 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Cough - Yoga remedies
Coughing is a reflex action that helps to clear the throat and airways of irritants, mucus, and foreign particles. It is a common symptom of many respiratory tract infections, allergies, and other conditions affecting the lungs, throat, and sinuses.
There are two main types of cough: productive and non-productive. A productive cough produces phlegm or mucus, while a non-productive cough is dry and does not produce any mucus.
Common causes of cough include viral or bacterial infections, allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and smoking. In some cases, coughing can be a symptom of a more serious condition, such as pneumonia or lung cancer.
Treatment for cough depends on the underlying cause. Over-the-counter cough suppressants or expectorants may be helpful in managing symptoms. If the cough is caused by an infection, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed. It is important to see a healthcare professional if a cough persists for more than a few weeks, is accompanied by chest pain or difficulty breathing, or if other concerning symptoms are present.
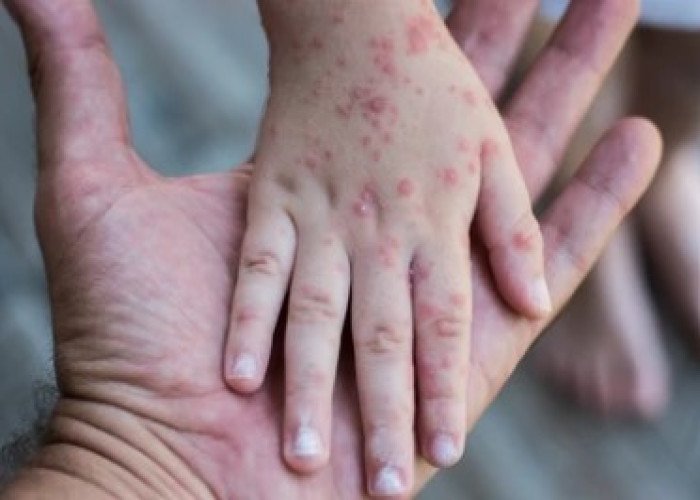
Pox

Nervousness
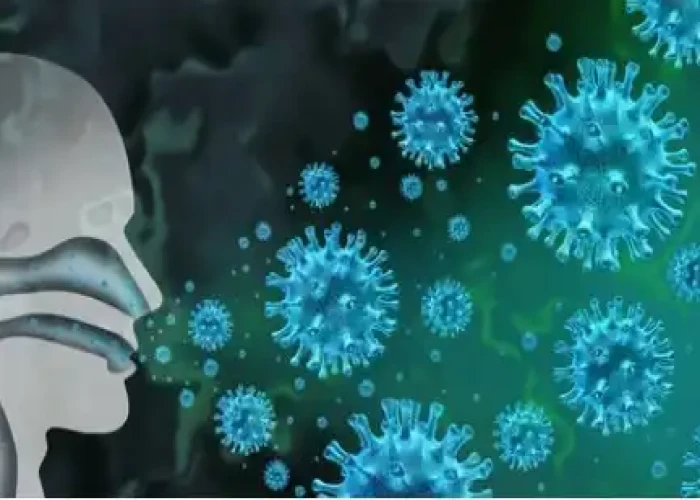

Influenza

Deafness

Sperm loss

Beriberi
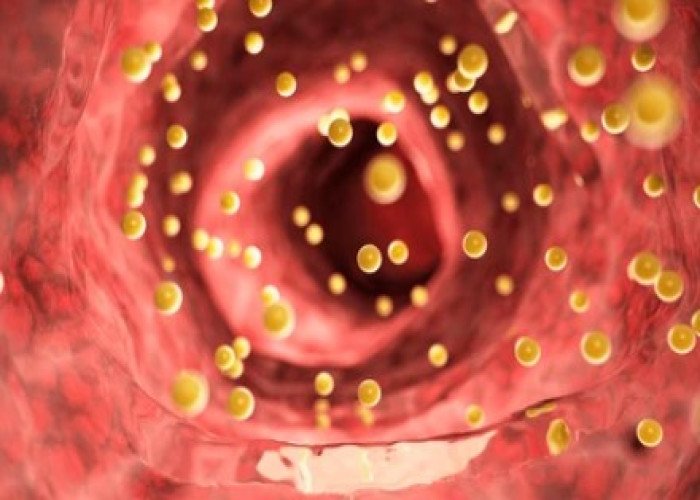
Colon inflammation

Maternal gland is weak
Cough, কাশি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.