 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Dengue fever
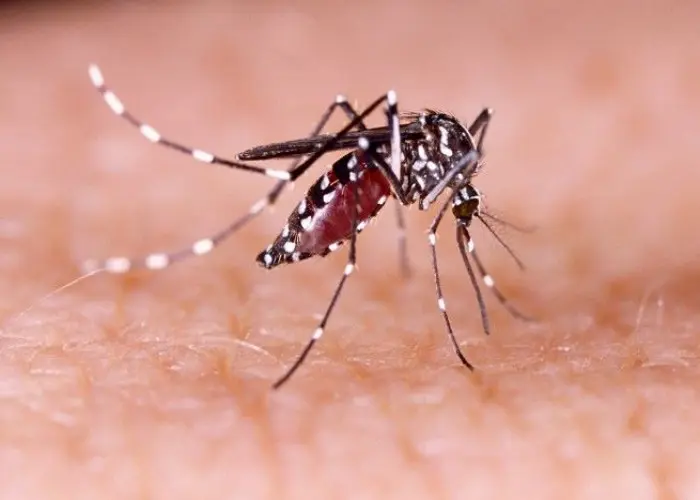
Dengue fever is a viral illness that is transmitted by the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito. The disease is found in tropical and subtropical regions of the world, including parts of Southeast Asia, the Americas, Africa, and the Western Pacific.
The symptoms of dengue fever typically develop 4-7 days after infection and can include a high fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, nausea and vomiting, and a skin rash. In severe cases, dengue fever can progress to a more severe form of the disease called dengue hemorrhagic fever, which can lead to bleeding, shock, and even death.
There is no specific treatment for dengue fever, but supportive care is provided to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment may include rest, fluid replacement therapy to prevent dehydration, and pain management with acetaminophen (paracetamol).
Prevention of dengue fever involves controlling mosquito populations and avoiding mosquito bites. This can include using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and ensuring that standing water is removed from the surrounding environment.
In areas where dengue fever is endemic, vaccination may also be available as a preventative measure. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you may have dengue fever, especially if you have recently traveled to an area where the disease is common.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Bleeding from gums
- Burning stomach pain
- Bleeding under the skin, which might look like bruising
- Skin rash
- Swollen glands
- Nausea or vomiting
- Muscle pain
- Bone pain
- Joint pain
- Anxiety, agitation or restlessness
Disease Causes
Dengue fever
Dengue fever is caused by any one of four types of dengue viruses. You can't get dengue fever from being around an infected person. Instead, dengue fever is spread through mosquito bites.
The two types of mosquitoes that most often spread the dengue viruses are common both in and around human lodgings. When a mosquito bites a person infected with a dengue virus, the virus enters the mosquito. Then, when the infected mosquito bites another person, the virus enters that person's bloodstream and causes an infection.
After you've recovered from dengue fever, you have long-term immunity to the type of virus that infected you — but not to the other three dengue fever virus types. This means you can be infected again in the future by one of the other three virus types. Your risk of developing severe dengue fever increases if you get dengue fever a second, third or fourth time.
Disease Prevents
Dengue fever
Vaccine
In areas of the world where dengue fever is common, one dengue fever vaccine (Dengvaxia) is approved for people ages 9 to 45 who have already had dengue fever at least once. The vaccine is given in three doses over the course of 12 months.
The vaccine is approved only for people who have a documented history of dengue fever or who have had a blood test that shows previous infection with one of the dengue viruses — called seropositivity. In people who have not had dengue fever in the past (seronegative), receiving the vaccine appears to increase the risk of severe dengue fever and hospitalization due to dengue fever in the future.
Dengvaxia is not available for travelers or for people who live in the continental United States. But in 2019, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the vaccine for people ages 9 to 16 who have had dengue fever in the past and who live in the U.S. territories of American Samoa, Guam, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands — where dengue fever is common.
Prevent mosquito bites
The World Health Organization stresses that the vaccine is not an effective tool on its own to reduce dengue fever in areas where the illness is common. Preventing mosquito bites and controlling the mosquito population are still the main methods for preventing the spread of dengue fever.
If you live in or travel to an area where dengue fever is common, these tips may help reduce your risk of mosquito bites:
- Stay in air-conditioned or well-screened housing. The mosquitoes that carry the dengue viruses are most active from dawn to dusk, but they can also bite at night.
- Wear protective clothing. When you go into mosquito-infested areas, wear a long-sleeved shirt, long pants, socks and shoes.
- Use mosquito repellent. Permethrin can be applied to your clothing, shoes, camping gear and bed netting. You can also buy clothing made with permethrin already in it. For your skin, use a repellent containing at least a 10% concentration of DEET.
- Reduce mosquito habitat. The mosquitoes that carry the dengue virus typically live in and around houses, breeding in standing water that can collect in such things as used automobile tires. You can help lower mosquito populations by eliminating habitats where they lay their eggs. At least once a week, empty and clean containers that hold standing water, such as planting containers, animal dishes and flower vases. Keep standing water containers covered between cleanings.
Disease Treatments
No specific treatment for dengue fever exists.
While recovering from dengue fever, drink plenty of fluids. Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following signs and symptoms of dehydration:
- Decreased urination
- Few or no tears
- Dry mouth or lips
- Lethargy or confusion
- Cold or clammy extremities
The over-the-counter (OTC) drug acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) can help reduce muscle pain and fever. But if you have dengue fever, you should avoid other OTC pain relievers, including aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve). These pain relievers can increase the risk of dengue fever bleeding complications.
If you have severe dengue fever, you may need:
- Supportive care in a hospital
- Intravenous (IV) fluid and electrolyte replacement
- Blood pressure monitoring
- Transfusion to replace blood loss
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Cephradine
Adults 1 250mg 6 hours after 5/7 days or 500mg 1 in the morning 1 evening 5/7 days after 8 hours.
-
Ciprofloxacin
1 to 2 times a day according to age. 1+0+1 makes 14 days.
-
Chloroquine Phosphate
First single dose is 4 pills 6 hours after 2 pills. From next day 1 pill daily 2 times a day for 3 days. In children, the dose should be determined according to the same rules according to age.
-
Promethazine Hydrochloride
For nasal allergies (runny nose) and abnormal accumulation of blood in any part of the body.
1 pill or 1/2, 1, 2 spoons 3 times a day according to age.
-
Pheniramine Maleate
For nasal allergies (runny nose) and abnormal accumulation of blood in any part of the body.
1 pill or 1/2, 1, 2 spoons 3 times a day according to age.
-
Loratadine
For nasal allergies (runny nose) and abnormal accumulation of blood in any part of the body.
Adults 1 pill daily at night. 1+0+1 in hard condition. 1/2 pill 1 time a day for 2-12 years or 1/2+0+1/2 in severe cases.
Cannot be given to children under 2 years of age.
-
Desloratadine
For nasal allergies (runny nose) and abnormal accumulation of blood in any part of the body.
1 daily.
-
Ketotifen Fumarate (Oral)
Antihistamines with ketotifen are given to patients who have a cold and have slight chest tightness or shortness of breath.
Adults take 1 tablet 1/2 time a day (1+0+1 in solid state).
Over 2 years, 1 spoon 1/2 time a day.
-
Xylometazoline Hydrochloride
Medicines containing xylometazoline hydrochloride or oxymetazoline for nasal congestion.
Adults 0.1% drops 2/3 drops in both nostrils 2/3 times a day.
Boys-Girls: 0.0% drop 1/2 drop 1/2 time a day.
They are not to be used for a long time.
-
Ferrous Sulfate
If the patient feels weak after the fever is cured, any medicine like blood thinners and vitamin complex can be given to improve the general health.
1/2 teaspoon daily 3 times a day after meals.
-
Vitamin B complex
If the patient feels weak after the fever is cured, any medicine like blood thinners and vitamin complex can be given to improve the general health.
Consume 1/2 teaspoon 3 times a day after meals. Liquid vitamins are not needed if the food tastes good.
-
Multivitamin & Multimineral
If the patient feels weak after the fever is cured, any medicine like blood thinners and vitamin complex can be given to improve the general health.
1 daily after breakfast.
-
Paracetamol
Medicines containing paracetamol for children for headache, body ache and fever.
1/2, 1, 2 3 times a day.
-
Phenoxymethyl Penicillin [Penicillin V]
Medicines containing phenoxymethyl penicillin if the cold is accompanied by inflammation of the chest or throat or if the patient has a fever.
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
250 mg 3 times a day for boys and girls. Adults 500mg 1 time 2/3 times a day.
Syrup 1/2 spoon 3 times a day.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Pulsatilla
6, 30 strength with little water.
-
Rhus toxicodendron
6, 30 strength 1 dose 4 times a day.
-
Aconite
Q, 1X strength 2/3 drops of medicine mixed with little water four times a day.
-
Bryonia alba
6, 30 energy in one dose every 3 hours.
-
Belladonna
3, 6 Shakti should be consumed four times a day.
-
Gelsemium
1X, 3X Strength 1 dose every 3 hours.
-
Arsenicum
6, 30 Shakti in one dose 4 times a day.
Disease yoga
Dengue fever and Learn More about Diseases
Sty

