 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Taste buds Tongue - Diseases
Taste buds are small sensory organs found on the tongue and other parts of the mouth. They are responsible for detecting different tastes such as sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami.
The human tongue has between 2,000 and 8,000 taste buds, which are located on the papillae, small bumps on the surface of the tongue. Each taste bud is made up of taste receptor cells, which are specialized cells that can detect specific tastes.
When food or drink is consumed, molecules from the food or drink interact with the taste receptor cells in the taste buds. This interaction triggers a signal that is sent to the brain, which then interprets the signal as a specific taste.
In addition to the tongue, taste buds can also be found on the roof of the mouth, the back of the throat, and even in the esophagus. Together, they help us to enjoy a wide range of flavors and to detect potential dangers in our food, such as spoiled or toxic substances.
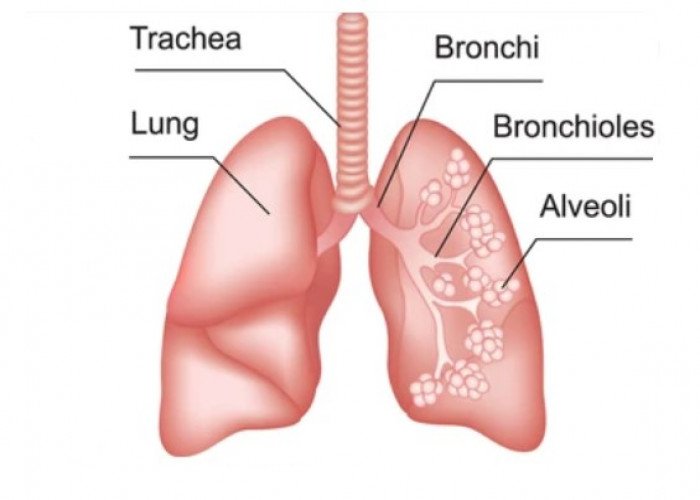
Trachea

Joints
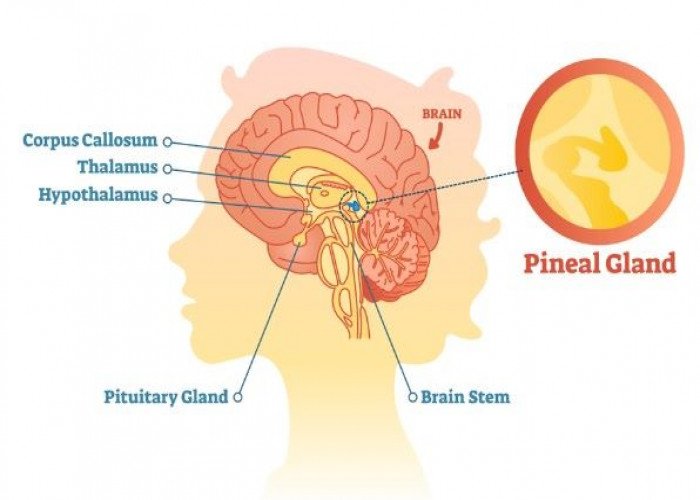
Pineal gland
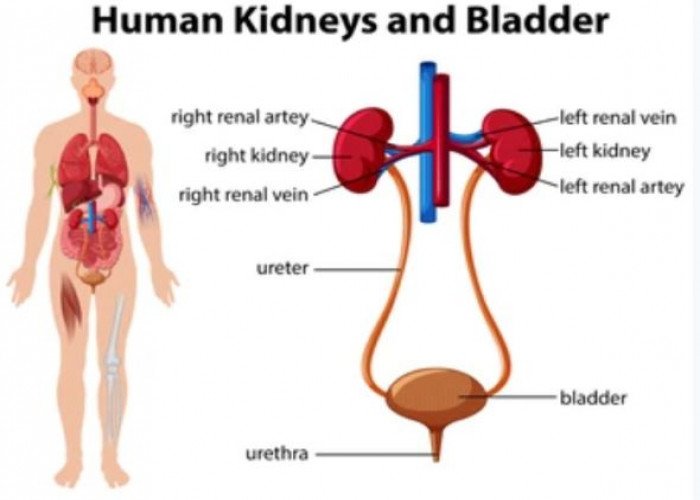
Kidneys
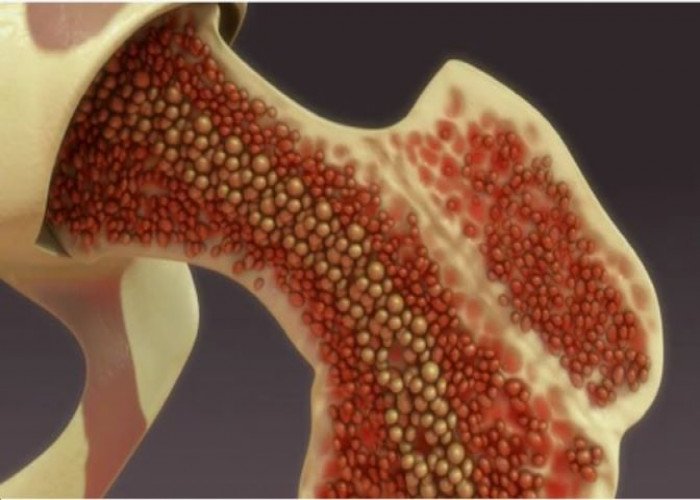
Bone marrow
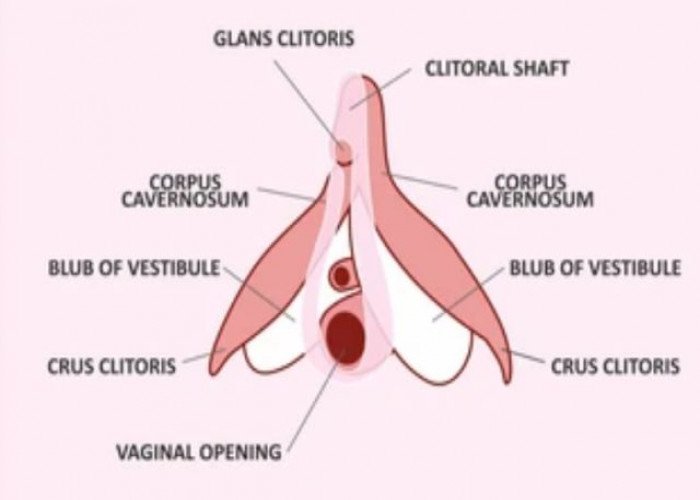
Clitoris
Jejunum intestine

Toe
Taste buds Tongue, Swollen taste bud, স্বাদ কুঁড়ি জিহ্বা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.