 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)

Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a kidney disease that affects the glomeruli, which are small blood vessels in the kidneys that filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood. In FSGS, some of the glomeruli become scarred and damaged, leading to problems with kidney function.
The exact cause of FSGS is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. It can occur in both children and adults, and it can be either primary (idiopathic), meaning there is no known cause, or secondary, meaning it is caused by an underlying condition such as HIV infection, obesity, or drug use.
Symptoms of FSGS can include swelling in the legs and ankles, foamy urine, fatigue, and high blood pressure. In some cases, there may be no symptoms and the condition is only detected through routine medical testing.
Treatment for FSGS typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Medications such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) may be used to reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and protect the kidneys from further damage. In some cases, dialysis or kidney transplantation may be needed if kidney function has severely declined.
Management of FSGS also involves maintaining a healthy diet, controlling blood pressure and blood sugar levels, quitting smoking, and exercising regularly. Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are important to manage the condition and prevent complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
Disease Causes
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis can be caused by a variety of conditions, such as diabetes, sickle cell disease, other kidney diseases and obesity. It can also be caused by an infection and drug toxicity. A rare form of FSGS is caused by inherited abnormal genes. Sometimes there's no identifiable cause.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) and Learn More about Diseases

Listeria infection
Heart disease
Delayed ejaculation
Gastric Ulcer

Hypopituitarism
Brain aneurysm
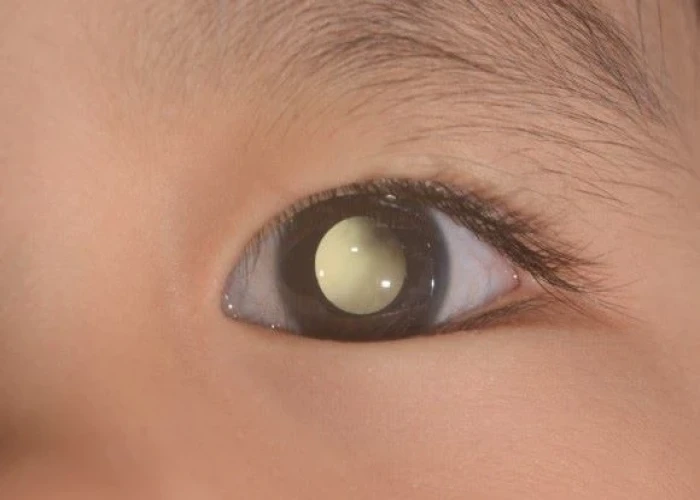
Retinoblastoma
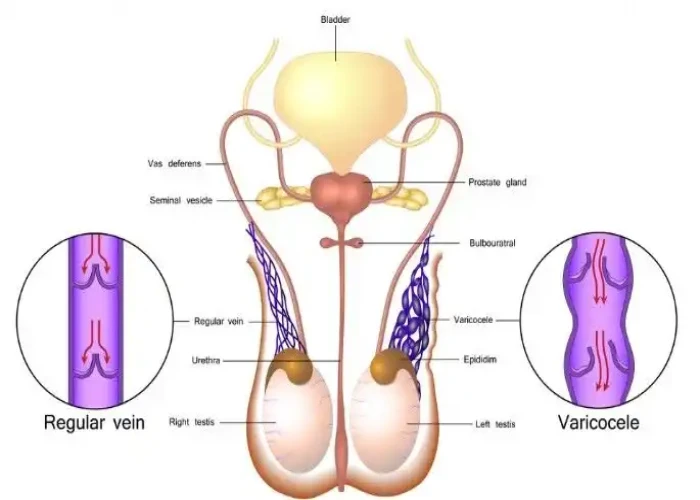
Varicocele
focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, fsgs, ফোকাল সেগমেন্টাল গ্লোমারুলোস্ক্লেরোসিস, এফএসজিএস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
