Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
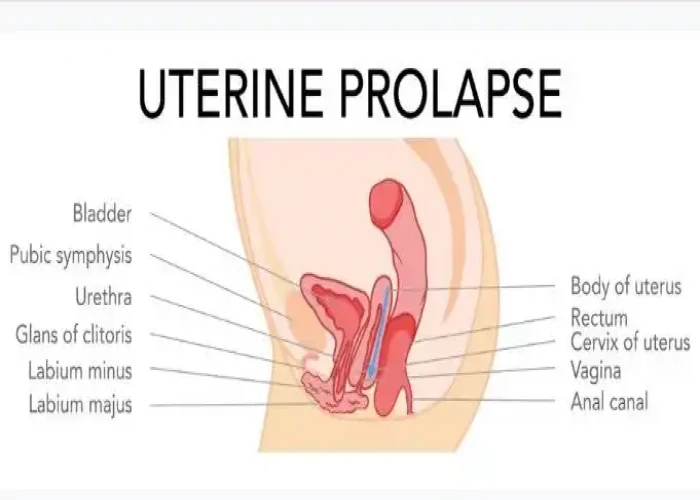
Uterine prolapse

Uterine prolapse occurs when the uterus descends from its normal position in the pelvis and into the vaginal canal, often causing discomfort or pain. This can happen when the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments that support the uterus become weakened or damaged, often due to pregnancy and childbirth, but can also occur due to age, menopause, obesity, chronic coughing, or straining during bowel movements.
Symptoms of uterine prolapse can include a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the pelvic region, difficulty urinating or having a bowel movement, lower back pain, and pain during intercourse. In severe cases, the uterus may protrude from the vaginal opening.
Diagnosis of uterine prolapse typically involves a pelvic exam, and in some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI. Treatment options depend on the severity of the prolapse and may include pelvic floor exercises, pessary use, or surgery. In cases where the uterus is protruding from the vaginal opening, surgery is typically required to remove the uterus or to perform a procedure to hold the uterus in place.
Preventive measures for uterine prolapse include maintaining a healthy weight, doing pelvic floor exercises regularly, avoiding heavy lifting or straining, and quitting smoking.
The prognosis for uterine prolapse is generally good with appropriate treatment, although the condition may recur in some cases. It is important to discuss treatment options with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action based on individual circumstances.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Pressure or heaviness deep within the pelvis
- Frequent bowel movements
- Urinary problems, such as urine leakage (incontinence) or urine retention
- Feeling as if sitting on a small ball or as if something is falling out of the vagina
Disease Causes
Uterine prolapse
Uterine prolapse results from the weakening of pelvic muscles and supportive tissues. Causes of weakened pelvic muscles and tissues include:
- Pregnancy
- Difficult labor and delivery or trauma during childbirth
- Delivery of a large baby
- Being overweight or obese
- Lower estrogen level after menopause
- Chronic constipation or straining with bowel movements
- Chronic cough or bronchitis
- Repeated heavy lifting
Disease Prevents
Uterine prolapse
To reduce your risk of uterine prolapse, try to:
- Perform Kegel exercises regularly. These exercises can strengthen your pelvic floor muscles — especially important after you have a baby.
- Treat and prevent constipation. Drink plenty of fluids and eat high-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, beans and whole-grain cereals.
- Avoid heavy lifting and lift correctly. When lifting, use your legs instead of your waist or back.
- Control coughing. Get treatment for a chronic cough or bronchitis, and don't smoke.
- Avoid weight gain. Talk with your doctor to determine your ideal weight and get advice on weight-loss strategies, if you need them.
Disease Treatments
Treatment depends on the severity of uterine prolapse. Your doctor might recommend:
- Self-care measures. If your uterine prolapse causes few or no symptoms, simple self-care measures may provide relief or help prevent worsening prolapse. Self-care measures include performing Kegel exercises to strengthen your pelvic muscles, losing weight and treating constipation.
- Pessary. A vaginal pessary is a plastic or rubber ring inserted into your vagina to support the bulging tissues. A pessary must be removed regularly for cleaning.
Surgery
Your doctor might recommend surgery to repair uterine prolapse. Minimally invasive (laparoscopic) or vaginal surgery might be an option.
Surgery can involve:
- Repair of weakened pelvic floor tissues. This surgery is generally approached through the vagina but sometimes through the abdomen. The surgeon might graft your own tissue, donor tissue or a synthetic material onto weakened pelvic floor structures to support your pelvic organs.
- Removal of your uterus (hysterectomy). Hysterectomy might be recommended for uterine prolapse in certain instances. A hysterectomy is generally very safe, but with any surgery comes the risk of complications.
Talk with your doctor about all your treatment options to be sure you understand the risks and benefits of each so that you can choose what's best for you.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Conium maculatum
6 strength.
-
Belladonna
30, 200 strength.
-
Lycopodium clavatum
30, 200 strength.
-
Hydrastis
Q strength.
-
Graphites
30, 200 strength.
-
Kreosotum
6, 30 strength.
-
Aurum muriaticum natronatum
3X strength.
-
Lilium tigrinum
Q strength.
-
Fraxinus americana
Q strength.
Disease yoga
Uterine prolapse and Learn More about Diseases

Melanoma

Dizziness

Child abuse
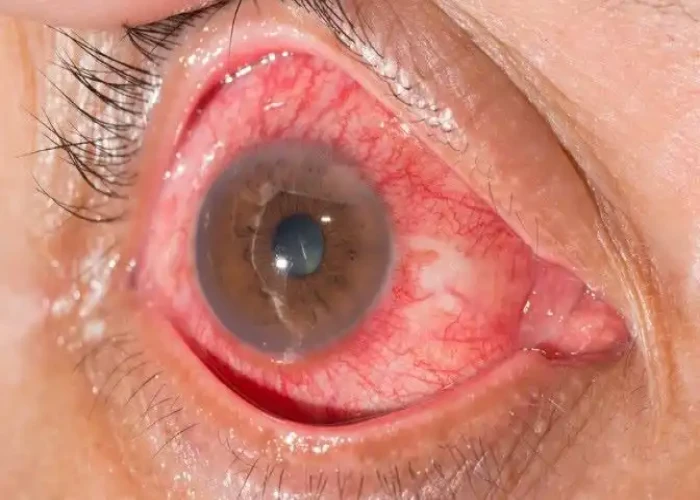
Uveitis
Pinched nerve
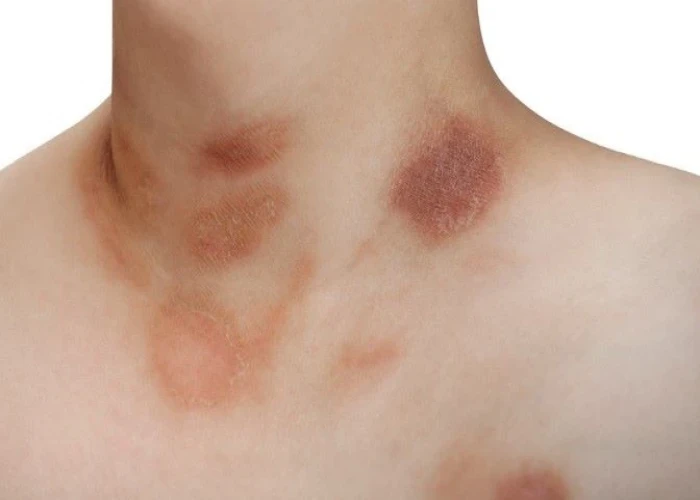
Pityriasis rosea

Bronchiectasis
Adult Stills disease
Uterine prolapse, জরায়ু প্রল্যাপস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.