Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Genitals - Diseases
The genitals are the reproductive organs in humans and other animals, which are responsible for sexual reproduction. In males, the genitals include the penis and testes, while in females, they include the vagina, uterus, and ovaries.
The genitals are involved in the process of sexual arousal, which can lead to sexual intercourse and the potential for reproduction. Sexual arousal involves a complex interplay of physical, emotional, and psychological factors.
Various conditions can affect the genitals, such as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), infertility, and certain types of cancer. Treatment options for genital conditions may include medication, surgery, lifestyle changes, and counseling, depending on the underlying problem.
Maintaining good genital health involves practicing safe sex, getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, and engaging in healthy behaviors, such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and avoiding exposure to certain chemicals and toxins.
It is also important to be aware of any changes or abnormalities in the genitals, such as unusual discharge, pain, or swelling, and to seek medical attention if any problems arise.

Spinal Nerves

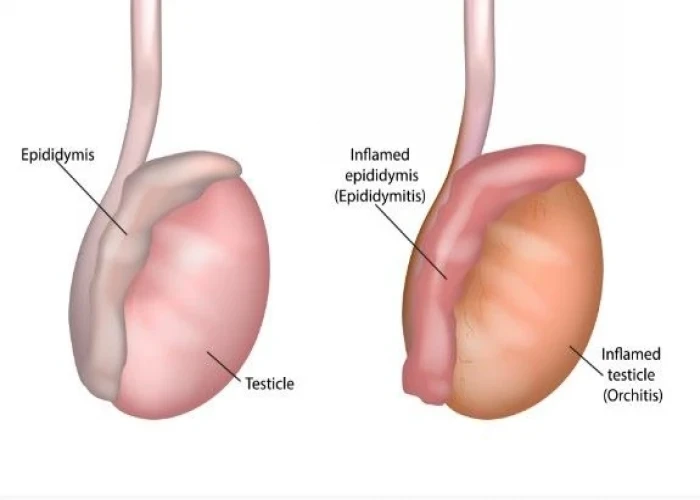
Epididymis
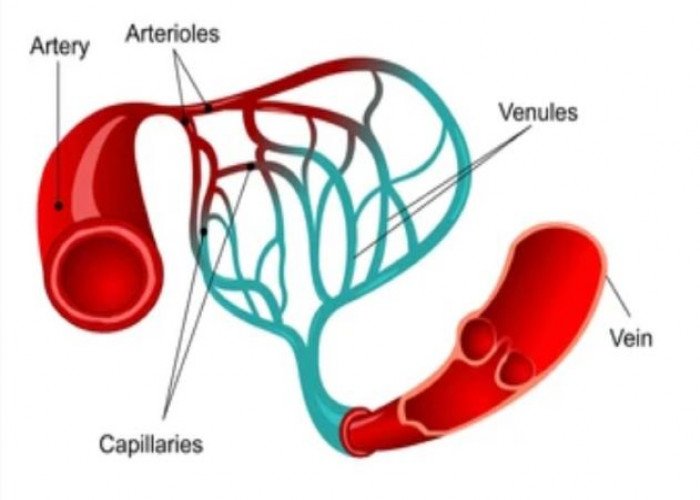
Capillaries
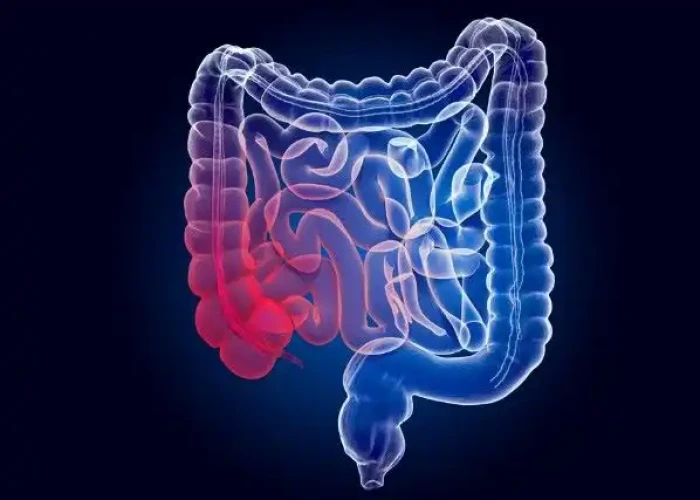
Duodenum intestine
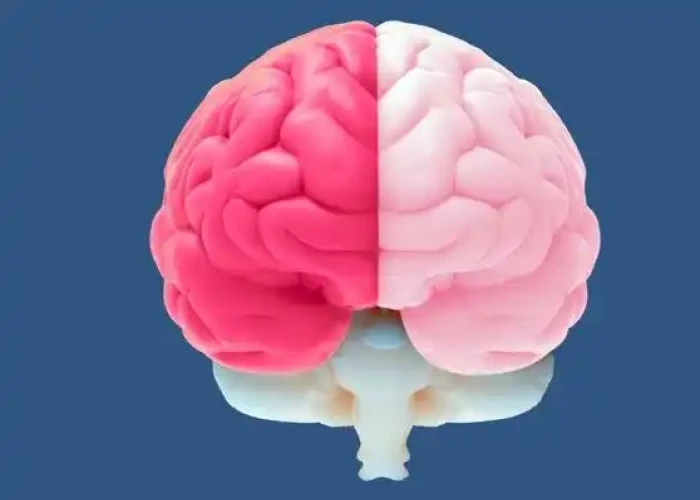
Cerebral hemispheres Brain

Head
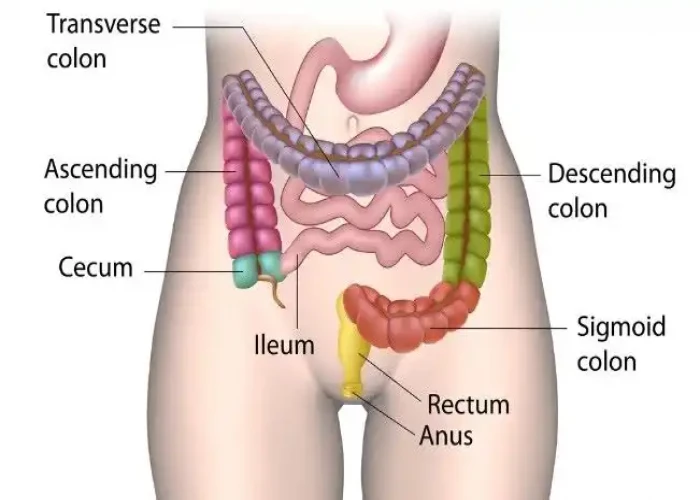
Descending colon intestine

Iris Eye
Genitals, যৌনাঙ্গ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.