Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
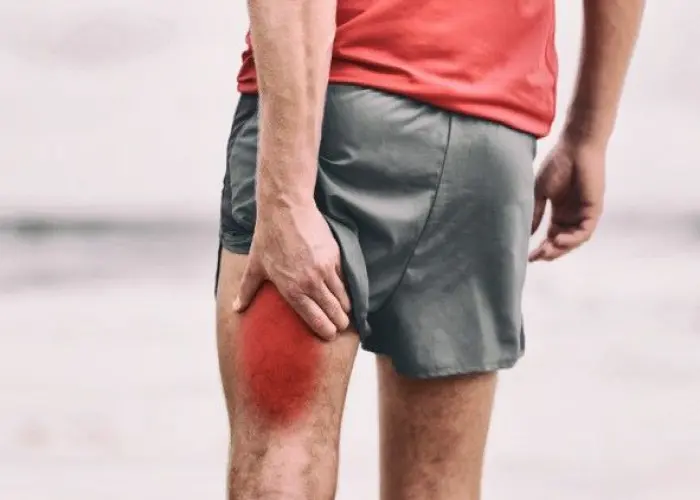
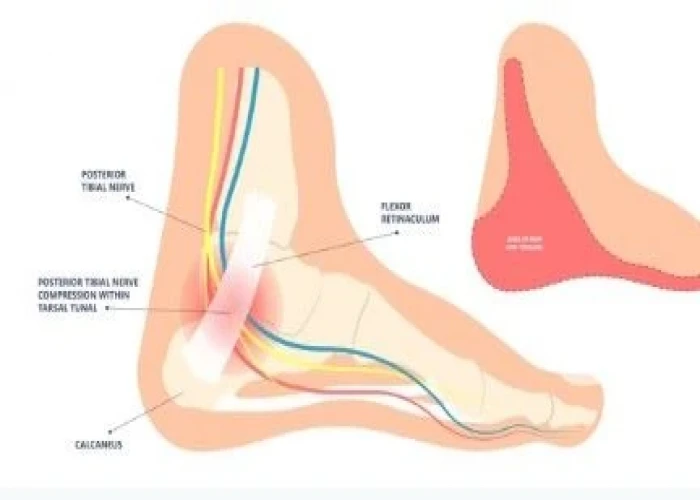
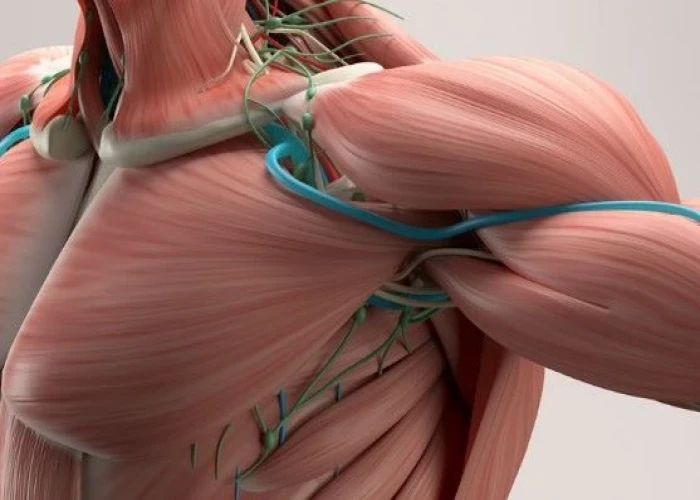
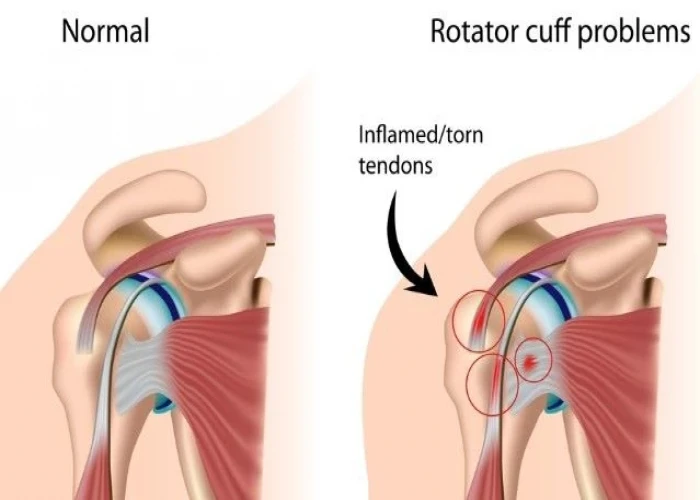
Muscles - Diseases
Muscles are the contractile tissues in the body that enable movement, stabilize joints, and generate heat. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and are responsible for voluntary movement, such as walking, running, and lifting weights. They are striated, meaning they have a striped appearance under a microscope.
Smooth muscles are found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the intestines, blood vessels, and urinary bladder. They are responsible for involuntary movements, such as peristalsis, which moves food through the digestive tract. They are not striated.
Cardiac muscles are found in the heart and are responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. They are striated like skeletal muscles, but they are involuntary like smooth muscles.
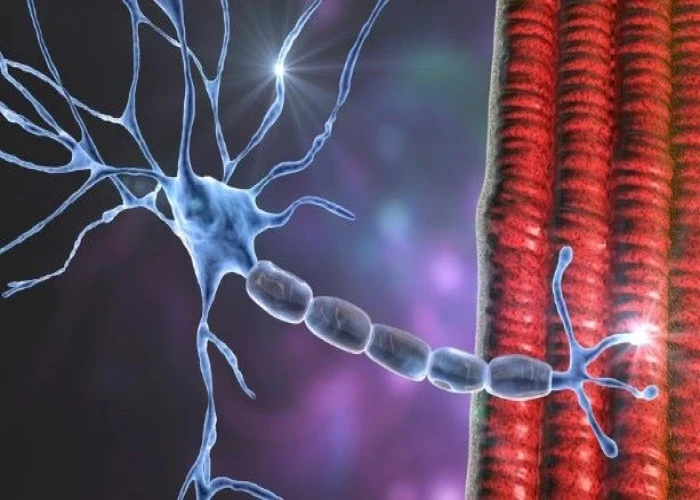
Muscles are made up of individual muscle fibers that are organized into bundles called fascicles. Each muscle fiber contains many myofibrils, which are made up of sarcomeres, the basic units of muscle contraction. When a muscle contracts, the sarcomeres within each muscle fiber shorten, causing the entire muscle to contract and generate force.
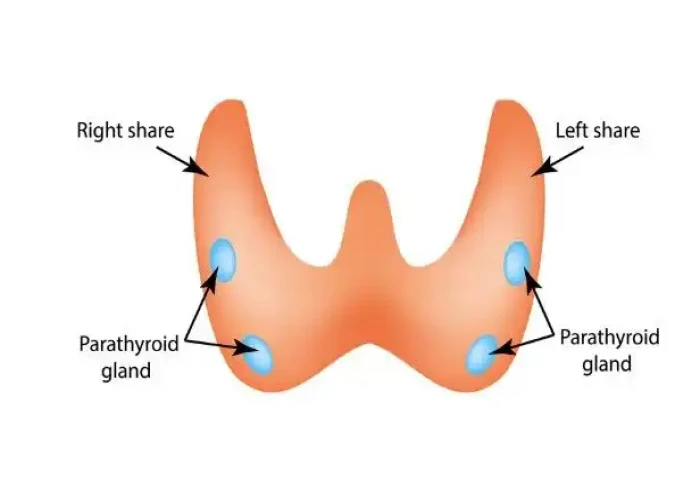
Parathyroid glands
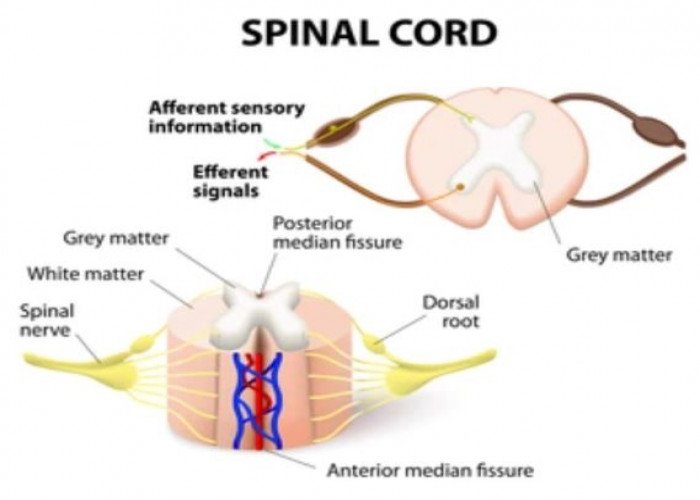
Spinal cord

