Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
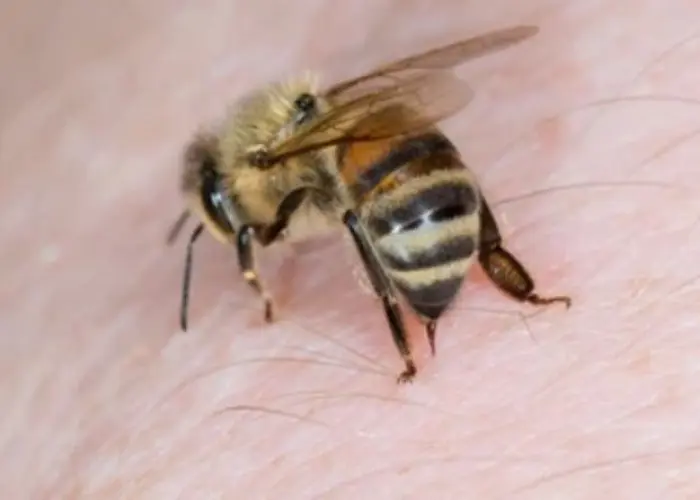
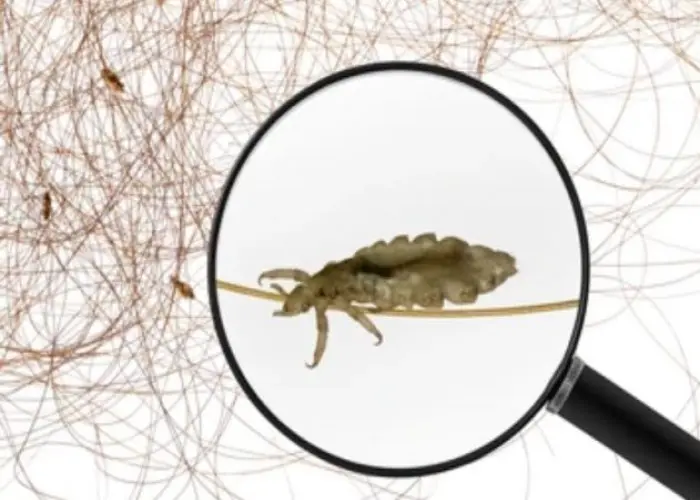
Whole body - Diseases
The body is the physical structure of an organism, including all its organs, tissues, and cells. In humans, the body is composed of various systems that work together to maintain homeostasis and ensure proper function, including the nervous system, cardiovascular system, digestive system, respiratory system, and reproductive system, among others.
The body is a complex biological machine that carries out a wide range of functions, including movement, sensory perception, and metabolic processes. It is capable of adapting to changes in the environment and responding to internal and external stimuli to maintain optimal health and function.
Various factors can affect the health of the body, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep are important for promoting optimal health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Regular medical check-ups and screenings can also help detect and prevent health problems before they become serious. Treatment for various health conditions may include medication, lifestyle changes, surgery, or a combination of these approaches, depending on the specific condition and individual circumstances.
Overall, the body is an intricate and complex organism that requires proper care and attention to maintain optimal health and function throughout life.
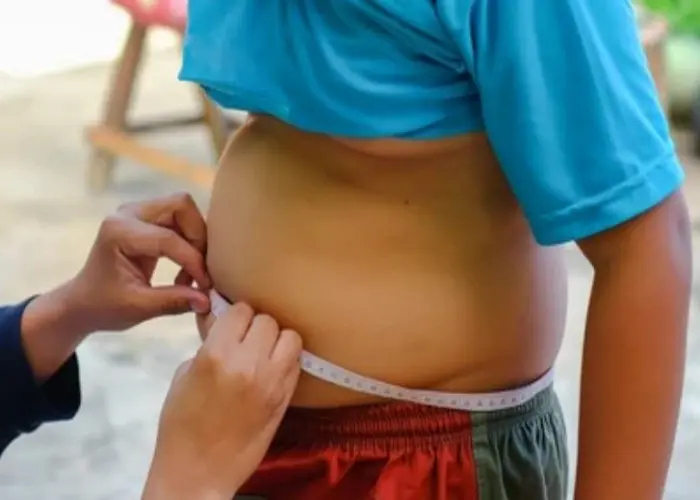
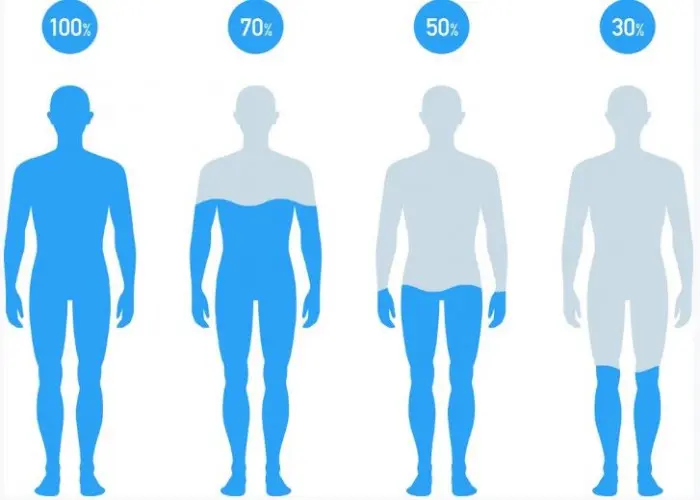
BMI stands for Body Mass Index, which is a measure of body fat based on an individual's height and weight. It is commonly used as a screening tool to determine whether a person has a healthy body weight or is at risk of health problems related to overweight or obesity.
To calculate BMI, a person's weight in kilograms is divided by their height in meters squared (BMI = weight in kg / (height in meters)²). Based on the BMI calculation, a person can be classified as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
However, it is important to note that BMI is not a perfect measure of body fat, and it does not take into account other factors that can affect health, such as muscle mass and body composition. For example, athletes or bodybuilders may have a high BMI due to their muscle mass, but they may not be overweight or at risk for health problems.
Despite its limitations, BMI is still a useful tool for assessing overall population health and identifying individuals who may be at risk of health problems related to weight. It is often used in combination with other measures, such as waist circumference and blood pressure, to provide a more comprehensive assessment of an individual's health status.
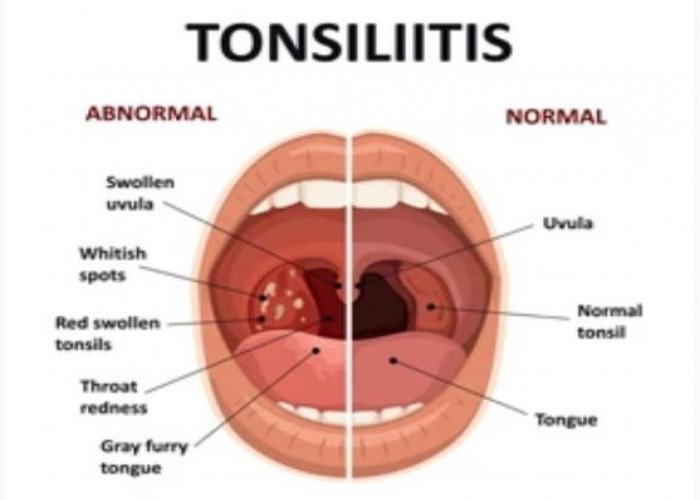
Tonsils

