 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Hydrocele - Yoga remedies
Hydrocele is a condition that occurs in males when there is an accumulation of fluid in the scrotum, causing it to swell. The scrotum is the sac-like structure that contains the testicles. The accumulation of fluid occurs between the two layers of the membrane that cover the testicles.
Hydrocele is a common condition, especially in newborns and older men. In newborns, it is usually harmless and goes away on its own within a year. In older men, hydrocele may be a sign of an underlying problem, such as an infection, injury, or tumor.
Symptoms of hydrocele include swelling of the scrotum, feeling of heaviness or discomfort in the affected area, and pain in the scrotum or groin. In some cases, the swelling may be so large that it causes embarrassment or difficulty in walking.
Hydrocele is usually diagnosed through a physical examination. In some cases, an ultrasound may be done to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions.
Treatment for hydrocele depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. In newborns, no treatment may be needed as the condition usually goes away on its own. In older men, treatment may be needed if the hydrocele is causing discomfort or affecting the quality of life.
In cases where the hydrocele is caused by an underlying condition, such as an infection or tumor, treatment of the underlying condition is necessary. In cases where the hydrocele is large and causing discomfort, surgery may be needed to remove the excess fluid and repair the membrane that covers the testicles.
In summary, hydrocele is a common condition in males that occurs when there is an accumulation of fluid in the scrotum. It can be harmless or a sign of an underlying problem, and treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause.
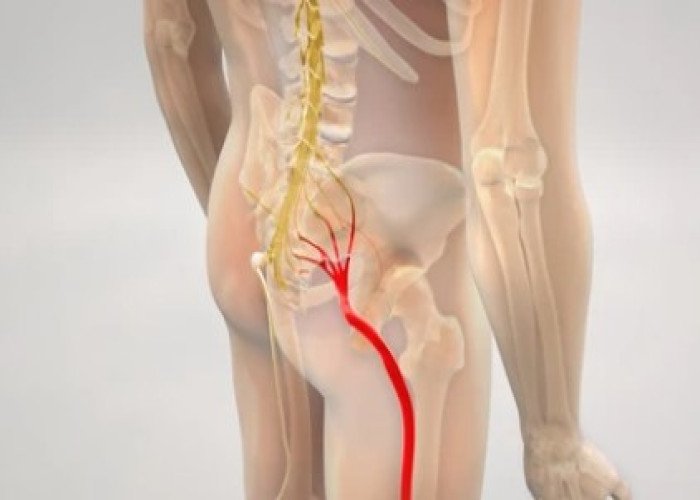
Sciatica
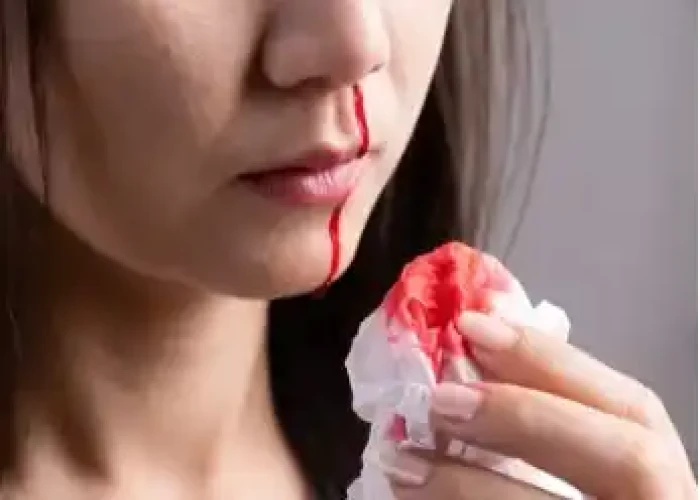

Bleeding from nose
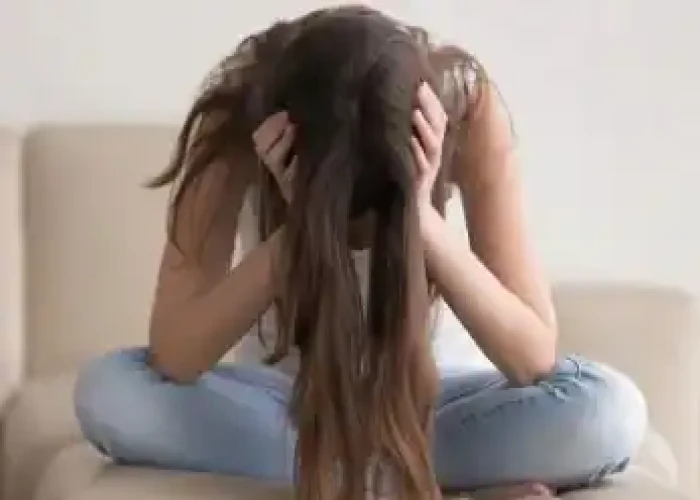

Hysteria (Fainting)
Laziness

Insanity
Pleurisy

Cholera
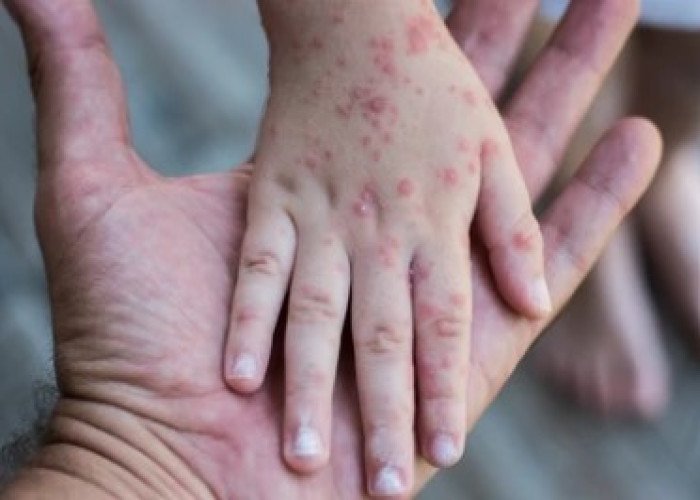
Pox
Hydrocele, একশিরা, হাইড্রোসিল
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.