 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Fistula - Yoga remedies
A fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway that develops between two organs or tissues that are not normally connected. In the medical context, fistula usually refers to an abnormal passage that forms between an organ and the skin, or between two internal organs.
The most common types of fistulas include anal fistulas, which occur between the anal canal and the skin surrounding the anus, and arteriovenous fistulas, which occur between an artery and vein. Other types of fistulas can occur in the urinary, reproductive, and digestive systems.
Fistulas can be caused by a variety of underlying conditions, including infections, inflammatory bowel disease, cancer, and trauma. Symptoms of fistulas may include drainage of pus or other fluids, pain, inflammation, and fever.
Treatment for fistulas depends on the underlying cause and location of the fistula. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove the affected tissue. In other cases, medications may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and control infection.
Preventing fistulas involves managing underlying medical conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, avoiding trauma or injury to the affected area, and practicing good hygiene to prevent infection. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have a fistula, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.

Slimness
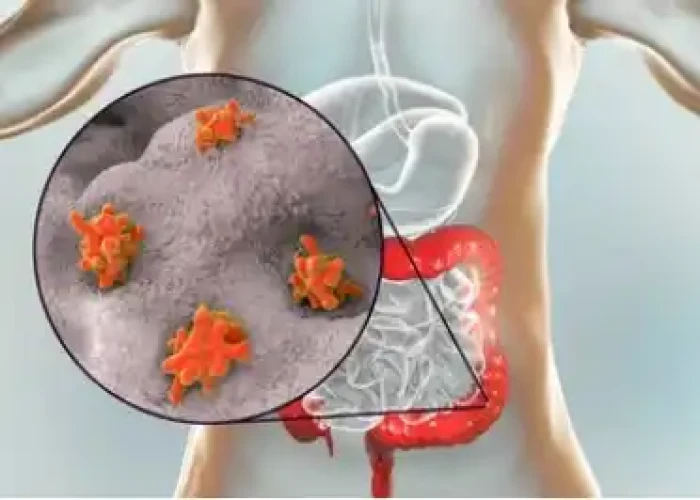
Dysentery

Nervousness
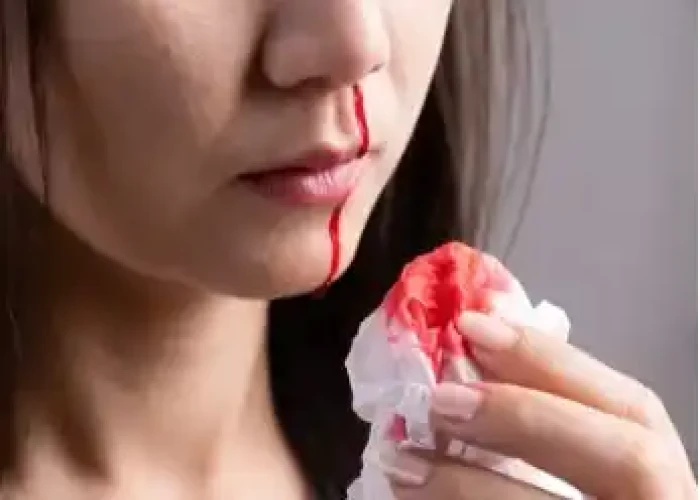

Bleeding from nose
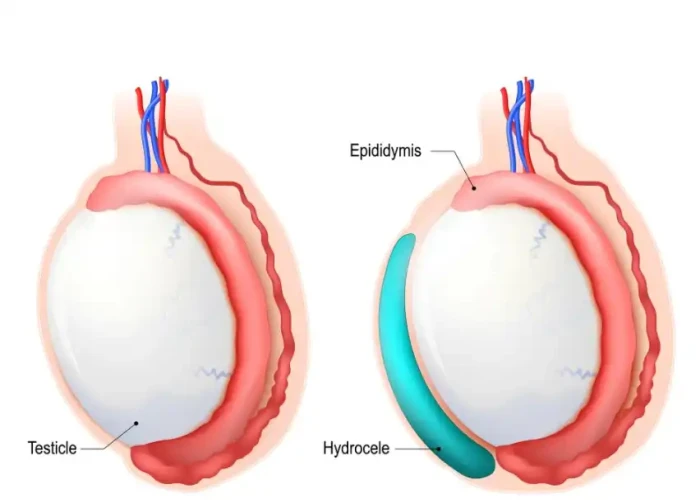
Hydrocele

Muscle spasms
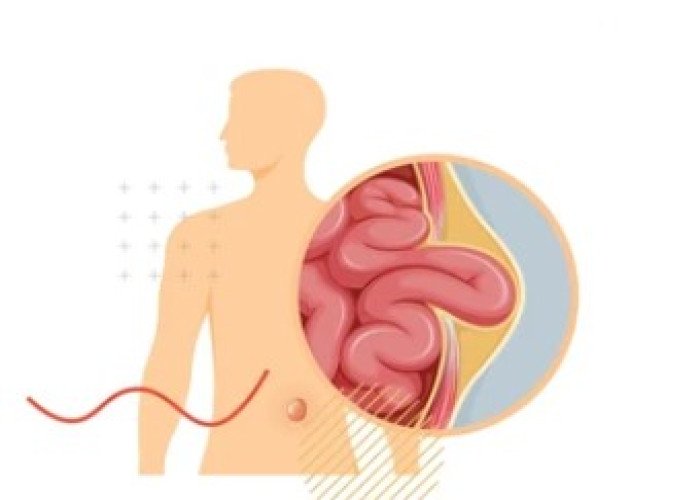
Intestinal muscle weaknes...
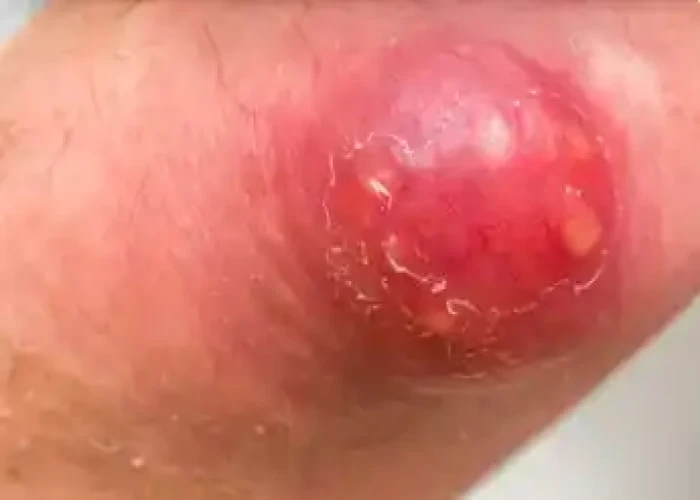
Boil
Fistula, ভগন্দর
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.

