Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Gangrene
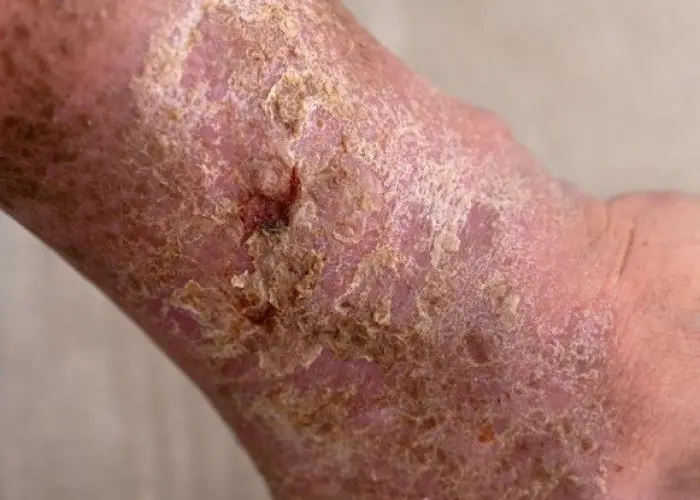
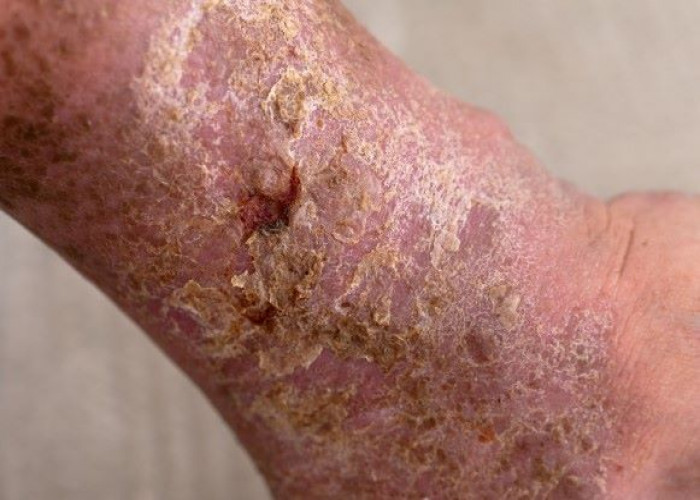
Gangrene is a serious condition that occurs when there is a loss of blood supply to an area of the body, leading to tissue death. It most commonly affects the extremities, such as the toes, fingers, hands, and feet. However, it can also occur in other parts of the body, such as the intestines or genitals.
There are several types of gangrene, including dry gangrene, which is a form of tissue death that occurs without infection, and wet gangrene, which is a more severe form of tissue death that is often associated with a bacterial infection. Gas gangrene is another form of condition that is caused by a bacterial infection that produces gas and toxins in the tissues.
Symptoms of gangrene can include skin discoloration, pain, swelling, and a foul odor from the affected area. Treatment for gangrene usually involves antibiotics to treat any associated infection, surgery to remove the dead tissue, and in some cases, amputation of the affected limb.
Gangrene is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. If you suspect that you may have gangrene or are experiencing symptoms such as persistent pain, swelling, or skin discoloration, you should seek medical care immediately. Early treatment can help to prevent the spread of the condition and improve the chances of a positive outcome.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Gangrene
- Thin, shiny skin, or skin without hair
- A foul-smelling discharge leaking from a sore
- Confusion (Hallucinations)
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Cool skin
- Numbness
- Blisters
- Swollen lump or skin nodules
- Fever, although some people may have a body temperature lower than the normal 98.6 F (37 C)
Disease Causes
Gangrene
Causes of gangrene include:
- Lack of blood supply. Your blood provides oxygen and nutrients to your body. It also provides your immune system with antibodies to ward off infections. Without a proper blood supply, your cells can't survive, and your tissue decays.
- Infection. An untreated bacterial infection can cause gangrene.
- Traumatic injury. Gunshot wounds or crushing injuries from car crashes can cause open wounds that let bacteria into the body. If the bacteria infect tissues and remain untreated, gangrene can occur.
Types of gangrene
- Dry gangrene. This type of gangrene involves dry and shriveled skin that looks brown to purplish blue or black. Dry gangrene may develop slowly. It occurs most commonly in people who have diabetes or blood vessel disease, such as atherosclerosis.
- Wet gangrene. Gangrene is referred to as wet if there's a bacterial infection in the affected tissue. Swelling, blistering and a wet appearance are common features of wet gangrene.
- Wet gangrene may develop after a severe burn, frostbite or injury. It often occurs in people with diabetes who unknowingly injure a toe or foot. Wet gangrene needs to be treated immediately because it spreads quickly and can be deadly.
- Gas gangrene. Gas gangrene typically affects deep muscle tissue. If you have gas gangrene, the surface of your skin may look normal at first.
- As the condition worsens, your skin may become pale and then turn gray or purplish red. The skin may look bubbly and may make a crackling sound when you press on it because of the gas within the tissue.
- Gas gangrene is most commonly caused by infection with a bacterium called Clostridium perfringens. Bacteria gather in an injury or surgical wound that has no blood supply. The bacterial infection produces toxins that release gas and cause tissue death. Like wet gangrene, gas gangrene is a life-threatening condition.
- Internal gangrene. Gangrene that affects one or more of your organs, such as your intestines, gallbladder or appendix, is called internal gangrene. This type of gangrene occurs when blood flow to an internal organ is blocked — for example, when your intestines bulge through a weakened area of muscle in your stomach area (hernia) and become twisted.
- Left untreated, internal gangrene can be deadly.
