Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Dystonia
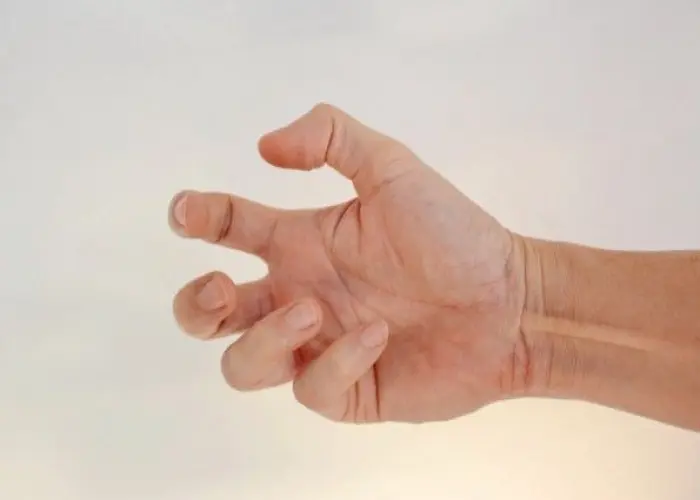
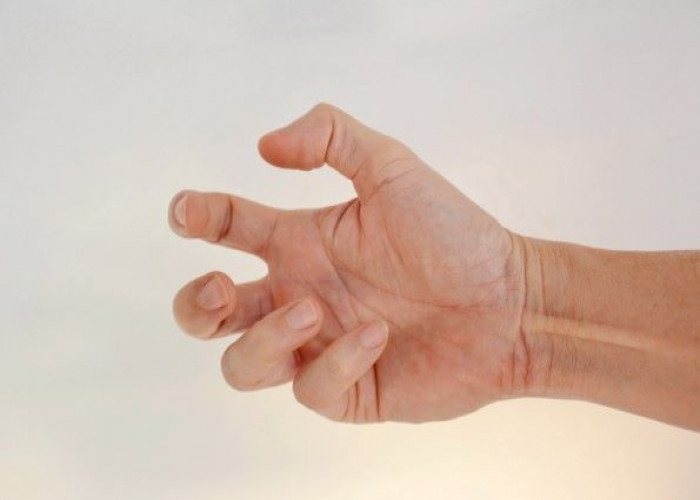
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that cause repetitive or twisting movements and abnormal postures. These movements can affect one or more parts of the body, such as the neck, face, arms, legs, or trunk, and can be painful and disabling. Dystonia can affect people of any age, although it most commonly begins in childhood or early adulthood.
The exact cause of dystonia is unknown, but it is believed to be related to a problem with the basal ganglia, a group of structures in the brain that help to control movement. Dystonia can also be inherited in some cases, and environmental factors may also play a role.
There are different types of dystonia, depending on which parts of the body are affected. Some common types include:
- Cervical dystonia: affects the neck muscles, causing the head to twist or turn involuntarily
- Blepharospasm: affects the muscles around the eyes, causing involuntary blinking and eyelid closure
- Writer's cramp: affects the hand and forearm muscles, causing difficulty with writing or other fine motor tasks
- Generalized dystonia: affects multiple parts of the body, sometimes including the torso, legs, and arms
Treatment options for dystonia depend on the type and severity of the condition. Some common treatments include medications, botulinum toxin injections, deep brain stimulation, and physical therapy. It is important to work with a healthcare professional experienced in treating dystonia to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Anxiety
- Neck pain
- Frequent eye blinking
- Dry eyes
- Slurred speech
- Weak voice or voice loss
- Worsen with stress, fatigue or anxiety.
- Diarrhea, which may range from mild and watery to severe and bloody
Disease Causes
Dystonia
The exact cause of dystonia isn't known. But it might involve altered nerve-cell communication in several regions of the brain. Some forms of dystonia are inherited.
Dystonia also can be a symptom of another disease or condition, including:
- Parkinson's disease
- Huntington's disease
- Wilson's disease
- Traumatic brain injury
- Birth injury
- Stroke
- Brain tumor or certain disorders that develop in some people with cancer (paraneoplastic syndromes)
- Oxygen deprivation or carbon monoxide poisoning
- Infections, such as tuberculosis or encephalitis
- Reactions to certain medications or heavy metal poisoning
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
To manage your muscle contractions, your doctor might recommend a combination of medications, therapy or surgery.
Medications
Injections of botulinum toxin (Botox, Dysport, others) into specific muscles might reduce or eliminate your muscle contractions and improve your abnormal postures. Injections are usually repeated every three to four months.
Side effects are generally mild and temporary. They can include weakness, dry mouth or voice changes.
Other medications target chemicals in your brain (neurotransmitters) that affect muscle movement. The options include:
- Carbidopa-levodopa (Duopa, Rytary, others). This medication can increase levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
- Trihexyphenidyl and benztropine (Cogentin). These two medications act on neurotransmitters other than dopamine. Side effects can include memory loss, blurred vision, drowsiness, dry mouth and constipation.
- Tetrabenazine (Xenazine) and deutetrabenazine (Austedo). These two medications block dopamine. Side effects can include sedation, nervousness, depression or insomnia.
- Diazepam (Valium), clonazepam (Klonopin) and baclofen (Lioresal, Gablofen). These medications reduce neurotransmission and might help some forms of dystonia. They may cause side effects, such as drowsiness.
Therapy
Your doctor might suggest:
- Physical therapy or occupational therapy or both to help ease symptoms and improve function
- Speech therapy if dystonia affects your voice
- Stretching or massage to ease muscle pain
Surgery
If your symptoms are severe, your doctor might recommend:
- Deep brain stimulation. Electrodes are surgically implanted into a specific part of your brain and connected to a generator implanted in your chest. The generator sends electrical pulses to your brain that might help control your muscle contractions. The settings on the generator can be adjusted to treat your specific condition.
- Selective denervation surgery. This procedure, which involves cutting the nerves that control muscle spasms, might be an option to treat some types of dystonia that haven't been successfully treated using other therapies.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Dystonia and Learn More about Diseases

