Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Orchitis
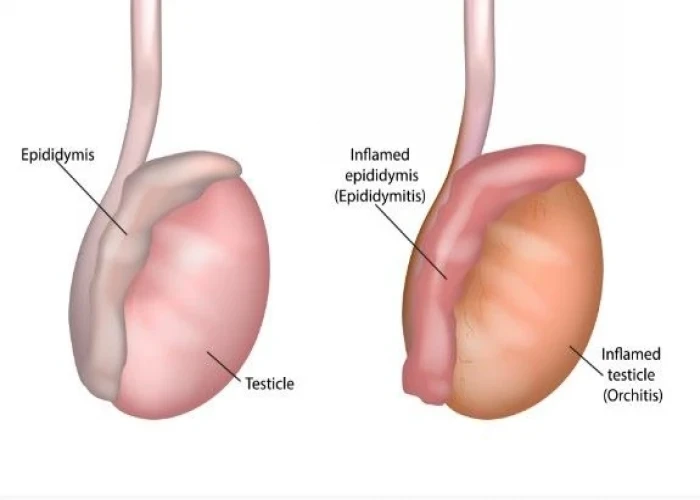
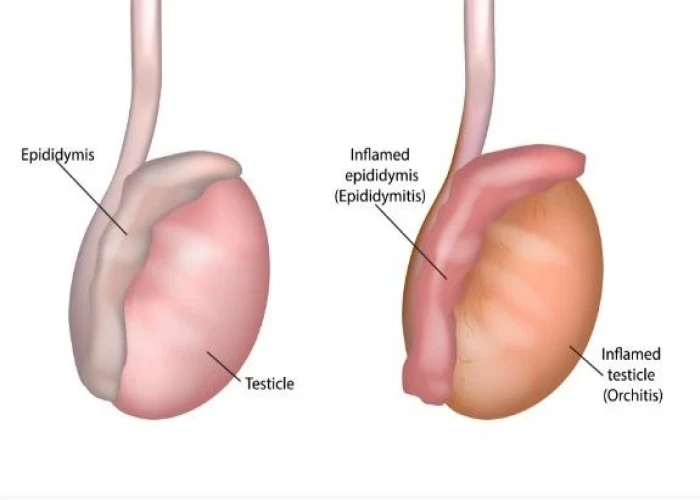
Orchitis is the inflammation of one or both testicles, which can cause pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area. It is commonly caused by a bacterial or viral infection, including sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Symptoms of orchitis may include:
- Pain, tenderness, or swelling in one or both testicles
- Redness and warmth in the scrotum
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain or discomfort during urination
Diagnosis of orchitis may involve a physical exam of the testicles and scrotum, as well as blood and urine tests to identify the underlying cause of the infection. In some cases, imaging tests such as an ultrasound may be performed to assess the extent of inflammation.
Treatment of orchitis may involve antibiotics or antiviral medications to treat the underlying infection, as well as pain medications and supportive care such as rest, elevation of the scrotum, and application of ice packs to reduce swelling and discomfort. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required.
Complications of orchitis may include infertility, chronic pain, and the development of a testicular abscess. It is important to seek prompt medical attention if you experience any symptoms of orchitis, as early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and prevent complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen testicle
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
Disease Causes
Orchitis
Orchitis can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection. Sometimes a cause of orchitis can't be determined.
Bacterial orchitis
Most often, bacterial orchitis is associated with or the result of epididymitis. Epididymitis usually is caused by an infection of the urethra or bladder that spreads to the epididymis.
Often, the cause of the infection is an STI. Other causes of infection can be related to having been born with abnormalities in your urinary tract or having had a catheter or medical instruments inserted into your penis.
Viral orchitis
The mumps virus usually causes viral orchitis. Nearly one-third of males who contract the mumps after puberty develop orchitis, usually four to seven days after onset of the mumps.
Disease Prevents
Orchitis
To prevent orchitis:
- Get immunized against mumps, the most common cause of viral orchitis
- Practice safe sex, to help protect against STIs that can cause bacterial orchitis
Disease Treatments
Treatment depends on the cause of orchitis.
Treating bacterial orchitis
Antibiotics are needed to treat bacterial orchitis and epididymo-orchitis. If the cause of the bacterial infection is an STI, your sexual partner also needs treatment.
Take the entire course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor, even if your symptoms ease sooner, to ensure that the infection is gone.
It may take several weeks for the tenderness to disappear. Resting, supporting the scrotum with an athletic strap, applying ice packs and taking pain medication can help relieve discomfort.
Treating viral orchitis
Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms. Your doctor might recommend:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve)
- Bed rest and elevating your scrotum
- Cold packs
Most people with viral orchitis start to feel better in three to 10 days, although it can take several weeks for the scrotal tenderness to disappear.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Aurum metalicum
6, 30 strength.
-
Silicea
30, 200 strength.
-
Hamamelis verginica
6, 30 strength.
-
Rhododendron chrysanthum
6, 30 strength.
-
Mercurius solubilis
30, 200 strength.
-
Lycopodium clavatum
30, 200 strength.
-
Spongia tosta
30, 200 strength.
-
Euphorbia hypericifolia
6, 30 strength.
-
Aconite
6, 30 strength.
-
Arnica montana
Q strength.
Disease yoga
Orchitis and Learn More about Diseases

