Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
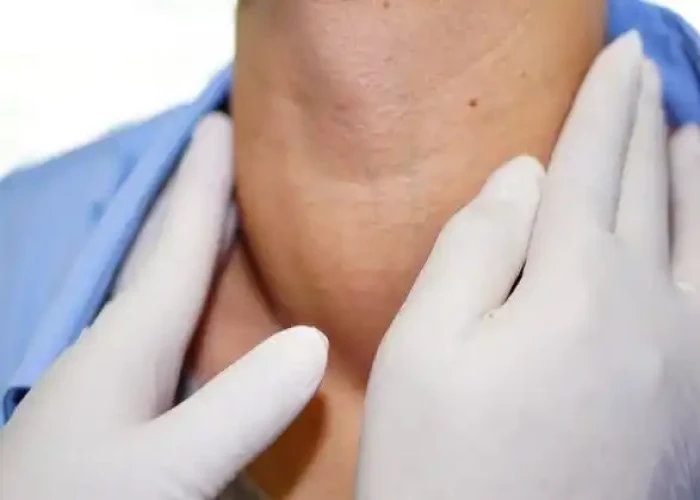
Thyroid gland - Diseases
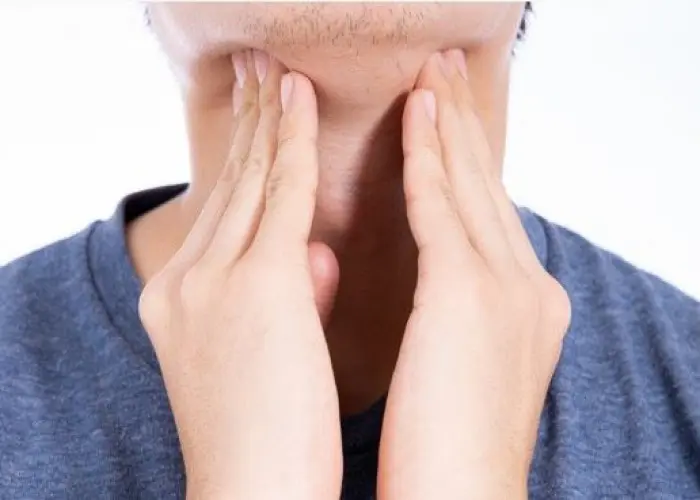
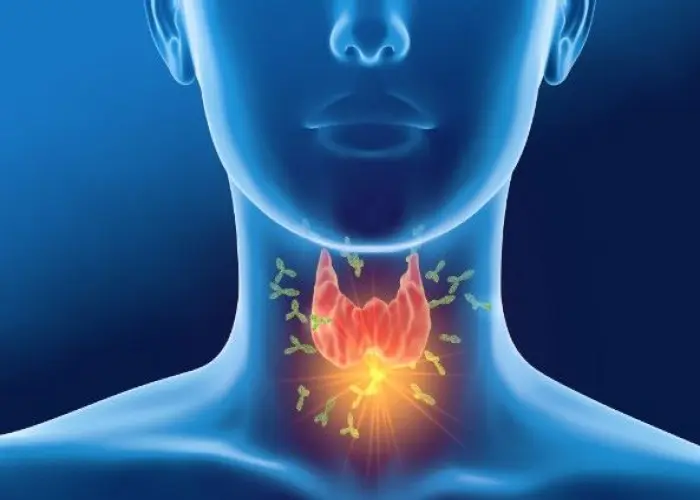
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam's apple. It produces hormones that regulate the body's metabolism, heart rate, and energy levels.
The thyroid gland produces two main hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones play a crucial role in regulating the body's metabolic rate, which is the rate at which the body uses energy. They also affect heart rate, body temperature, and other important bodily functions.
The thyroid gland is regulated by the pituitary gland, which is located in the brain. The pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce more hormones when needed.
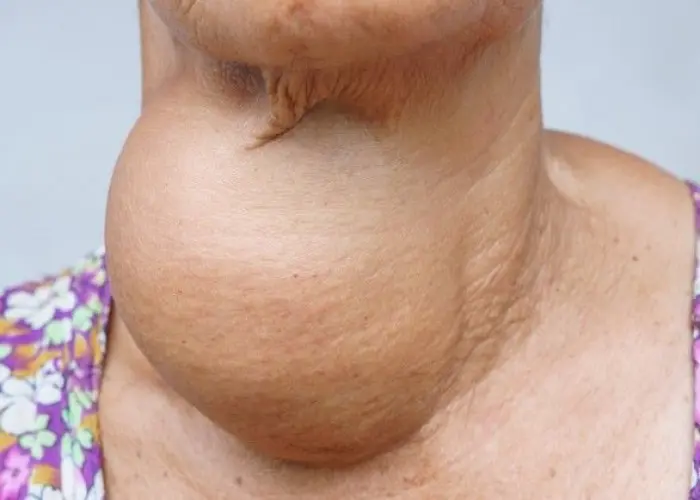
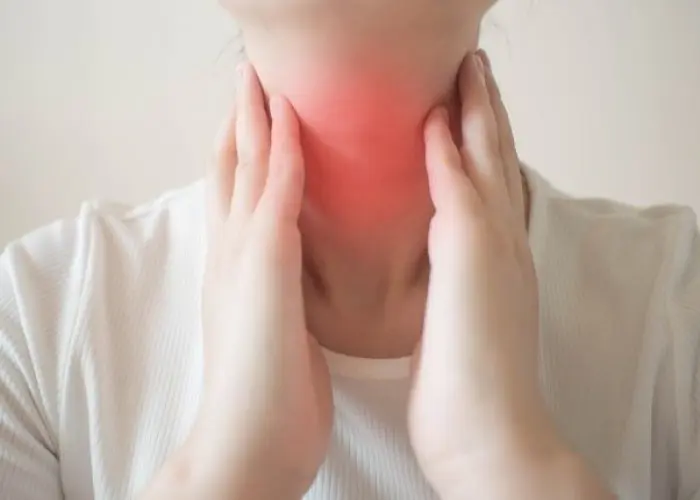
Several conditions can affect the thyroid gland, including hyperthyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid produces too much hormone, and hypothyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid produces too little hormone. Other conditions that can affect the thyroid gland include thyroid nodules, which are abnormal growths within the gland, and thyroid cancer.
Treatment for thyroid disorders may include medication, radiation therapy, or surgery, depending on the specific condition. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are important for managing thyroid disorders and ensuring that the thyroid gland is functioning properly.

