying placenta or placenta previa.
- Cancer. Uterine cancer and cervical cancer can cause excessive menstrual bleeding, especially if you are postmenopausal or have had an abnormal Pap test in the past.
- Inherited bleeding disorders. Some bleeding disorders — such as von Willebrand's disease, a condition in which an important blood-clotting factor is deficient or impaired — can cause abnormal menstrual bleeding.
- Medications. Certain medications, including anti-inflammatory medications, hormonal medications such as estrogen and progestins, and anticoagulants such as warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven) or enoxaparin (Lovenox), can contribute to heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
- Other medical conditions. A number of other medical conditions, including liver or kidney disease, may be associated with menorrhagia.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Specific treatment for menorrhagia is based on a number of factors, including:
- Your overall health and medical history
- The cause and severity of the condition
- Your tolerance for specific medications, procedures or therapies
- The likelihood that your periods will become less heavy soon
- Your future childbearing plans
- Effects of the condition on your lifestyle
- Your opinion or personal preference
Medications
Medical therapy for menorrhagia may include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve), help reduce menstrual blood loss. NSAIDs have the added benefit of relieving painful menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea).
- Tranexamic acid. Tranexamic acid (Lysteda) helps reduce menstrual blood loss and only needs to be taken at the time of the bleeding.
- Oral contraceptives. Aside from providing birth control, oral contraceptives can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce episodes of excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
- Oral progesterone. The hormone progesterone can help correct hormone imbalance and reduce menorrhagia.
- Hormonal IUD (Liletta, Mirena). This intrauterine device releases a type of progestin called levonorgestrel, which makes the uterine lining thin and decreases menstrual blood flow and cramping.
If you have menorrhagia from taking hormone medication, you and your doctor may be able to treat the condition by changing or stopping your medication.
If you also have anemia due to your menorrhagia, your doctor may recommend that you take iron supplements regularly. If your iron levels are low but you're not yet anemic, you may be started on iron supplements rather than waiting until you become anemic.
Procedures
You may need surgical treatment for menorrhagia if medical therapy is unsuccessful. Treatment options include:
- Dilation and curettage (D&C). In this procedure, your doctor opens (dilates) your cervix and then scrapes or suctions tissue from the lining of your uterus to reduce menstrual bleeding. Although this procedure is common and often treats acute or active bleeding successfully, you may need additional D&C procedures if menorrhagia recurs.
- Uterine artery embolization. For women whose menorrhagia is caused by fibroids, the goal of this procedure is to shrink any fibroids in the uterus by blocking the uterine arteries and cutting off their blood supply. During uterine artery embolization, the surgeon passes a catheter through the large artery in the thigh (femoral artery) and guides it to your uterine arteries, where the blood vessel is injected with materials that decrease blood flow to the fibroid.
- Focused ultrasound surgery. Similar to uterine artery embolization, focused ultrasound surgery treats bleeding caused by fibroids by shrinking the fibroids. This procedure uses ultrasound waves to destroy the fibroid tissue. There are no incisions required for this procedure.
- Myomectomy. This procedure involves surgical removal of uterine fibroids. Depending on the size, number and location of the fibroids, your surgeon may choose to perform the myomectomy using open abdominal surgery, through several small incisions (laparoscopically), or through the vagina and cervix (hysteroscopically).
- Endometrial ablation. This procedure involves destroying (ablating) the lining of your uterus (endometrium). The procedure uses a laser, radiofrequency or heat applied to the endometrium to destroy the tissue.
- After endometrial ablation, most women have much lighter periods. Pregnancy after endometrial ablation has many associated complications. If you have endometrial ablation, the use of reliable or permanent contraception until menopause is recommended.
- Endometrial resection. This surgical procedure uses an electrosurgical wire loop to remove the lining of the uterus. Both endometrial ablation and endometrial resection benefit women who have very heavy menstrual bleeding. Pregnancy isn't recommended after this procedure.
- Hysterectomy. Hysterectomy — surgery to remove your uterus and cervix — is a permanent procedure that causes sterility and ends menstrual periods. Hysterectomy is performed under anesthesia and requires hospitalization. Additional removal of the ovaries (bilateral oophorectomy) may cause premature menopause.
Many of these surgical procedures are done on an outpatient basis. Although you may need a general anesthetic, it's likely that you can go home later on the same day. An abdominal myomectomy or a hysterectomy usually requires a hospital stay.
When menorrhagia is a sign of another condition, such as thyroid disease, treating that condition usually results in lighter periods.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
- Calcium Lactate Gluconate + Calcium Carbonate + Vitamin C
-
Ferrous Sulfate
for blood 1 pill 2 times a day after meals.
-
Vitamin B complex
Medicines to build strength in the body. 1 serving 2 times a day after meals.
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
1 each 3 times a day for 7-10 days.
-
Cephalexin
1 pill every 6 hours.
-
Cephradine
1 pill every 6 hours. 5/7 days.
-
Paracetamol
If you have back or waist pain, massage your body with paracetamol.
1 each 3 times a day.
-
Oxyphenonium Bromide
Medicines containing oxyphenonium bromide for lower abdominal pain.
1 pill 2 times a day.
-
Hyoscine Butylbromide
1 injection into the flesh every 8 hours.
-
Metronidazole
1 pill 2 times a day for 7 days.
-
Trifluoperazine
Medicines containing trifluperazine for mental instability.
1 pill 2 times a day.
-
Clobazam
1 pill 2 times a day.
-
Ergometrine Maleate
Medicines containing ergometrine maleate to stop bleeding. 1 pill 3 times a day.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Platina muriaticum
30, 200 strength.
-
Erigeron
Q strength.
-
China officinalis
Q, 30 strength.
-
Sepia
30, 200 strength.
-
Sabina
30, 200 strength.
-
Janosia ashoka
Q strength.
-
Magnesium carbonicum xx
6, 30 strength.
-
Hydrastis
Q, 30 strength.
-
Cimicifuga racemosa
30 strength.
-
Millefolium
Q strength.
-
Ignatia amara
30, 200 strength.
-
Chamomilla
30, 200 strength.
-
Ficus religiosa
3X, 6 strength.
-
Crocus sativus
30 strength.
-
Ipecacuanha
Q, 30 strength.
-
Silicea
12X strength.
Disease yoga
Menorrhagia (Heavy menstrual bleeding) and Learn More about Diseases
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Acne
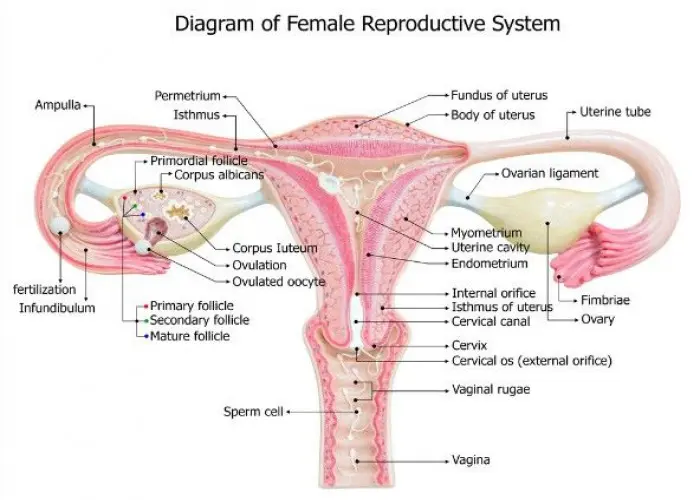
Female infertility

