Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
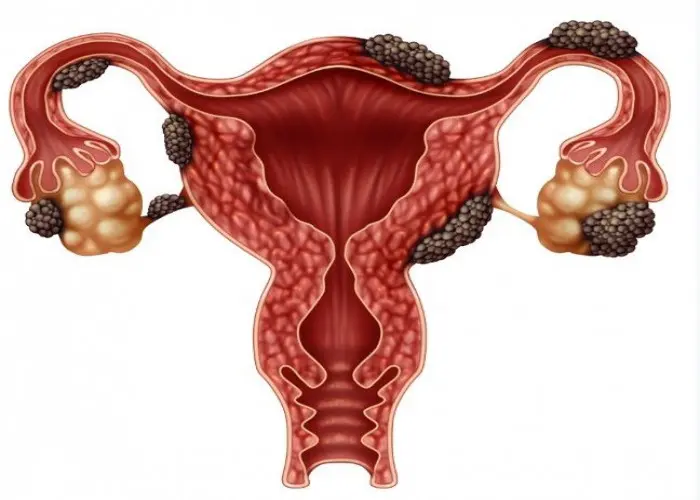
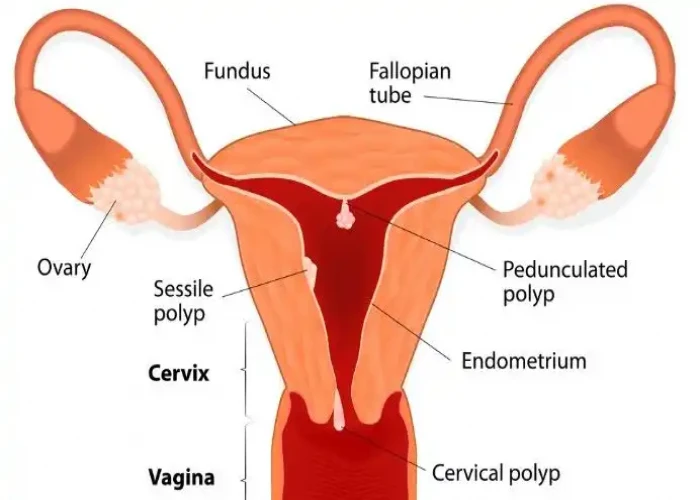
Uterus - Diseases
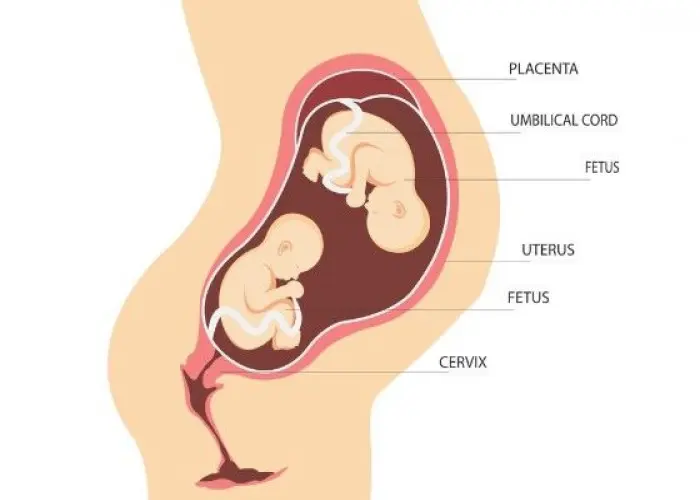
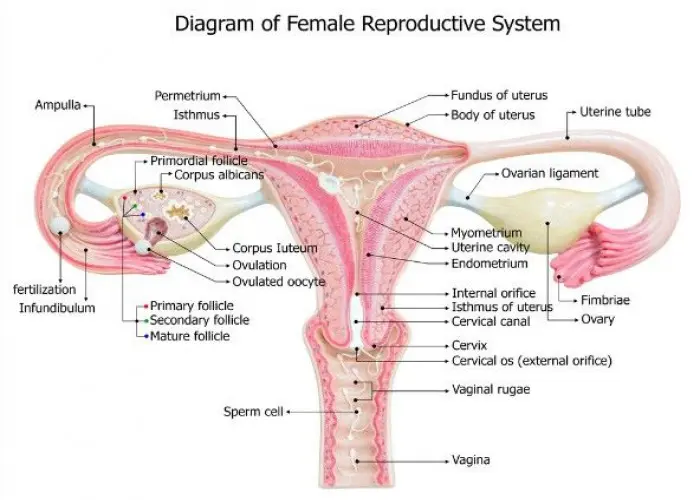
The uterus, also known as the womb, is a reproductive organ in female mammals where the fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus during pregnancy. It is a hollow, muscular organ located in the pelvis between the bladder and the rectum.