- Fournier's gangrene. Fournier's gangrene involves the genital organs. Men are more often affected, but women also can develop this type of gangrene. An infection in the genital area or urinary tract causes this type of gangrene.
- Meleney's gangrene. This rare type of gangrene — also called progressive bacterial synergistic gangrene — is usually a complication of surgery. People with Meleney's gangrene develop painful skin lesions one to two weeks after their operations.
Disease Prevents
Gangrene
Here are a few suggestions to help you reduce your risk of developing gangrene:
- Care for your diabetes. If you have diabetes, make sure you examine your hands and feet daily for cuts, sores, and signs of infection, such as redness, swelling or drainage. Ask your doctor to examine your hands and feet at least once a year, and try to maintain control over your blood sugar levels.
- Lose weight. Excess pounds not only put you at risk of diabetes but also place pressure on your arteries, constricting blood flow and putting you at risk of infection and slow wound healing.
- Don't use tobacco. The chronic use of tobacco products can damage your blood vessels.
- Help prevent infections. Wash any open wounds with a mild soap and water and try to keep them clean and dry until they heal.
- Watch out when the temperature drops. Frostbitten skin can lead to gangrene because frostbite reduces blood circulation in an affected area. If you notice that any area of your skin has become pale, hard, cold and numb after prolonged exposure to cold temperatures, call your doctor.
Disease Treatments
Tissue that has been damaged by gangrene can't be saved, but steps can be taken to prevent gangrene from getting worse. The faster you get treatment, the better your chance for recovery.
Treatment for gangrene may involve medication, surgery or hyperbaric oxygen therapy — or a combination of these therapies — depending on the severity of your condition.
Medications
Medications to treat a bacterial infection (antibiotics) are given through an IV or taken by mouth.
Pain medications may be given to relieve your discomfort.
Surgery or other procedures
Depending on the type of gangrene you have and its severity, you may need more than one surgery. Surgery for gangrene includes:
- Debridement. This type of surgery is done to remove the infected tissue and stop the infection from spreading. Your doctor may also perform surgery to repair any damaged or diseased blood vessels to restore blood flow to the infected area. Your doctor may prescribe certain antibiotics until the infection is cleared.
- Amputation. In severe cases of gangrene, the infected body part — such as a toe, finger, arm or leg — may need to be surgically removed (amputated). You may later be fitted with an artificial limb (prosthesis).
- Skin grafting (reconstructive surgery). Sometimes, surgery is needed to repair damaged skin or to improve the appearance of gangrene-related scars. Such surgery may be done using a skin graft. During a skin graft, your doctor removes healthy skin from another part of your body — usually a place hidden by your clothing — and carefully spreads it over an affected area. The healthy skin may be held in place by a dressing or by a couple of small stitches. A skin graft can be done only if there is enough blood supply to the area.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is done inside a chamber pressurized with pure oxygen. You usually lie on a padded table that slides into a clear plastic tube. The pressure inside the chamber will slowly rise to about 2.5 times normal atmospheric pressure.
When you're safely exposed to increased pressure and oxygen, your blood can carry more oxygen. Oxygen-rich blood slows the growth of bacteria that live in tissue lacking oxygen and helps infected wounds heal more easily.
The treatment for gangrene generally lasts about 90 minutes. You may need two to three treatments every day until the infection clears.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Gangrene and Learn More about Diseases

Down syndrome
Gastritis

Hemorrhoids (Piles)

Kyphosis
Hives and angioedema

Absence seizure

Mental illness

Idiopathic hypersomnia
gangrene, গ্যাংগ্রিন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.