Suicide and suicidal thoughts
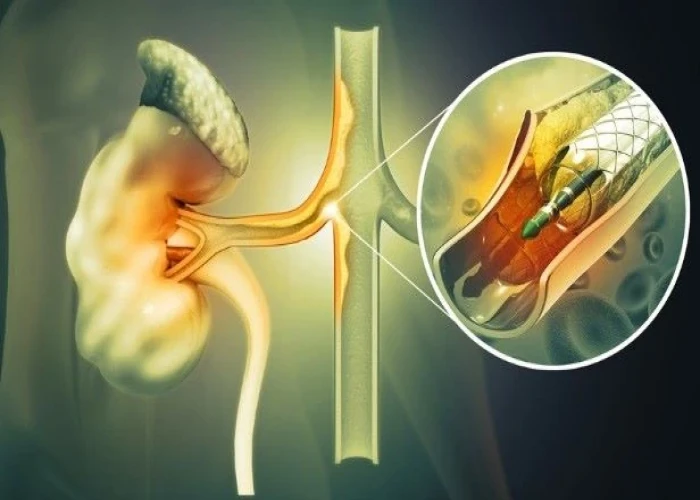
Renal artery stenosis
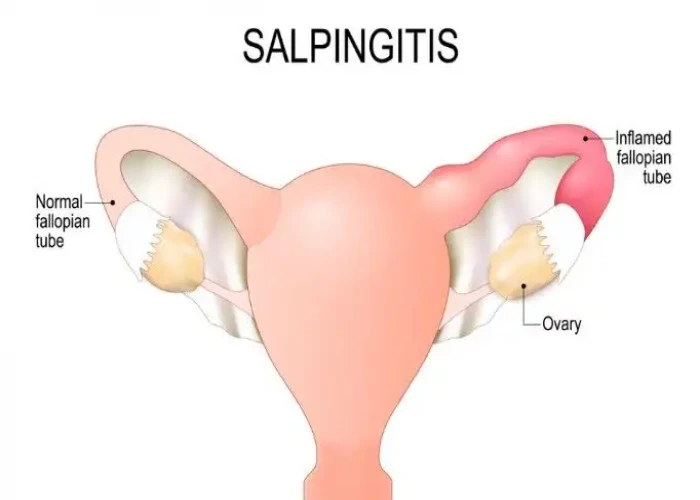
Salpingitis

Bell's palsy
Amnesia

Central nervous system vascular malformations

Zollinger-Ellison syndrome

Thunderclap headaches
dystonia, ডাইস্টোনিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.