Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
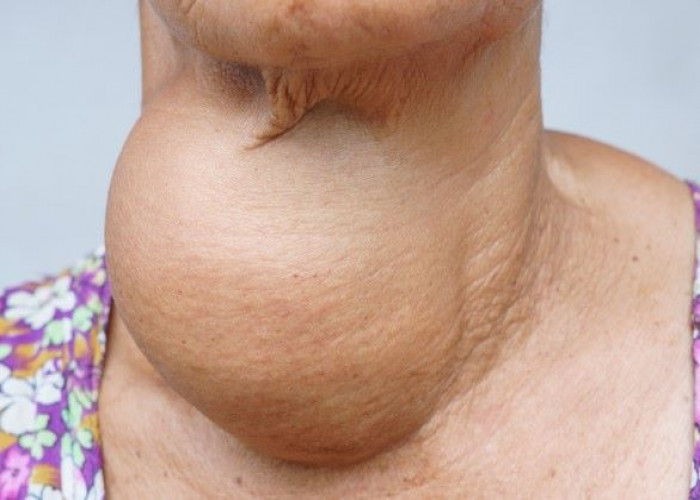
Goiter
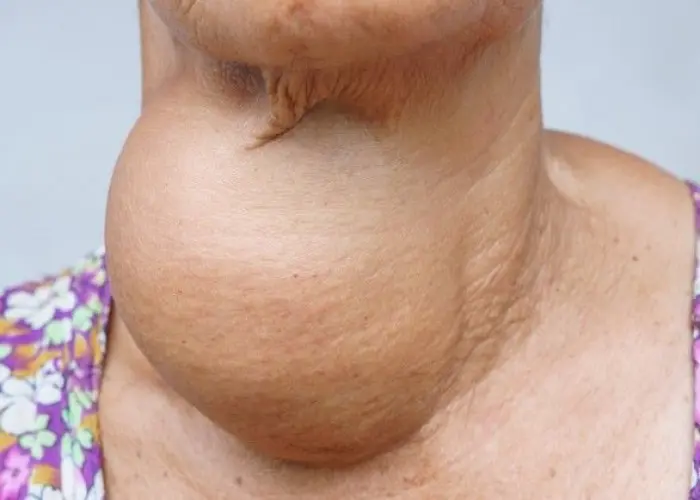
Goiter is a condition characterized by an enlarged thyroid gland, which is located in the neck and plays an important role in regulating metabolism. Goiter can be caused by a variety of factors, including iodine deficiency, autoimmune disorders, certain medications, and genetic factors.
Symptoms of goiter may include swelling in the neck, difficulty breathing or swallowing, coughing, and hoarseness. In some cases, there may be no symptoms present, and the condition may be detected during a routine physical exam.
Diagnosis of goiter usually involves a physical exam, blood tests to assess thyroid function, and imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans, to visualize the thyroid gland and detect any abnormalities.
Treatment for goiter depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In some cases, the condition may not require treatment, but if it is causing symptoms or affecting thyroid function, medication or surgery may be necessary to manage the condition.
Prevention of goiter involves maintaining good thyroid health and ensuring adequate intake of iodine, which is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones. Iodine is found in a variety of foods, including seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt.
If you are experiencing symptoms of goiter or have a family history of thyroid problems, it is important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early detection and treatment can help to manage the condition and prevent complications associated with goiter.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Cough
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Increased appetite
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Absent or irregular menstrual periods
- Frequent bowel movements
- Irritability
- Tremors of lips or jaw
- Excessive sweat
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Weight loss
- Muscle weakness
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Lack of sleep (Sleep apnea)
- Sensitivity to touch or cold
- Hoarseness
Disease Causes
Goiter
How the thyroid gland works
Two hormones produced by the thyroid are thyroxine (T-4) and triiodothyronine (T-3). When the thyroid releases T-4 and T-3 into the bloodstream, they play a role in many functions in the body, including the regulation of:
- The conversion of food into energy (metabolism)
- Body temperature
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Other hormone interactions
- Growth during childhood
The thyroid gland also produces calcitonin, a hormone that helps regulate the amount of calcium in the blood.
How the thyroid is regulated
The pituitary gland and hypothalamus control the rate at which T-4 and T-3 are produced and released.
The hypothalamus is a specialized region at the base of the brain. It acts as a thermostat for maintaining balance in multiple body systems. The hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland to make a hormone known as thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
The pituitary gland — located below the hypothalamus — releases a certain amount of TSH, depending on how much T-4 and T-3 are in the blood. The thyroid gland, in turn, regulates its production of hormones based on the amount of TSH it receives from the pituitary gland.
Causes of goiter
A number of factors that influence thyroid function or growth can result in a goiter.
- Iodine deficiency. Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. If a person does not get enough dietary iodine, hormone production drops and the pituitary gland signals the thyroid to make more. This increased signal results in thyroid growth. In the United States, this cause is uncommon because of iodine added to table salt.