Fetal alcohol syndrome

Snoring

Neck pain
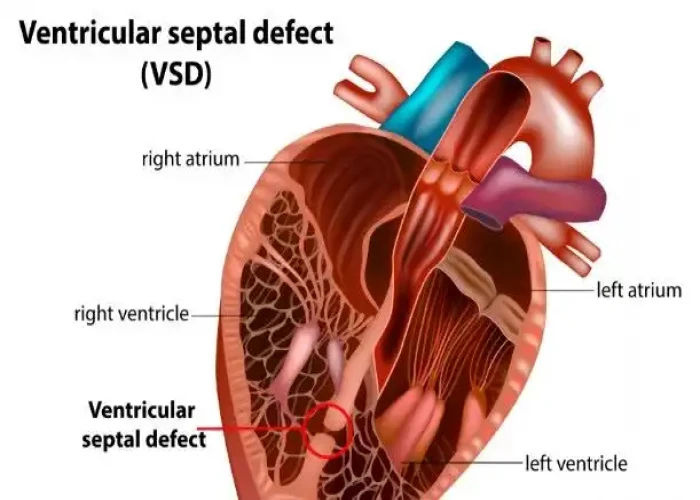
Ventricular septal defect (VSD)

Syphilis

Tuberculosis of Skin (Lupus Valgaris)

Genital herpes
Dengue fever, Dengue symptoms, Dengue mosquito, Dengue treatment ডেঙ্গু জ্বর
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