Central nervous system vascular malformations

Sacroiliitis
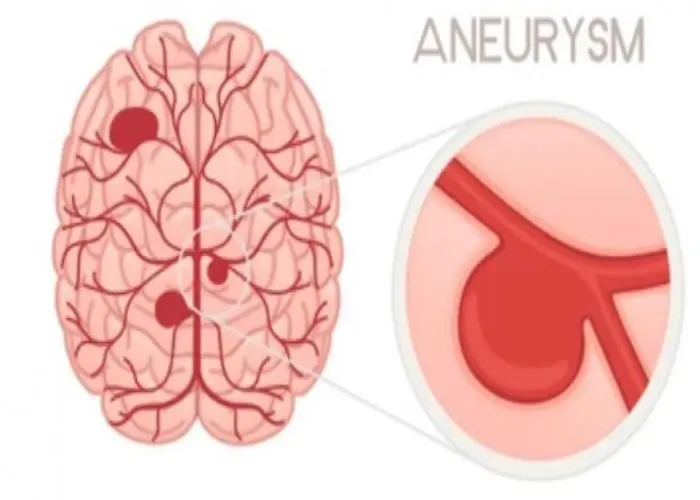
Brain aneurysm

Calciphylaxis

Scabies
menorrhagia, heavy menstrual bleeding, মেনোর্রাহিয়া, ভারী ঋতুস্রাবের রক্তপাত
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.