Tape Worm
Hyperglycemia in diabetes
Lupus
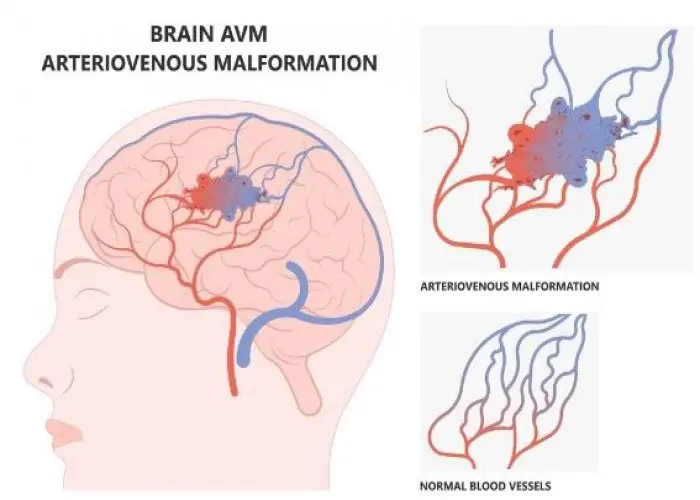
Dural arteriovenous fistulas
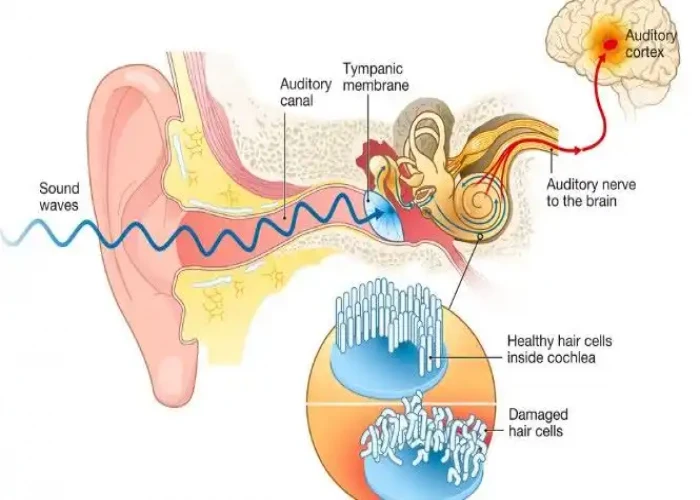
Tinnitus

Transient global amnesia
Systemic mastocytosis

Postpartum depression
orchitis, অর্কিটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.