Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
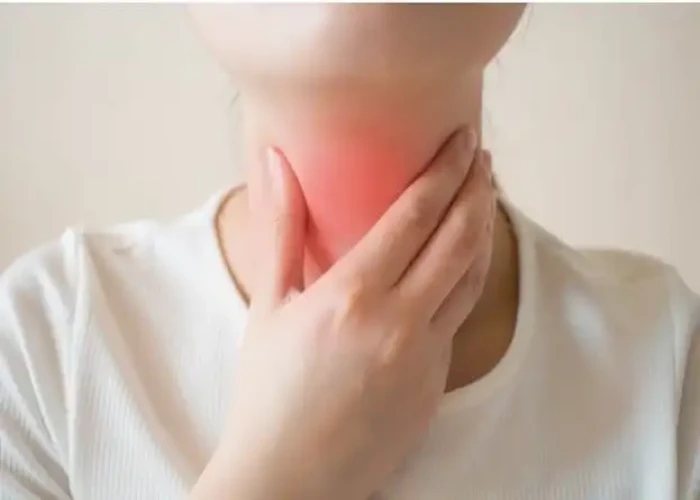
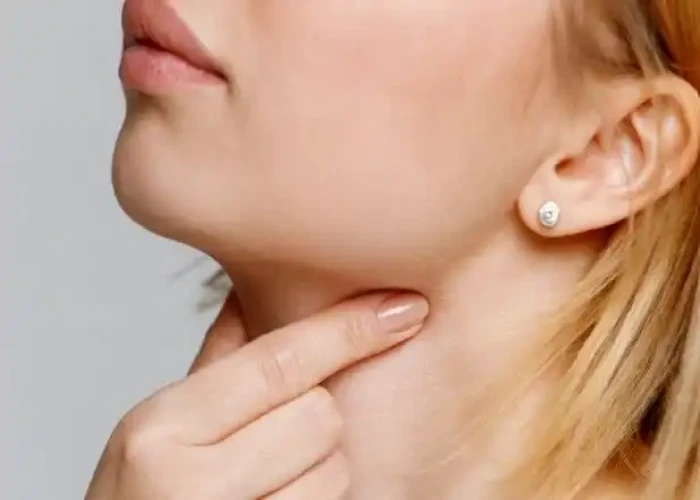
Throat - Diseases
The throat is a muscular tube that connects the mouth and nasal passages to the esophagus and trachea. It is an important part of the respiratory and digestive systems and plays a critical role in speech and communication.
The throat is divided into three parts: the pharynx, the larynx, and the esophagus. The pharynx is a muscular tube that extends from the back of the nose and mouth down to the larynx and esophagus. The larynx, also known as the voice box, is located at the top of the trachea and contains the vocal cords, which are responsible for producing sound. The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach and is responsible for transporting food and liquid to the digestive system.
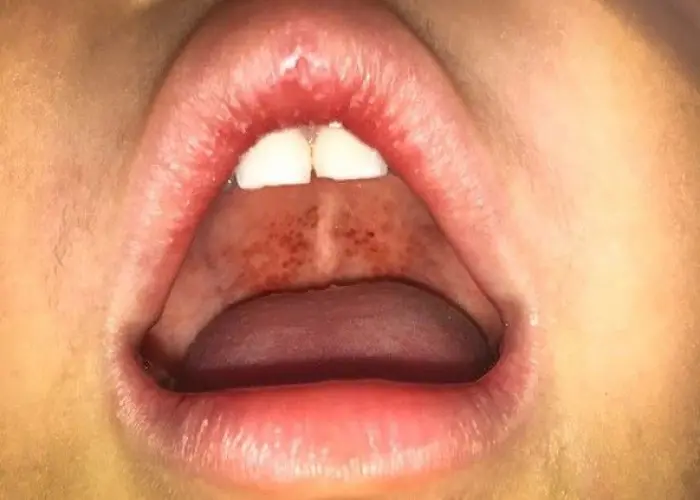
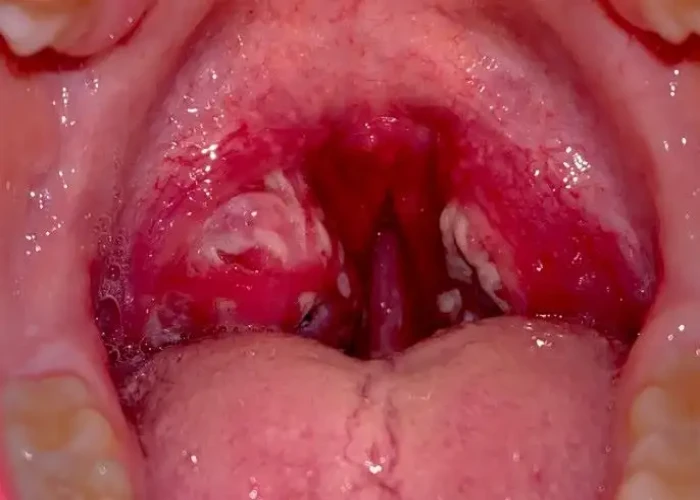
The throat also contains several important structures, including the tonsils, adenoids, and epiglottis. The tonsils are located in the back of the throat and help to filter out bacteria and other harmful substances. The adenoids are similar structures located at the back of the nasal cavity. The epiglottis is a flap of tissue that closes off the trachea during swallowing to prevent food or liquid from entering the lungs.
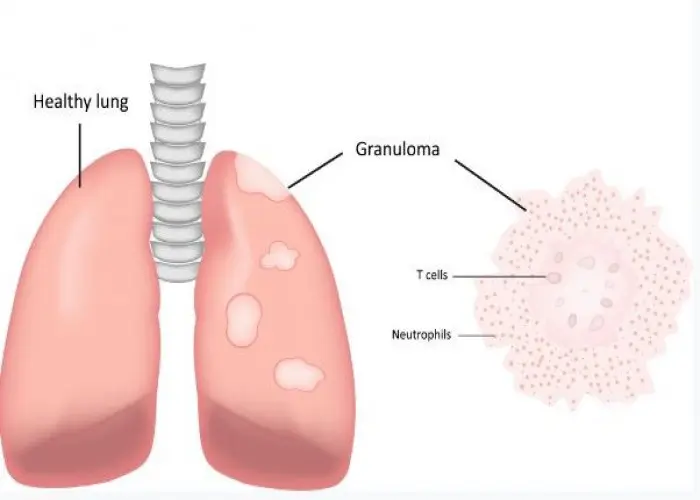
Several conditions can affect the throat, including sore throat, laryngitis, tonsillitis, and pharyngitis. These conditions can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, allergies, or other factors. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medication, or other interventions.