The uterus is about the size and shape of a pear, and its walls are made up of three layers: the outer layer called the perimetrium, the middle layer called the myometrium (which is made up of smooth muscle tissue), and the inner layer called the endometrium. The endometrium is the layer that thickens and sheds each month during the menstrual cycle if pregnancy does not occur.
The uterus is supported by a network of ligaments and muscles, and it has an opening at the bottom called the cervix, which connects to the vagina. During labor, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through and be born.
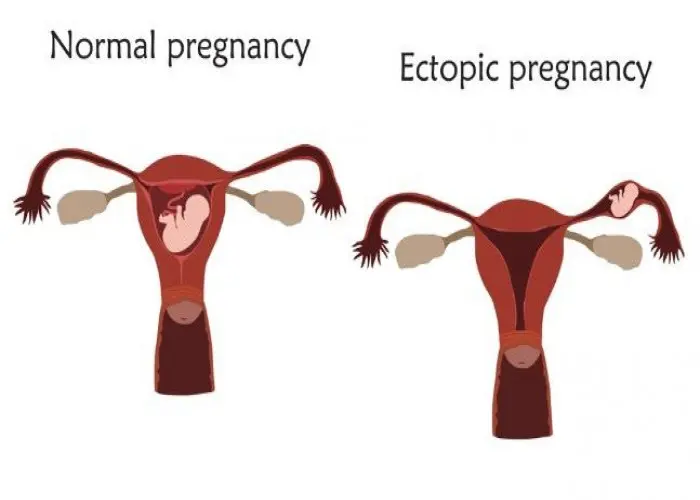
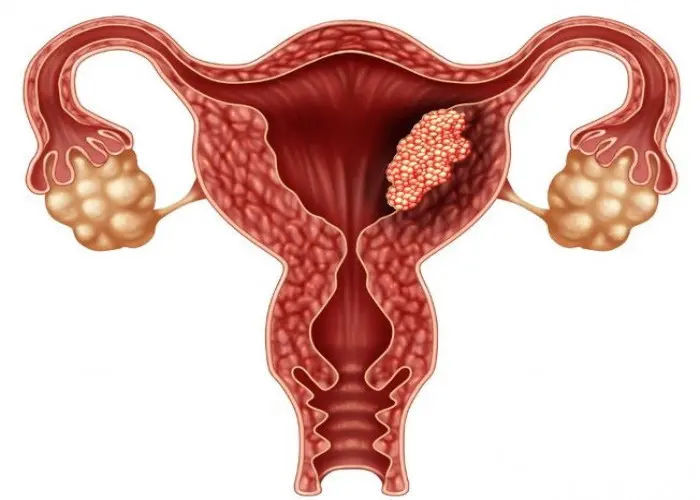
