Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
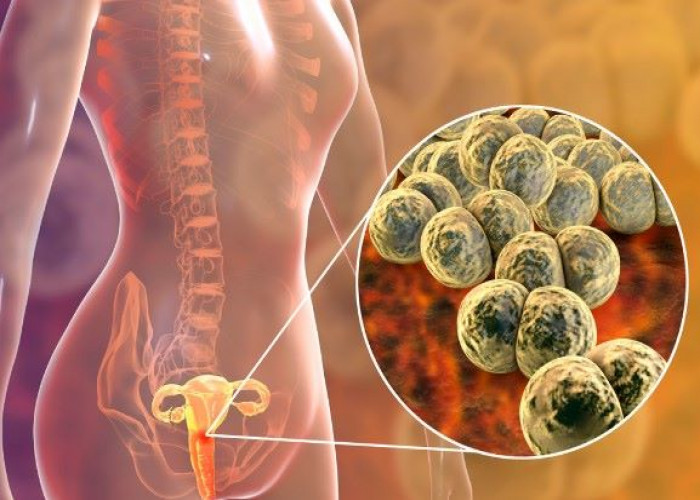
Gonorrhea

Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It can affect both men and women and is spread through sexual contact with an infected person, including vaginal, oral, and anal sex.
Symptoms of gonorrhea may include painful urination, increased vaginal or penile discharge, and pain or swelling in the testicles or ovaries. In some cases, there may be no symptoms present, and the infection may go undetected.
Diagnosis of gonorrhea usually involves a physical exam, urine or blood tests, or swabs of the genital area or throat to detect the presence of the bacterium.
Treatment for gonorrhea typically involves a course of antibiotics to eliminate the infection. It is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Prevention of gonorrhea involves practicing safe sex, including using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners. Regular testing and screening for STIs is also recommended, especially for individuals who are sexually active or have multiple partners.
If you suspect you may have gonorrhea or have been exposed to someone with the infection, it is important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early detection and treatment can help to manage the condition and prevent long-term complications associated with gonorrhea.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Burning during urination
- Discharge from penis
- Swollen testicle
- Testicle pain
- Watery vaginal discharge
- Vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Abdomen pain
Disease Causes
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The gonorrhea bacteria are most often passed from one person to another during sexual contact, including oral, anal or vaginal intercourse.
Disease Prevents
Gonorrhea
To reduce your gonorrhea risk:
- Use a condom if you have sex. Abstaining from sex is the surest way to prevent gonorrhea. But if you choose to have sex, use a condom during any type of sexual contact, including anal sex, oral sex or vaginal sex.
- Limit your number of sex partners. Being in a monogamous relationship in which neither partner has sex with anyone else can lower your risk.
- Be sure you and your partner are tested for sexually transmitted infections. Before you have sex, get tested and share your results with each other.
- Don't have sex with someone who appears to have a sexually transmitted infection. If your partner has signs or symptoms of a sexually transmitted infection, such as burning during urination or a genital rash or sore, don't have sex with that person.
- Consider regular gonorrhea screening. Annual screening is recommended for sexually active women younger than 25 and for older women at increased risk of infection. This includes women who have a new sex partner, more than one sex partner, a sex partner with other partners, or a sex partner who has a sexually transmitted infection.
- Regular screening is also recommended for men who have sex with men, as well as their partners.
To avoid getting gonorrhea again, abstain from sex until after you and your sex partner have completed treatment and after symptoms are gone.
Disease Treatments
Gonorrhea treatment in adults
Adults with gonorrhea are treated with antibiotics. Due to emerging strains of drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that uncomplicated gonorrhea be treated with the antibiotic ceftriaxone — given as an injection — with oral azithromycin (Zithromax).
If you're allergic to cephalosporin antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone, you might be given oral gemifloxacin (Factive) or injectable gentamicin and oral azithromycin.
Gonorrhea treatment for partners
Your partner also should go through testing and treatment for gonorrhea, even if he or she has no signs or symptoms. Your partner receives the same treatment you do. Even if you've been treated for gonorrhea, a partner who isn't treated can pass it to you again.
Gonorrhea treatment for babies
Babies born to mothers with gonorrhea who develop the infection can be treated with antibiotics.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Tetracycline Hydrochloride (Oral)
500 mg every 6 hours after taking 6 capsules for 4 days.
-
Doxycycline Hydrochloride
3 capsules together 1 time. Or 1 time 2 times a day for 4 days.
Gonorrhea in women 1 capsule 2 times a day until disease is cleared.
-
Ampicillin Sodium
3 grams (12 capsules) 1 time at a time.
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
3 g (12 capsules) 1 time together with probinicid.
-
Cotrimoxazole
5 pills 3 doses every 12 hours.
-
Erythromycin (Oral)
1 pill every 6 hours for 10 days.
-
Ciprofloxacin
1 pill 1 time dose.
-
Cefotaxime
0.5 or 1 mg intramuscularly 1 time.
-
Cefuroxime Axetil
1 gram 1 time.
-
Spectinomycin
Males should be injected 2 grams deep into the flesh, females 4 grams deep into the flesh.
-
Ceftriaxone Sodium
1 vial of 250mg should be injected into the flesh.
-
Diclofenac Sodium
1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Vitamin C [Ascorbic acid]
1 pill of 250mg should be swallowed twice a day.
-
Vitamin B complex
Medicines containing vitamin B for weakness.
2 spoons 3 times a day after meals.
-
Clobazam
Medicines containing clobazam for discomfort.
1 pill 2 times a day.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Gonorrhea and Learn More about Diseases

DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome)
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome

Autoimmune hepatitis
Cushing syndrome

Dysphagia
ACL injury

Gastrogenous Diarrhoea

X-linked agammaglobulinemia
gonorrhea, গনোরিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.