Brain
Urine
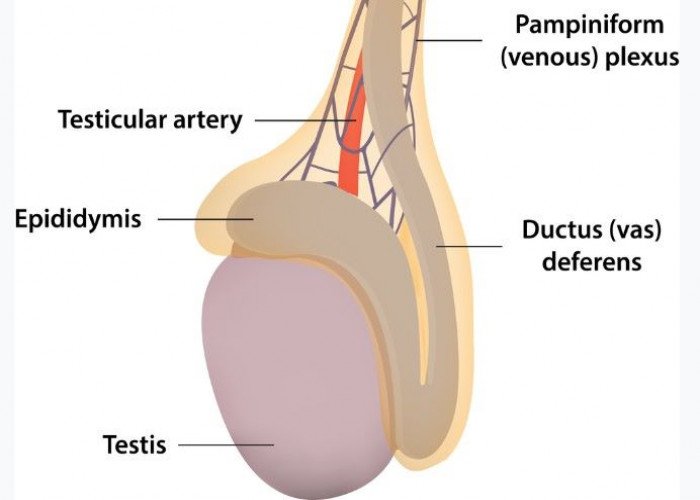
Vas deferens

Toe

Prostate
Collarbone

Ileum intestine
Cecum intestine
Throat, Sore throat, Strep throat, গলা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.