Pharynx
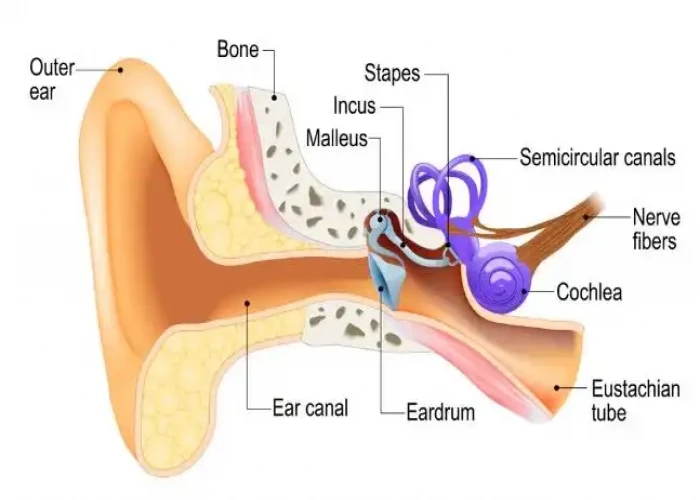
Ossicles Middle ear

Mental

Hip

Enteric Nerves
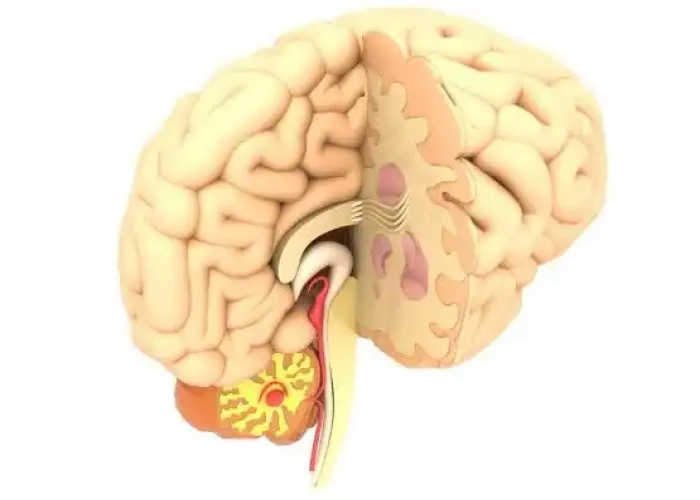
Midbrain Brainstem

Bile ducts
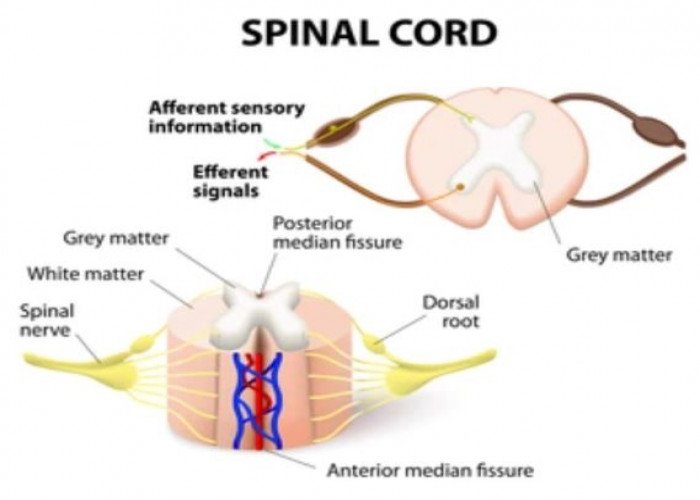
Spinal cord
Thyroid gland, থাইরয়েড গ্রন্থি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.