- Hashimoto's disease. Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disorder, an illness caused by the immune system attacking healthy tissues. The damaged and inflamed tissues of the thyroid don't produce enough hormones (hypothyroidism). When the pituitary gland detects the decline and prompts the thyroid to create more hormones, the thyroid can become enlarged.
- Graves' disease. Another autoimmune disorder called Graves' disease occurs when the immune system produces a protein that mimics TSH. This rogue protein prompts the thyroid to overproduce hormones (hyperthyroidism) and can result in thyroid growth.
- Thyroid nodules. A nodule is the irregular growth of thyroid cells that form a lump. A person may have one nodule or several nodules (multinodular goiter). The cause of nodules is not clear, but there may be multiple factors — genetics, diet, lifestyle and environment. Most thyroid nodules are noncancerous (benign).
- Thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer is less common than other cancers and generally treatable. About 5% of people with thyroid nodules are found to have cancer.
- Pregnancy. A hormone produced during pregnancy, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), may cause the thyroid gland to be overactive and enlarge slightly.
- Inflammation. Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid caused by an autoimmune disorder, bacterial or viral infection, or medication. The inflammation may cause hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Goiter treatment depends on the size of the goiter, your signs and symptoms, and the underlying cause. If your goiter is small and your thyroid function is healthy, your health care provider may suggest a wait-and-see approach with regular checkups.
Medications
Medications for goiters may include one of the following:
- For increasing hormone production. An underactive thyroid is treated with a thyroid hormone replacement. The drug levothyroxine (Levoxyl, Thyquidity, others) replaces T-4 and results in the pituitary gland releasing less TSH. The drug liothyronine (Cytomel) may be prescribed as a T-3 replacement. These treatments may decrease the size of the goiter.
- For reducing hormone production. An overactive thyroid may be treated with an anti-thyroid drug that disrupts hormone production. The most commonly used drug, methimazole (Tapazole), may also reduce the size of the goiter.
- For blocking hormone activities. Your health care provider may prescribe a drug called a beta blocker for managing symptoms of hyperthyroidism. These drugs — including atenolol (Tenormin), metoprolol (Lopressor) and others — can disrupt the excess thyroid hormones and lower symptoms.
- For managing pain. If inflammation of the thyroid results in pain, it's usually treated with aspirin, naproxen sodium (Aleve), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or related pain relievers. Severe pain may be treated with a steroid.
Surgery
You may need surgery to remove all or part of your thyroid gland (total or partial thyroidectomy) may be used to treat goiter with the following complications:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Thyroid nodules that cause hyperthyroidism
- Thyroid cancer
You may need to take thyroid hormone replacement, depending on the amount of thyroid removed.
Radioactive iodine treatment
Radioactive iodine is a treatment for an overactive thyroid gland. The dose of radioactive iodine is taken orally. The thyroid takes up the radioactive iodine, which destroys cells in the thyroid. The treatment lowers or eliminates hormone production and may decrease the size of the goiter.
As with surgery, you may need to take thyroid hormone replacement to maintain the appropriate levels of hormones.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Goiter and Learn More about Diseases
Dengue fever
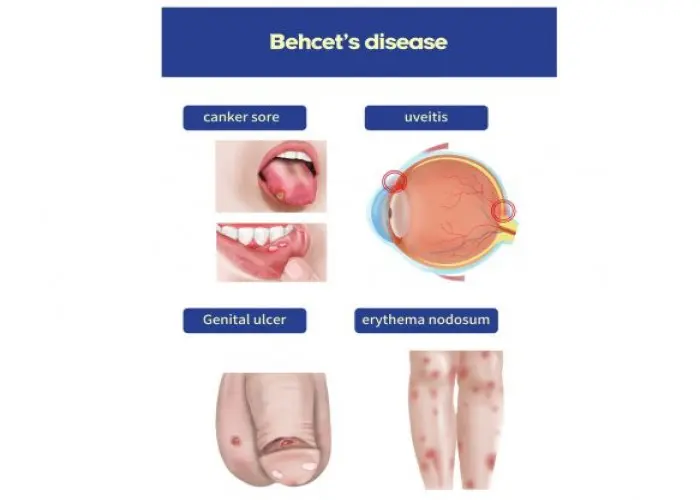
Behcet's disease
Cardiac Failure
Atrial flutter

Insomnia

Trigeminal neuralgia
Bone cancer

Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS)
goiter, গলগণ্ড
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.