 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Uterine fibroids

Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in the wall of the uterus. They are also known as leiomyomas or myomas. Fibroids can range in size from small, pea-sized growths to larger ones that can distort the shape of the uterus.
Uterine fibroids are very common, with up to 80% of women experiencing them at some point in their lives. They are more common in women who are in their 30s and 40s, and African American women are more likely to develop them.
The cause of uterine fibroids is not well understood, but hormones, especially estrogen, and progesterone, are thought to play a role in their growth. Risk factors for developing uterine fibroids include a family history of fibroids, obesity, and early onset of menstruation.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids can include heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, constipation, and lower back pain. Some women with fibroids may not experience any symptoms at all.
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids typically involves a pelvic exam, ultrasound, or other imaging tests such as an MRI. Treatment options for fibroids can vary depending on the size and location of the growths, as well as the severity of symptoms. Treatment options may include medications to control symptoms, such as pain or heavy bleeding, or surgical options such as myomectomy, which involves removing the fibroids while leaving the uterus intact, or hysterectomy, which involves removing the uterus.
The prognosis for uterine fibroids is generally good, as they are not cancerous and do not increase the risk of developing uterine cancer. However, if fibroids are causing severe symptoms or affecting a woman's quality of life, it is important to discuss treatment options with a healthcare provider.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Heavy menstrual period or bleeding
- Menstrual periods more than a week
- Sensation of pelvic pressure
- Pelvic pain
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty emptying bladder
- Constipation
- Leg pain
Disease Causes
Uterine fibroids
Doctors don't know the cause of uterine fibroids, but research and clinical experience point to these factors:
- Genetic changes. Many fibroids contain changes in genes that differ from those in typical uterine muscle cells.
- Hormones. Estrogen and progesterone, two hormones that stimulate development of the uterine lining during each menstrual cycle in preparation for pregnancy, appear to promote the growth of fibroids.
- Fibroids contain more estrogen and progesterone receptors than typical uterine muscle cells do. Fibroids tend to shrink after menopause due to a decrease in hormone production.
- Other growth factors. Substances that help the body maintain tissues, such as insulin-like growth factor, may affect fibroid growth.
- Extracellular matrix (ECM). ECM is the material that makes cells stick together, like mortar between bricks. ECM is increased in fibroids and makes them fibrous. ECM also stores growth factors and causes biologic changes in the cells themselves.
Doctors believe that uterine fibroids develop from a stem cell in the smooth muscular tissue of the uterus (myometrium). A single cell divides repeatedly, eventually creating a firm, rubbery mass distinct from nearby tissue.
The growth patterns of uterine fibroids vary — they may grow slowly or rapidly, or they may remain the same size. Some fibroids go through growth spurts, and some may shrink on their own.
Many fibroids that have been present during pregnancy shrink or disappear after pregnancy, as the uterus goes back to its usual size.
Disease Prevents
Uterine fibroids
Although researchers continue to study the causes of fibroid tumors, little scientific evidence is available on how to prevent them. Preventing uterine fibroids may not be possible, but only a small percentage of these tumors require treatment.
But, by making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a healthy weight and eating fruits and vegetables, you may be able to decrease your fibroid risk.
Also, some research suggests that using hormonal contraceptives may be associated with a lower risk of fibroids.
Disease Treatments
There's no single best approach to uterine fibroid treatment — many treatment options exist. If you have symptoms, talk with your doctor about options for symptom relief.
Watchful waiting
Many women with uterine fibroids experience no signs or symptoms, or only mildly annoying signs and symptoms that they can live with. If that's the case for you, watchful waiting could be the best option.
Fibroids aren't cancerous. They rarely interfere with pregnancy. They usually grow slowly — or not at all — and tend to shrink after menopause, when levels of reproductive hormones drop.
Medications
Medications for uterine fibroids target hormones that regulate your menstrual cycle, treating symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pressure. They don't eliminate fibroids, but may shrink them. Medications include:
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists. Medications called GnRH agonists treat fibroids by blocking the production of estrogen and progesterone, putting you into a temporary menopause-like state. As a result, menstruation stops, fibroids shrink and anemia often improves.
