Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
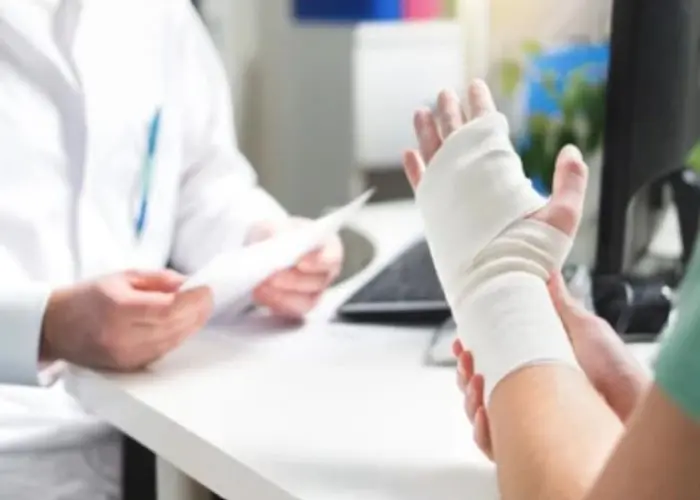
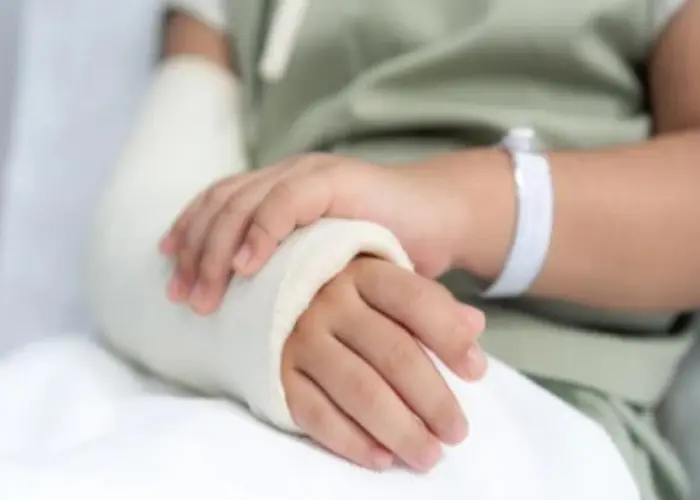
Hand - Diseases
The hand is a complex part of the body that is made up of bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels. It plays a vital role in carrying out everyday activities such as grasping, gripping, and manipulating objects. The human hand has five fingers, including the thumb, which is opposable and allows for fine motor skills.
The bones of the hand are divided into three groups: the carpal bones in the wrist, the metacarpals in the palm, and the phalanges in the fingers. The muscles of the hand are responsible for movement and are controlled by nerves that originate in the spinal cord. The tendons attach the muscles to the bones and allow for movement of the hand and fingers.
The hand can be affected by various injuries and conditions, such as fractures, sprains, arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and repetitive strain injuries. Treatment for hand injuries or conditions may include rest, immobilization, physical therapy, medications, and surgery.
Hand hygiene is essential for preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Washing hands with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers can help reduce the risk of infection. Regular hand exercises and stretches can also help improve hand strength and flexibility.
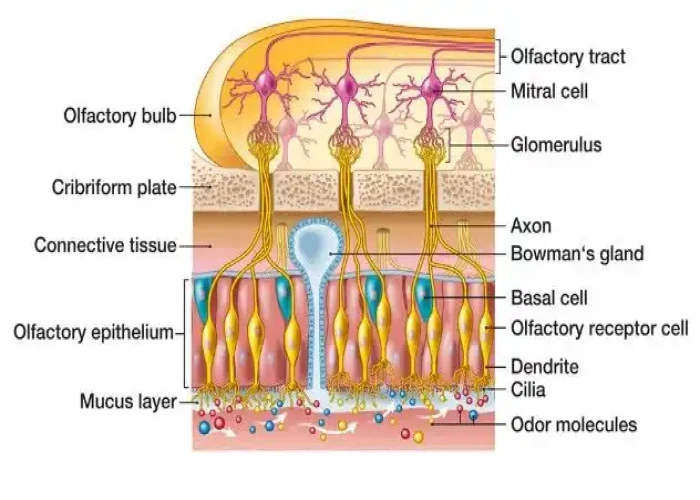
Olfactory epithelium
Throat

Brainstem

Thymus

Ear
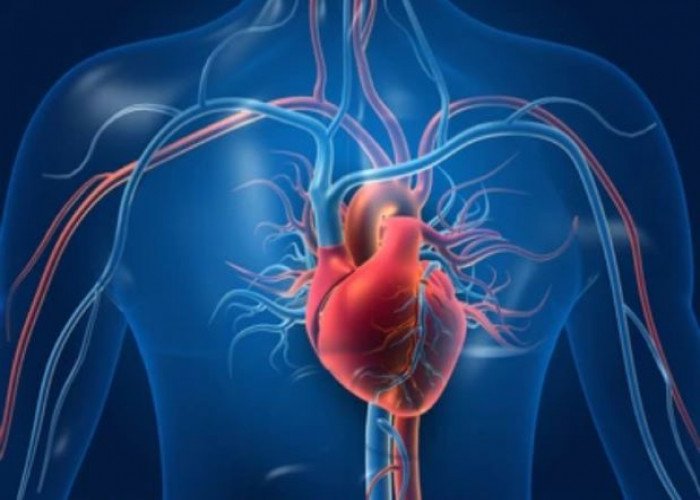
Veins

Arm

Iris Eye
Hand, হাত
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.