Retina Eye
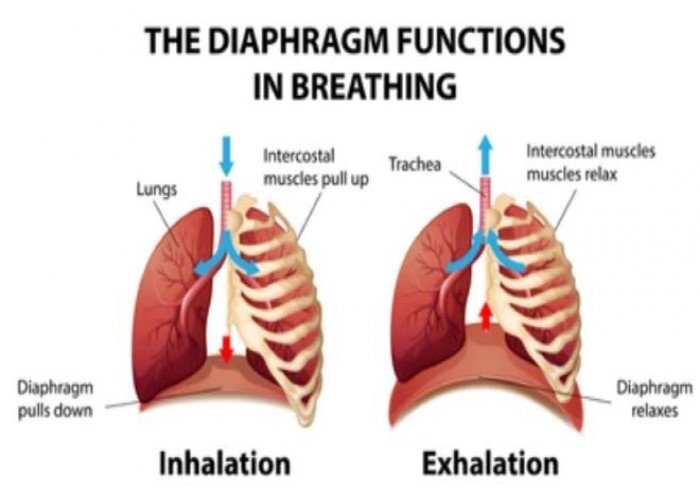
Diaphragm

Blood

Brain

Ileum intestine
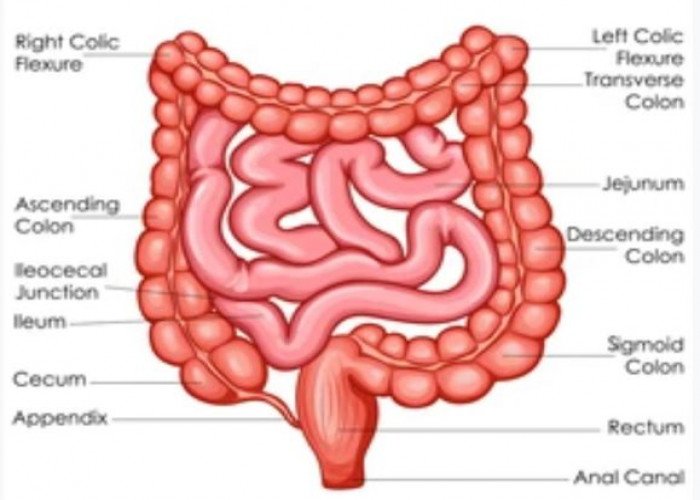
Intestine
Muscles, পেশী
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.