- GnRH agonists include leuprolide (Lupron Depot, Eligard, others), goserelin (Zoladex) and triptorelin (Trelstar, Triptodur Kit).
- Many women have significant hot flashes while using GnRH agonists. GnRH agonists typically are used for no more than three to six months because symptoms return when the medication is stopped and long-term use can cause loss of bone.
- Your doctor may prescribe a GnRH agonist to shrink the size of your fibroids before a planned surgery or to help transition you to menopause.
- Progestin-releasing intrauterine device (IUD). A progestin-releasing IUD can relieve heavy bleeding caused by fibroids. A progestin-releasing IUD provides symptom relief only and doesn't shrink fibroids or make them disappear. It also prevents pregnancy.
- Tranexamic acid (Lysteda, Cyklokapron). This nonhormonal medication is taken to ease heavy menstrual periods. It's taken only on heavy bleeding days.
- Other medications. Your doctor might recommend other medications. For example, oral contraceptives can help control menstrual bleeding, but they don't reduce fibroid size.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which are not hormonal medications, may be effective in relieving pain related to fibroids, but they don't reduce bleeding caused by fibroids. Your doctor may also suggest that you take vitamins and iron if you have heavy menstrual bleeding and anemia.
Noninvasive procedure
MRI-guided focused ultrasound surgery (FUS) is:
- A noninvasive treatment option for uterine fibroids that preserves your uterus, requires no incision and is done on an outpatient basis.
- Performed while you're inside an MRI scanner equipped with a high-energy ultrasound transducer for treatment. The images give your doctor the precise location of the uterine fibroids. When the location of the fibroid is targeted, the ultrasound transducer focuses sound waves (sonications) into the fibroid to heat and destroy small areas of fibroid tissue.
- Newer technology, so researchers are learning more about the long-term safety and effectiveness. But so far data collected show that FUS for uterine fibroids is safe and effective.
Minimally invasive procedures
Certain procedures can destroy uterine fibroids without actually removing them through surgery. They include:
- Uterine artery embolization. Small particles (embolic agents) are injected into the arteries supplying the uterus, cutting off blood flow to fibroids, causing them to shrink and die.
- This technique can be effective in shrinking fibroids and relieving the symptoms they cause. Complications may occur if the blood supply to your ovaries or other organs is compromised. However, research shows that complications are similar to surgical fibroid treatments and the risk of transfusion is substantially reduced.
- Radiofrequency ablation. In this procedure, radiofrequency energy destroys uterine fibroids and shrinks the blood vessels that feed them. This can be done during a laparoscopic or transcervical procedure. A similar procedure called cryomyolysis freezes the fibroids.
- With laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation (Acessa), also called Lap-RFA, your doctor makes two small incisions in the abdomen to insert a slim viewing instrument (laparoscope) with a camera at the tip. Using the laparoscopic camera and a laparoscopic ultrasound tool, your doctor locates fibroids to be treated.
- After locating a fibroid, your doctor uses a specialized device to deploy several small needles into the fibroid. The needles heat up the fibroid tissue, destroying it. The destroyed fibroid immediately changes consistency, for instance from being hard like a golf ball to being soft like a marshmallow. During the next three to 12 months, the fibroid continues to shrink, improving symptoms.
- Because there's no cutting of uterine tissue, doctors consider Lap-RFA a less invasive alternative to hysterectomy and myomectomy. Most women who have the procedure get back to regular activities after 5 to 7 days of recovery.
- The transcervical — or through the cervix — approach to radiofrequency ablation (Sonata) also uses ultrasound guidance to locate fibroids.
- Laparoscopic or robotic myomectomy. In a myomectomy, your surgeon removes the fibroids, leaving the uterus in place.
- If the fibroids are few in number, you and your doctor may opt for a laparoscopic or robotic procedure, which uses slender instruments inserted through small incisions in your abdomen to remove the fibroids from your uterus.