Liver
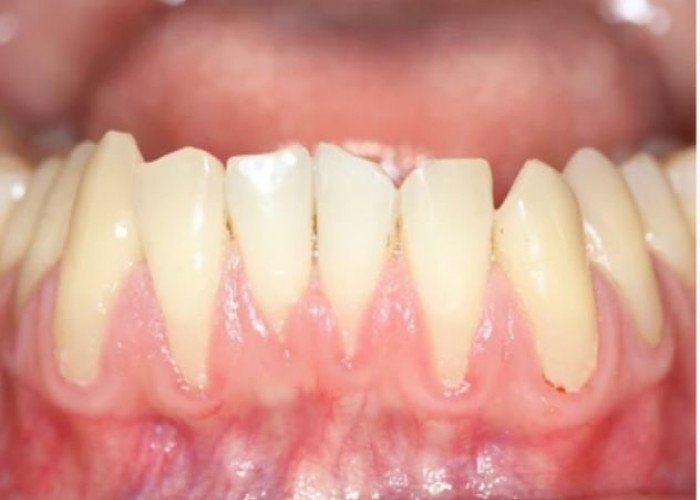
Gum

Tooth
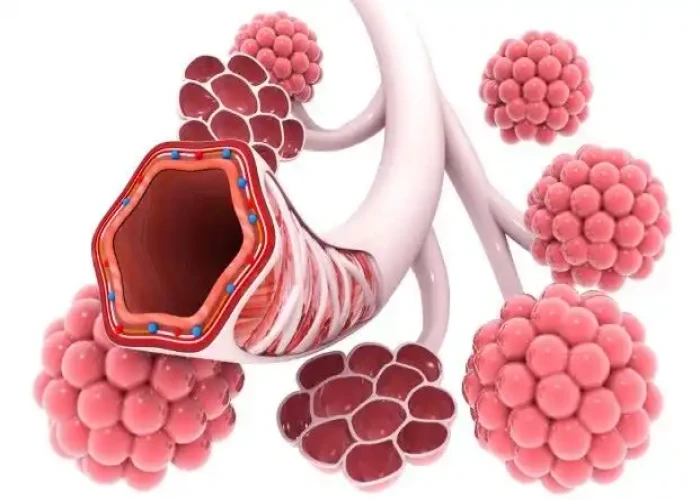
Bronchioles and smaller air passages

Pelvic
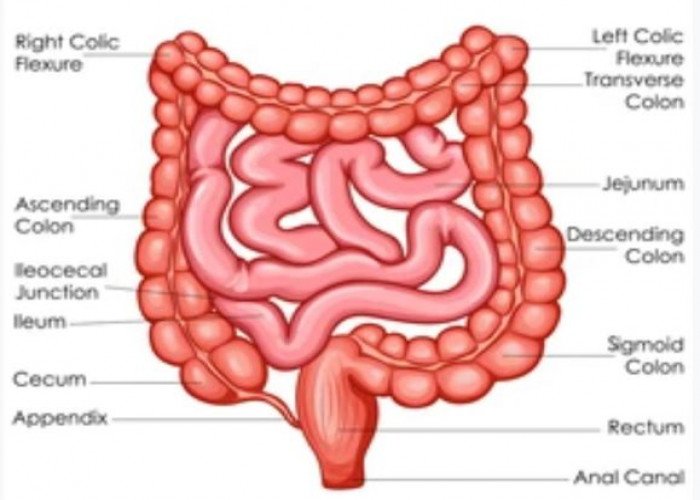
Intestine

Iris Eye
Whole body, bmis, শরীর
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.