Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Lymphedema
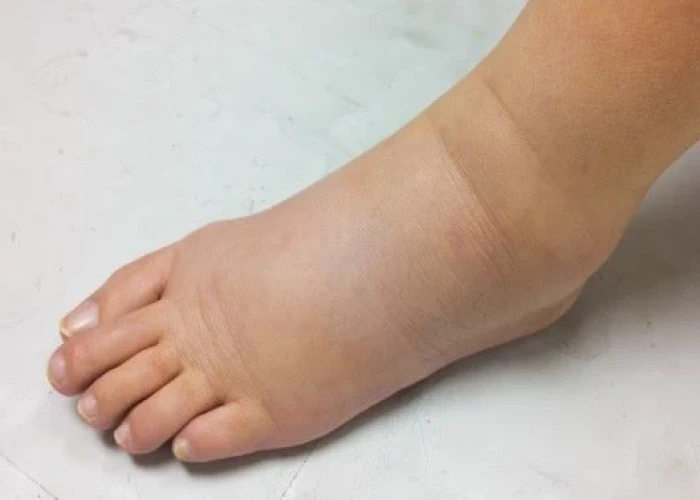
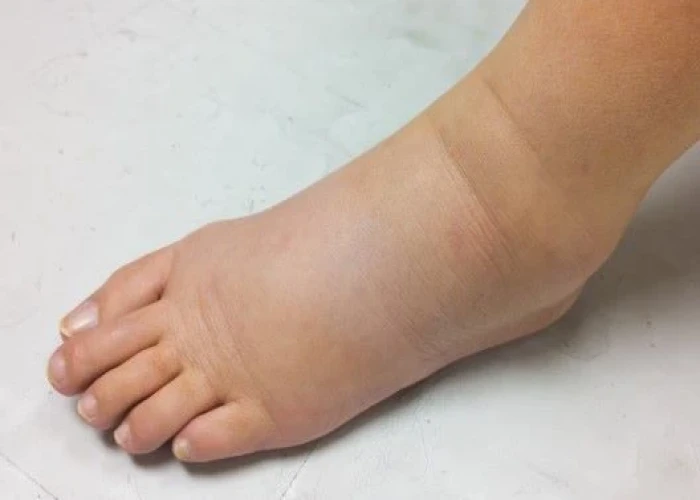
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by the buildup of lymphatic fluid in the tissues, usually in the arms or legs, but it can also occur in other parts of the body. The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and organs that helps to maintain fluid balance in the body and fight infections.
Lymphedema can occur when the lymphatic system is damaged or blocked, such as after surgery or radiation therapy for cancer, or as a result of infection or inflammation. It can also be a result of a congenital or hereditary condition.
Symptoms of lymphedema may include swelling, heaviness or tightness in the affected limb, decreased range of motion, and skin changes such as thickening, hardening, or discoloration.
There is no cure for lymphedema, but treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment may include compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, exercise, and skin care. In some cases, surgery may be recommended to remove excess tissue or repair damaged lymphatic vessels.
Prevention of lymphedema involves taking precautions to avoid injury or infection to the affected limb, and managing the condition through regular monitoring and treatment. It is important for people with lymphedema to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a treatment plan that is right for them.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen arms or hands
- Swollen leg
- Swollen fingers
- Frequent infections
- Colon cancer that occurs at a younger age, especially before age 50
Disease Causes
Lymphedema
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels that carry protein-rich lymph fluid throughout the body. It's part of your immune system. Lymph nodes act as filters and contain cells that fight infection and cancer.
The lymph fluid is pushed through the lymph vessels by muscle contractions as you move through the tasks of your day and small pumps in the wall of the lymph vessels. Lymphedema occurs when the lymph vessels are not able to adequately drain lymph fluid, usually from an arm or leg.
The most common causes of lymphedema include:
- Cancer. If cancer cells block lymph vessels, lymphedema may result. For instance, a tumor growing near a lymph node or lymph vessel could enlarge enough to block the flow of the lymph fluid.
- Radiation treatment for cancer. Radiation can cause scarring and inflammation of lymph nodes or lymph vessels.
- Surgery. In cancer surgery, lymph nodes are often removed to see if the disease has spread. However, this doesn't always result in lymphedema.
- Parasites. In developing countries in the tropics, the most common cause of lymphedema is infection with threadlike worms that clog the lymph nodes.
Less commonly, lymphedema results from inherited conditions in which the lymphatic system doesn't develop properly.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
There's no cure for lymphedema. Treatment focuses on reducing the swelling and preventing complications.
Medications
Lymphedema greatly increases the risk of skin infections (cellulitis). Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics for you to keep on hand so that you can start taking them immediately once symptoms appear.
Therapy
Specialized lymphedema therapists can teach you about techniques and equipment that can help reduce lymphedema swelling. Examples include:
- Exercises. Gentle contraction of the muscles in the arm or leg can help move the excess fluid out of the swollen limb.
- Manual lymph drainage. Therapists trained in this massage-like technique use very light pressure to move the trapped fluid in the swollen limb toward an area with working lymph vessels. People should avoid manual lymph drainage if they have a skin infection, blood clots or active cancer in the affected limb.
- Compression bandages. Using low-stretch bandages to wrap the entire limb encourages lymph fluid to flow back toward the trunk of the body.
- Compression garments. Close-fitting elastic sleeves or stockings can compress the arm or leg to encourage lymph fluid drainage. These garments often require a prescription to ensure that the proper amount of compression is used. You may need to be measured by a professional to ensure proper fit.
- Sequential pneumatic compression. A sleeve worn over the affected arm or leg connects to a pump that intermittently inflates the sleeve, putting pressure on the limb and moving lymph fluid away from the fingers or toes.
Surgical and other procedures
Surgical treatment for lymphedema may include:
- Lymph node transplant. Lymph nodes are taken from a different area of the body and then attached to the network of lymph vessels in the affected limb. Many people with early-stage lymphedema see good results from this surgery and can decrease the amount of compression needed.
- New drainage paths. Another option for early-stage lymphedema, this procedure creates new connections between the lymph network and blood vessels. The excess lymph fluid is then removed from the limb via blood vessels.
- Removal of fibrous tissue. In severe lymphedema, the soft tissues in the limb become fibrous and hardened. Removing some of this hardened tissue, often through liposuction, can improve the limb's function. In very severe cases, hardened tissue and skin may be removed with a scalpel.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Lymphedema and Learn More about Diseases

Atrophy of Stomach

Vulvar cancer

Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children

Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Colon polyps
CSF leak (Cerebrospinal fluid leak)

Chemo brain
Polyhydramnios
lymphedema, লিম্ফিডেমা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.