 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
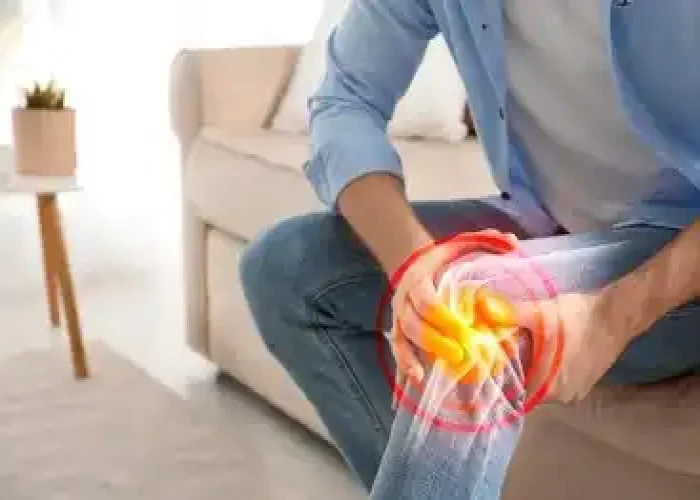
Hip gout - Yoga remedies
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. While it most commonly affects the big toe, it can also occur in other joints such as the hip.
Hip gout typically presents as sudden and intense pain in the hip joint, along with swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected area. The pain may be severe enough to limit mobility and can last for several days or even weeks.
Risk factors for gout include a family history of the condition, obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, and certain medications such as diuretics. A diet high in purines, which are found in foods such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol, can also increase the risk of developing gout.
Diagnosis of hip gout typically involves a physical exam, blood tests to check for high levels of uric acid, and imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasound to examine the affected joint.
Treatment for hip gout typically involves medications to relieve pain and inflammation, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or colchicine. Medications to lower uric acid levels in the blood may also be prescribed, including allopurinol or probenecid.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can help manage and prevent hip gout. This may include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding foods high in purines, staying hydrated, and limiting alcohol consumption.
In summary, hip gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the hip joint. Treatment involves medications to relieve pain and inflammation and lower uric acid levels, as well as lifestyle changes to manage and prevent gout attacks. If you suspect you may have hip gout, it's important to consult with your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Mucus or phlegm

Rheumatism

Pneumonia
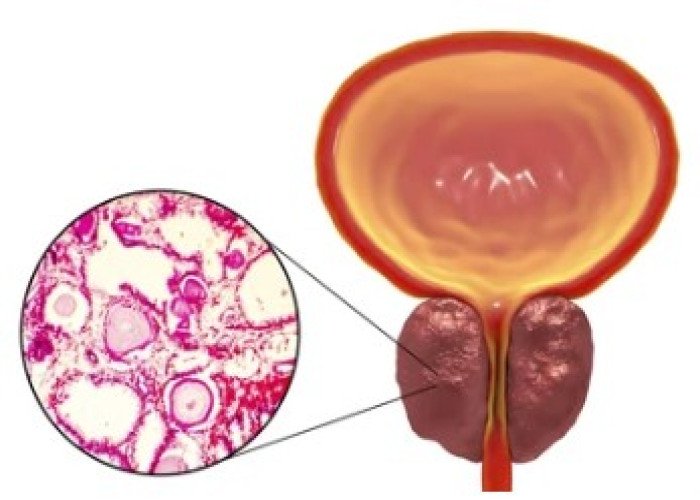
Prostate gland enlargemen...
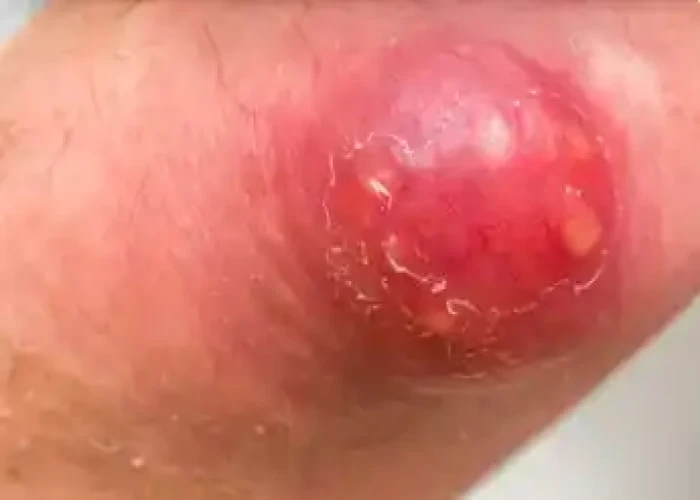
Boil

Hip gout

Neuralgia

One leg is short
Hip gout, কটিবাত
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.




