Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Tissue - Diseases
Tissue refers to a group of similar cells that perform a particular function in an organism. In multicellular organisms, tissues are organized into organs, which work together to carry out specific functions necessary for the survival of the organism.
There are four main types of tissues in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue lines the surfaces of organs and cavities, and is responsible for functions such as secretion, absorption, and protection. Connective tissue provides support and structure to organs and other tissues, and includes types such as bone, cartilage, and blood. Muscle tissue is responsible for movement and includes types such as skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. Nervous tissue is involved in communication and coordination within the body, and includes neurons and supporting cells such as glia.
In plants, tissues are organized into three main types: dermal, ground, and vascular. Dermal tissue covers and protects the plant, while ground tissue carries out functions such as photosynthesis and storage. Vascular tissue is responsible for transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant.
The study of tissues is known as histology, and involves examining the structure and function of tissues at the microscopic level. Understanding the properties of tissues is important for diagnosing and treating a variety of medical conditions, as well as for developing new treatments and technologies in fields such as tissue engineering.
Urine

Bulbourethral glands
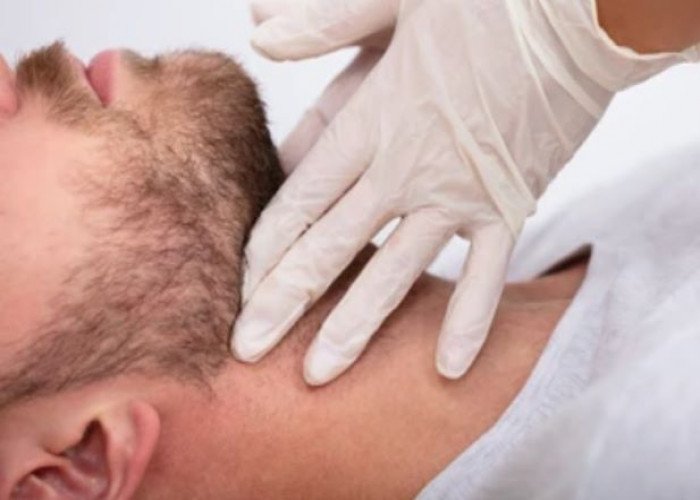
Lymph node
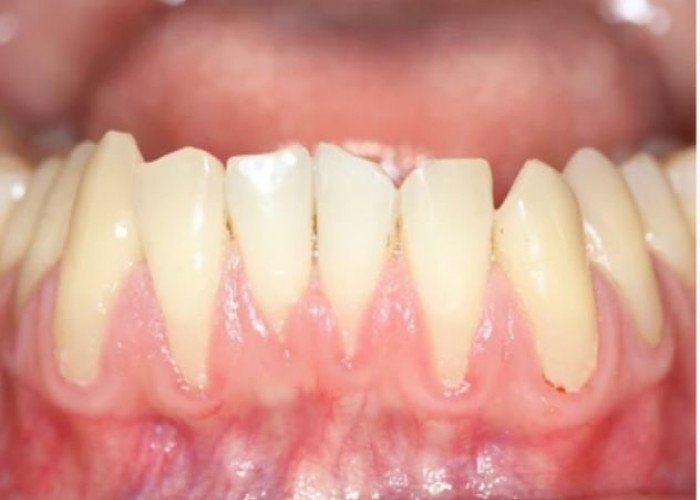
Gum
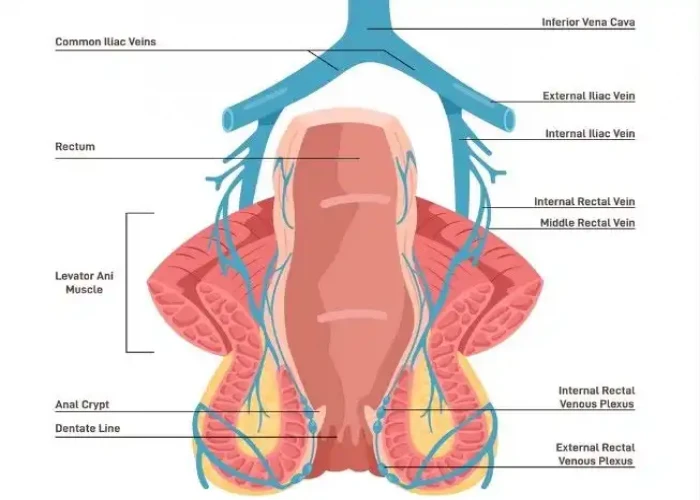
Anus
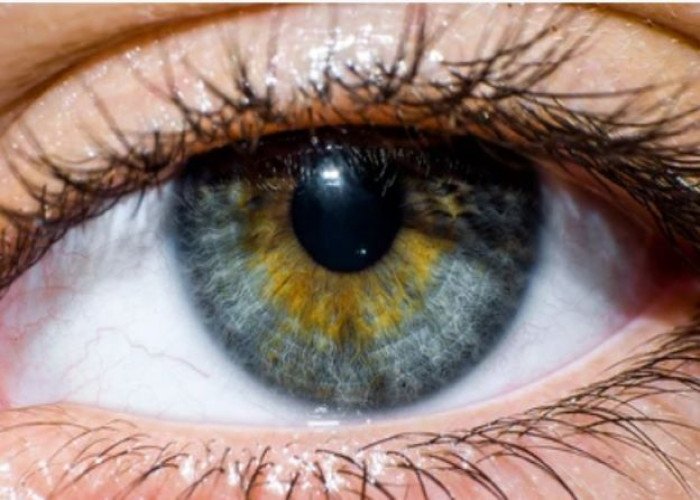
Cornea Eye
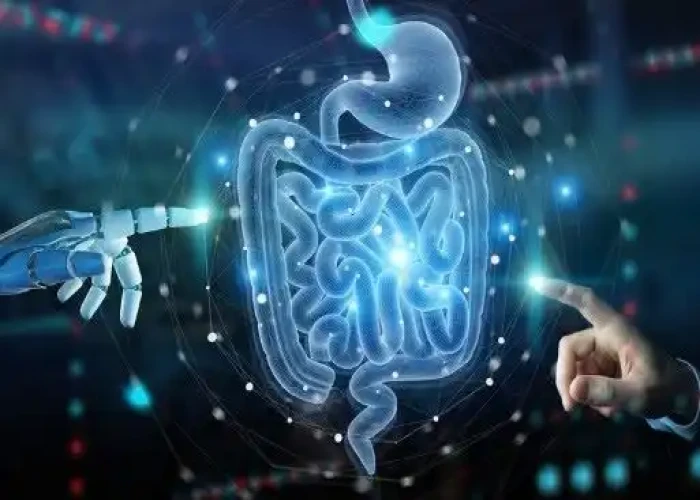

Ileum intestine

Pharynx
Tissue, Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue, কলা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.