- Larger fibroids can be removed through smaller incisions by breaking them into pieces (morcellation), which can be done inside a surgical bag, or by extending one incision to remove the fibroids.
- Your doctor views your abdominal area on a monitor using a small camera attached to one of the instruments. Robotic myomectomy gives your surgeon a magnified, 3D view of your uterus, offering more precision, flexibility and dexterity than is possible using some other techniques.
- Hysteroscopic myomectomy. This procedure may be an option if the fibroids are contained inside the uterus (submucosal). Your surgeon accesses and removes fibroids using instruments inserted through your vagina and cervix into your uterus.
- Endometrial ablation. This treatment, performed with a specialized instrument inserted into your uterus, uses heat, microwave energy, hot water or electric current to destroy the lining of your uterus, either ending menstruation or reducing your menstrual flow.
- Typically, endometrial ablation is effective in stopping abnormal bleeding. Submucosal fibroids can be removed at the time of hysteroscopy for endometrial ablation, but this doesn't affect fibroids outside the interior lining of the uterus.
- Women aren't likely to get pregnant following endometrial ablation, but birth control is needed to prevent a pregnancy from developing in a fallopian tube (ectopic pregnancy).
With any procedure that doesn't remove the uterus, there's a risk that new fibroids could grow and cause symptoms.
Traditional surgical procedures
Options for traditional surgical procedures include:
- Abdominal myomectomy. If you have multiple fibroids, very large fibroids or very deep fibroids, your doctor may use an open abdominal surgical procedure to remove the fibroids.
- Many women who are told that hysterectomy is their only option can have an abdominal myomectomy instead. However, scarring after surgery can affect future fertility.
- Hysterectomy. This surgery removes the uterus. It remains the only proven permanent solution for uterine fibroids.
- Hysterectomy ends your ability to bear children. If you also elect to have your ovaries removed, the surgery brings on menopause and the question of whether you'll take hormone replacement therapy. Most women with uterine fibroids may be able to choose to keep their ovaries.
Morcellation during fibroid removal
Morcellation — a process of breaking fibroids into smaller pieces — may increase the risk of spreading cancer if a previously undiagnosed cancerous mass undergoes morcellation during myomectomy. There are several ways to reduce that risk, such as evaluating risk factors before surgery, morcellating the fibroid in a bag or expanding an incision to avoid morcellation.
All myomectomies carry the risk of cutting into an undiagnosed cancer, but younger, premenopausal women generally have a lower risk of undiagnosed cancer than do older women.
Also, complications during open surgery are more common than the chance of spreading an undiagnosed cancer in a fibroid during a minimally invasive procedure. If your doctor is planning to use morcellation, discuss your individual risks before treatment.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advises against the use of a device to morcellate the tissue (power morcellator) for most women having fibroids removed through myomectomy or hysterectomy. In particular, the FDA recommends that women who are approaching menopause or who have reached menopause avoid power morcellation. Older women in or entering menopause may have a higher cancer risk, and women who are no longer concerned about preserving their fertility have additional treatment options for fibroids.
If you're trying to get pregnant or might want to have children
Hysterectomy and endometrial ablation won't allow you to have a future pregnancy. Also, uterine artery embolization and radiofrequency ablation may not be the best options if you're trying to optimize future fertility.
Have a full discussion of the risks and benefits of these procedures with your doctor if you want to preserve the ability to become pregnant. Before deciding on a treatment plan for fibroids, a complete fertility evaluation is recommended if you're actively trying to get pregnant.
If fibroid treatment is needed — and you want to preserve your fertility — myomectomy is generally the treatment of choice. However, all treatments have risks and benefits. Discuss these with your doctor.
Risk of developing new fibroids
For all procedures except hysterectomy, seedlings — tiny tumors that your doctor doesn't detect during surgery — could eventually grow and cause symptoms that warrant treatment. This is often termed the recurrence rate. New fibroids, which may or may not require treatment, also can develop.