Various medical conditions can affect the uterus, including uterine fibroids, endometriosis, adenomyosis, and uterine prolapse. Treatment for these conditions can range from medication to surgery, depending on the severity of the condition and the woman's individual circumstances.
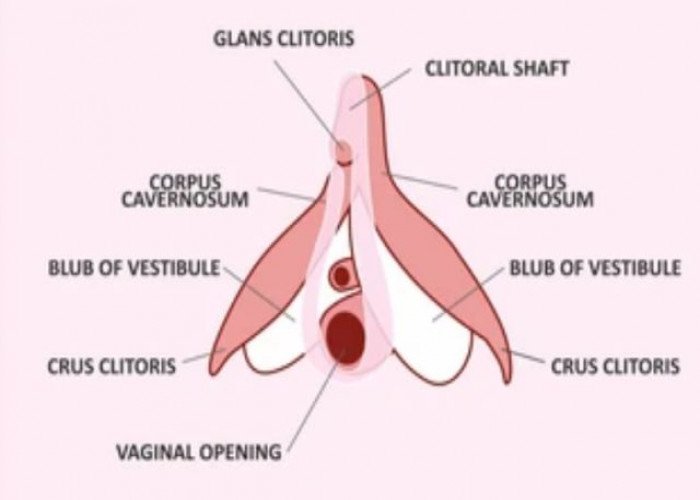
Clitoris
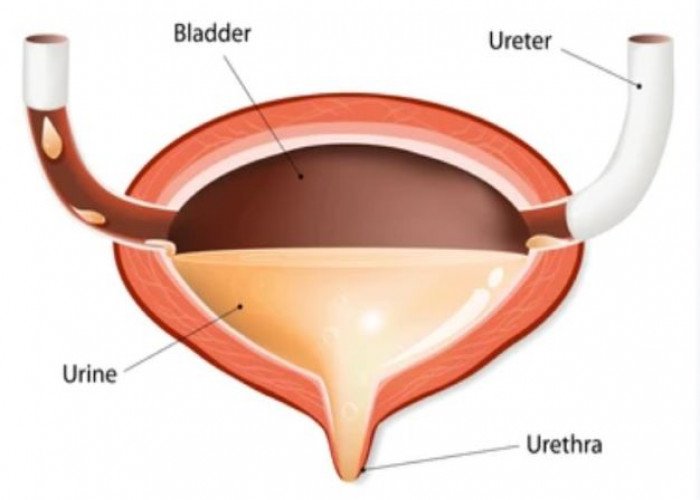
Urethra

Mouth
Leg
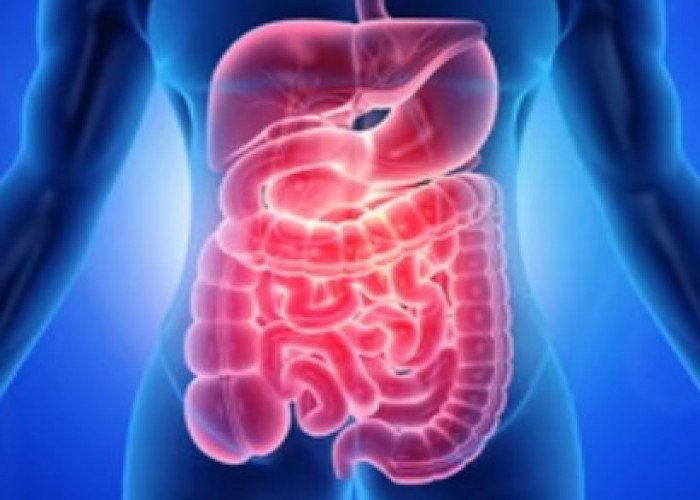
Colon
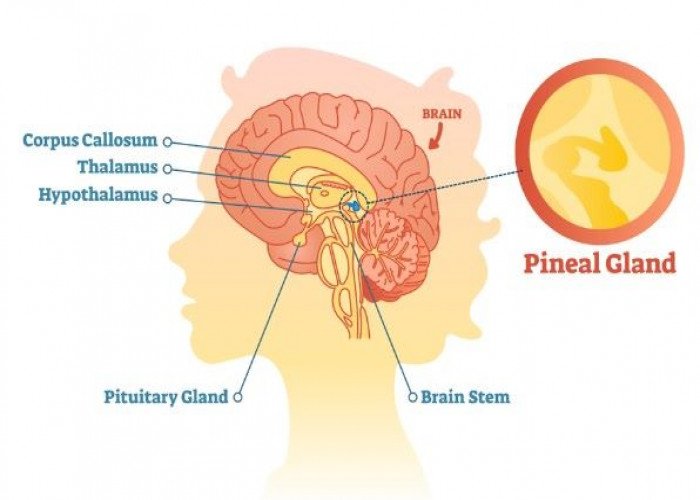
Pineal gland

Bladder
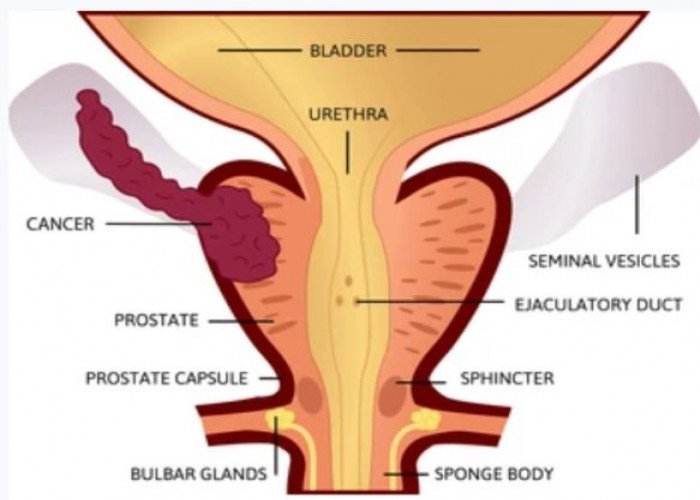
Seminal vesicles
Uterus, Fibroid uterus, Bulky uterus, Womb, জরায়ু
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.