Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Lupus
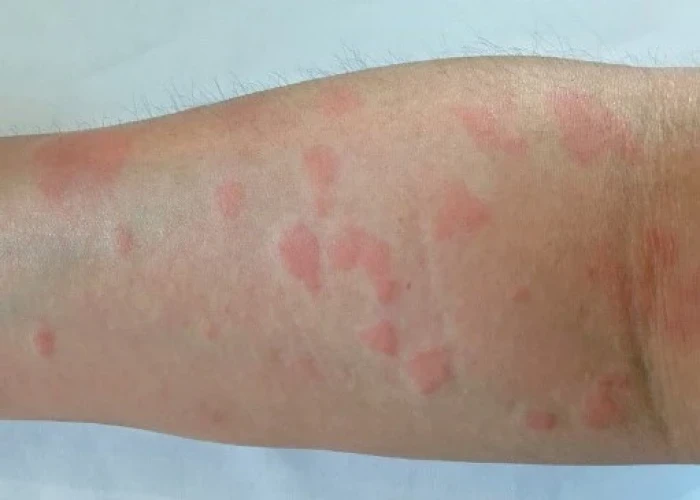
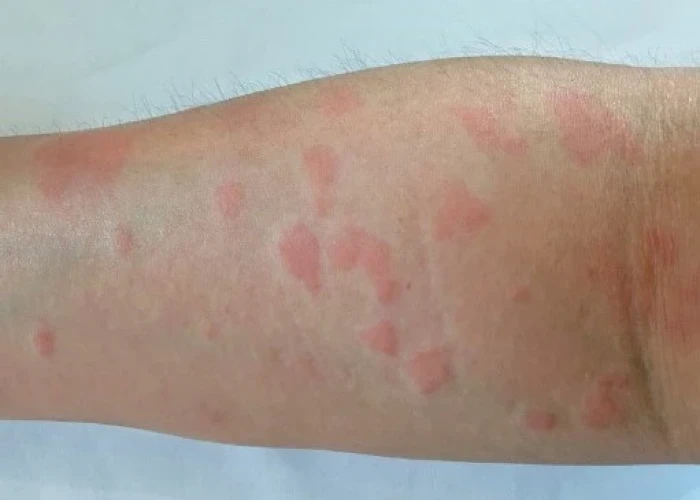
Lupus, also known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various organs and tissues in the body. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, causing inflammation and damage.
Lupus can affect different parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, lungs, heart, and brain. Symptoms can vary widely, but may include fatigue, joint pain and swelling, skin rashes, fever, and chest pain.
The cause of lupus is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Women are more likely to develop lupus than men, and it is more common in people of African, Asian, and Hispanic descent.
There is no cure for lupus, but treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antimalarial drugs, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologic drugs. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, stress management, and sun protection, can also help manage symptoms.
It's important for people with lupus to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a treatment plan that is right for them. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are also important to manage the disease and prevent complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- A butterfly-shaped rash on the face that covers the cheeks and bridge of the nose or rashes elsewhere on the body
- Memory loss
- Headaches
- Dry eyes
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Skin lesions
- Swollen skin
- Body stiffness
- Joint pain
- Fever
- Fingers and toes that turn white or blue when exposed to cold or during stressful periods
Disease Causes
Lupus
As an autoimmune disease, lupus occurs when your immune system attacks healthy tissue in your body. It's likely that lupus results from a combination of your genetics and your environment.
It appears that people with an inherited predisposition for lupus may develop the disease when they come into contact with something in the environment that can trigger lupus. The cause of lupus in most cases, however, is unknown. Some potential triggers include:
- Sunlight. Exposure to the sun may bring on lupus skin lesions or trigger an internal response in susceptible people.
- Infections. Having an infection can initiate lupus or cause a relapse in some people.
- Medications. Lupus can be triggered by certain types of blood pressure medications, anti-seizure medications and antibiotics. People who have drug-induced lupus usually get better when they stop taking the medication. Rarely, symptoms may persist even after the drug is stopped.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treatment for lupus depends on your signs and symptoms. Determining whether you should be treated and what medications to use requires a careful discussion of the benefits and risks with your doctor.
As your signs and symptoms flare and subside, you and your doctor may find that you'll need to change medications or dosages. The medications most commonly used to control lupus include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as naproxen sodium (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), may be used to treat pain, swelling and fever associated with lupus. Stronger NSAIDs are available by prescription. Side effects of NSAIDs may include stomach bleeding, kidney problems and an increased risk of heart problems.
- Antimalarial drugs. Medications commonly used to treat malaria, such as hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), affect the immune system and can help decrease the risk of lupus flares. Side effects can include stomach upset and, very rarely, damage to the retina of the eye. Regular eye exams are recommended when taking these medications.
- Corticosteroids. Prednisone and other types of corticosteroids can counter the inflammation of lupus. High doses of steroids such as methylprednisolone (Medrol) are often used to control serious disease that involves the kidneys and brain. Side effects include weight gain, easy bruising, thinning bones, high blood pressure, diabetes and increased risk of infection. The risk of side effects increases with higher doses and longer term therapy.
- Immunosuppressants. Drugs that suppress the immune system may be helpful in serious cases of lupus. Examples include azathioprine (Imuran, Azasan), mycophenolate (Cellcept), methotrexate (Trexall, Xatmep, others), cyclosporine (Sandimmune, Neoral, Gengraf) and leflunomide (Arava). Potential side effects may include an increased risk of infection, liver damage, decreased fertility and an increased risk of cancer.
- Biologics. A different type of medication, belimumab (Benlysta) administered intravenously, also reduces lupus symptoms in some people. Side effects include nausea, diarrhea and infections. Rarely, worsening of depression can occur.
- Rituximab (Rituxan, Truxima) may be beneficial for some people in whom other medications haven't helped. Side effects include allergic reaction to the intravenous infusion and infections.
In clinical trials, voclosporin has been shown to be effective in treating lupus.
Other potential drugs to treat lupus are currently being studied, including abatacept (Orencia), anifrolumab and others.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Lupus and Learn More about Diseases

Infertility (Sterility)
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea
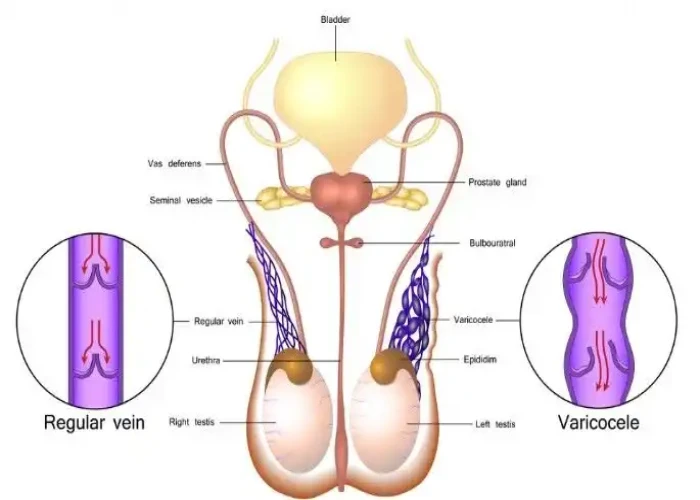
Varicocele

Soft tissue sarcoma
Paget's disease of bone

Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)

Membranous nephropathy

Childhood schizophrenia
lupus, লুপাস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.