 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Menopause

Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman's reproductive years. It typically occurs when a woman's ovaries stop producing eggs and her menstrual periods stop. Menopause is officially diagnosed when a woman has gone 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period.
The average age for menopause in women is around 51 years, but it can occur earlier or later. Perimenopause, the transition period leading up to menopause, can start several years before a woman's periods stop and may be characterized by irregular periods, hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood changes.
Symptoms of menopause can vary widely between women and may include:
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Mood changes, such as irritability or depression
- Sleep disturbances
- Vaginal dryness and discomfort during sex
- Urinary incontinence or urgency
- Changes in libido or sexual function
- Osteoporosis (thinning of the bones)
Treatment options for menopausal symptoms may include hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to replace declining estrogen and progesterone levels, non-hormonal medications such as antidepressants, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and a healthy diet, and alternative therapies such as acupuncture or herbal supplements.
It's important for women to talk to their healthcare provider about their individual symptoms and treatment options, as well as any potential risks and benefits of HRT. Women should also continue to receive regular preventive care, such as breast and cervical cancer screening, as they age.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Irregular or absent menstruation periods
- Vaginal dryness
- Fever and chills
- Night sweats
- Rapid weight gain
- Dry skin
Disease Causes
Menopause
Menopause can result from:
- Naturally declining reproductive hormones. As you approach your late 30s, your ovaries start making less estrogen and progesterone — the hormones that regulate menstruation — and your fertility declines.
- In your 40s, your menstrual periods may become longer or shorter, heavier or lighter, and more or less frequent, until eventually — on average, by age 51 — your ovaries stop releasing eggs, and you have no more periods.
- Surgery that removes the ovaries (oophorectomy). Your ovaries produce hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, that regulate the menstrual cycle. Surgery to remove your ovaries causes immediate menopause. Your periods stop, and you're likely to have hot flashes and experience other menopausal signs and symptoms. Signs and symptoms can be severe, as hormonal changes occur abruptly rather than gradually over several years.
- Surgery that removes your uterus but not your ovaries (hysterectomy) usually doesn't cause immediate menopause. Although you no longer have periods, your ovaries still release eggs and produce estrogen and progesterone.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy. These cancer therapies can induce menopause, causing symptoms such as hot flashes during or shortly after the course of treatment. The halt to menstruation (and fertility) is not always permanent following chemotherapy, so birth control measures may still be desired. Radiation therapy only affects ovarian function if radiation is directed at the ovaries. Radiation therapy to other parts of the body, such as breast tissue or the head and neck, won't affect menopause.
- Primary ovarian insufficiency. About 1% of women experience menopause before age 40 (premature menopause). Premature menopause may result from the failure of your ovaries to produce normal levels of reproductive hormones (primary ovarian insufficiency), which can stem from genetic factors or autoimmune disease. But often no cause of premature menopause can be found. For these women, hormone therapy is typically recommended at least until the natural age of menopause in order to protect the brain, heart and bones.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Menopause requires no medical treatment. Instead, treatments focus on relieving your signs and symptoms and preventing or managing chronic conditions that may occur with aging. Treatments may include:
- Hormone therapy. Estrogen therapy is the most effective treatment option for relieving menopausal hot flashes. Depending on your personal and family medical history, your doctor may recommend estrogen in the lowest dose and the shortest time frame needed to provide symptom relief for you. If you still have your uterus, you'll need progestin in addition to estrogen. Estrogen also helps prevent bone loss. Long-term use of hormone therapy may have some cardiovascular and breast cancer risks, but starting hormones around the time of menopause has shown benefits for some women. Talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks of hormone therapy and whether it's a safe choice for you.
- Vaginal estrogen. To relieve vaginal dryness, estrogen can be administered directly to the vagina using a vaginal cream, tablet or ring. This treatment releases just a small amount of estrogen, which is absorbed by the vaginal tissues. It can help relieve vaginal dryness, discomfort with intercourse and some urinary symptoms.
- Low-dose antidepressants. Certain antidepressants related to the class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may decrease menopausal hot flashes. A low-dose antidepressant for management of hot flashes may be useful for women who can't take estrogen for health reasons or for women who need an antidepressant for a mood disorder.
- Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant, Neurontin). Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures, but it has also been shown to help reduce hot flashes. This drug is useful in women who can't use estrogen therapy and in those who also have nighttime hot flashes.
- Clonidine (Catapres, Kapvay). Clonidine, a pill or patch typically used to treat high blood pressure, might provide some relief from hot flashes.
- Medications to prevent or treat osteoporosis. Depending on individual needs, doctors may recommend medication to prevent or treat osteoporosis. Several medications are available that help reduce bone loss and risk of fractures. Your doctor might prescribe vitamin D supplements to help strengthen bones.
Before deciding on any form of treatment, talk with your doctor about your options and the risks and benefits involved with each. Review your options yearly, as your needs and treatment options may change.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Menopause and Learn More about Diseases
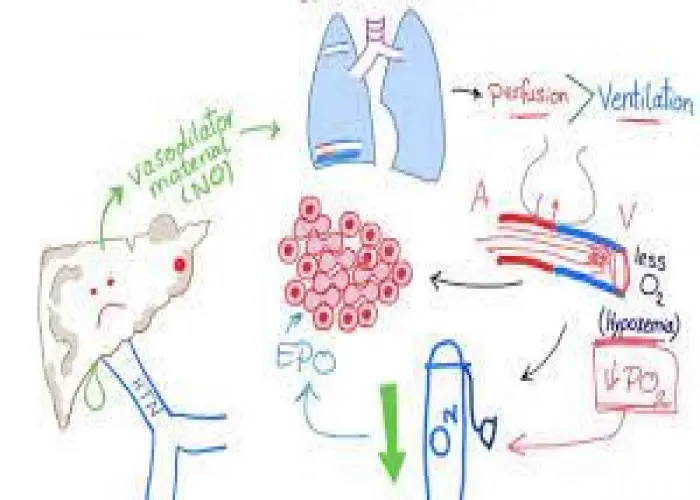
Hepatopulmonary syndrome
Dystonia
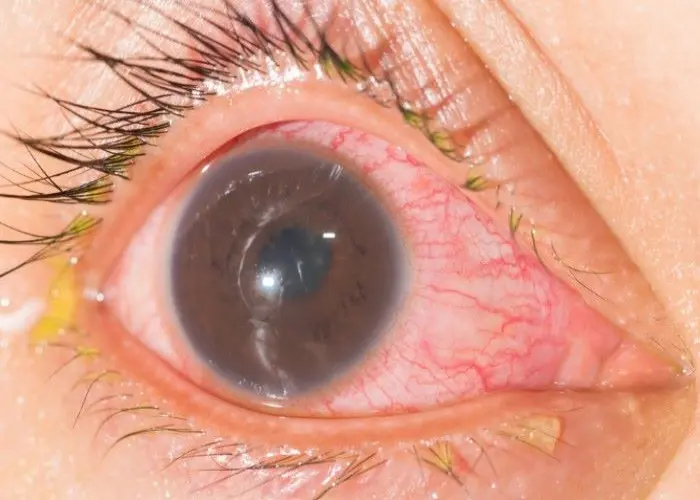
Iritis

Whiplash
Heart palpitations
Pinworm infection
Vaginal agenesis

Tension headache
menopause, মেনোপজ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