Also, some procedures — such as laparoscopic or robotic myomectomy, radiofrequency ablation, or MRI-guided focused ultrasound surgery (FUS) — may only treat some of the fibroids present at the time of treatment.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Uterine fibroids and Learn More about Diseases

TEN
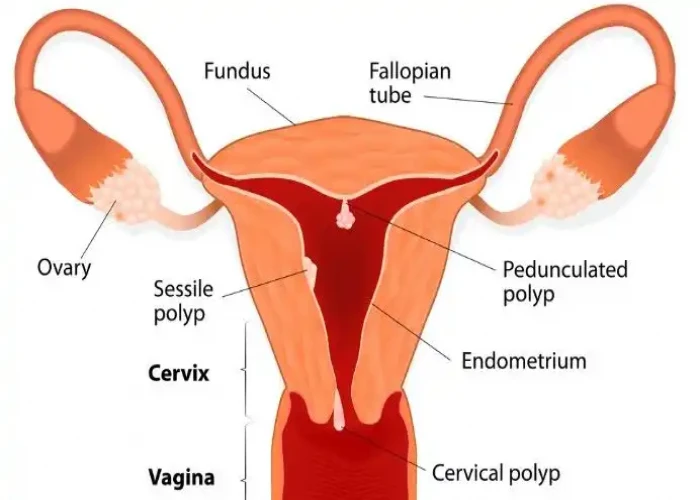
Uterine polyps

Rheumatic fever
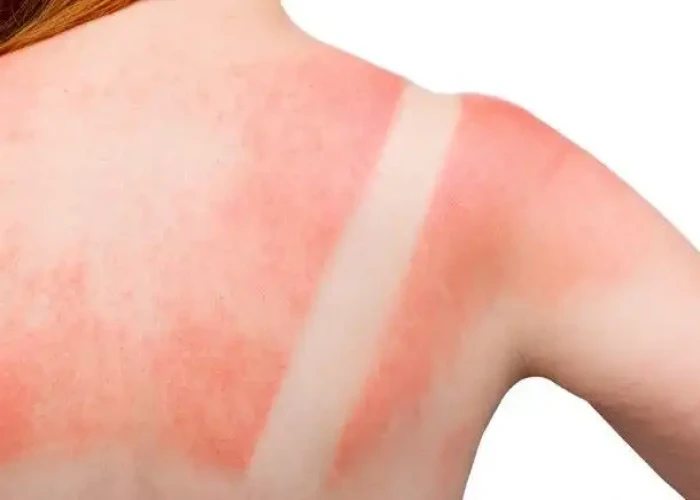

Sunburn
Metachromatic leukodystrophy

Central nervous system vascular malformations
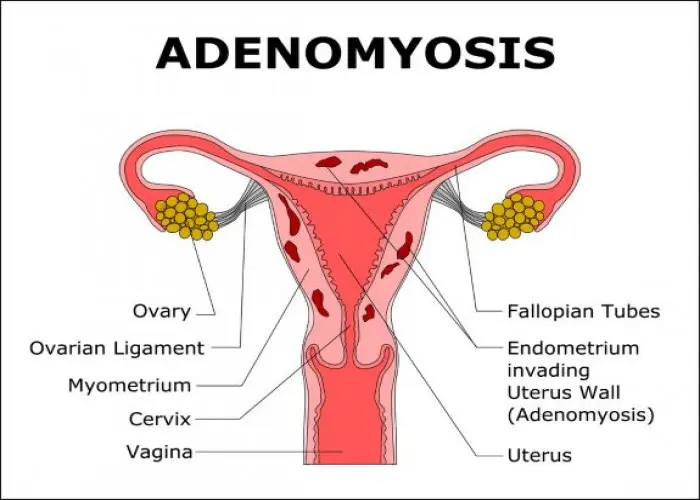
Adenomyosis
Myocarditis
uterine fibroids, জরায়ু ফাইব্রয়েডস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
