Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Claudication
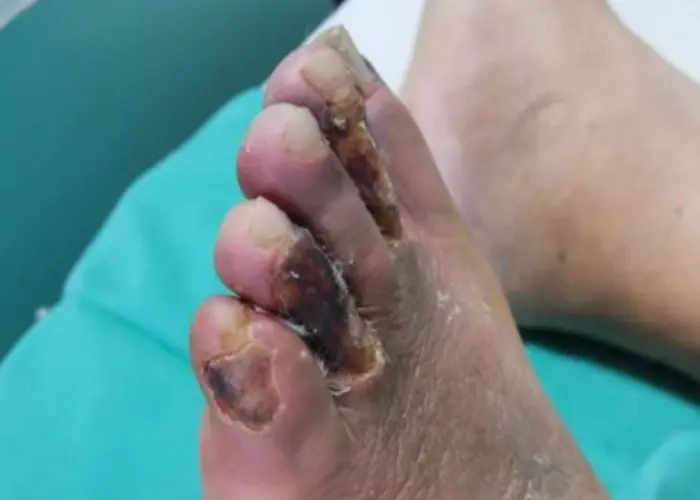
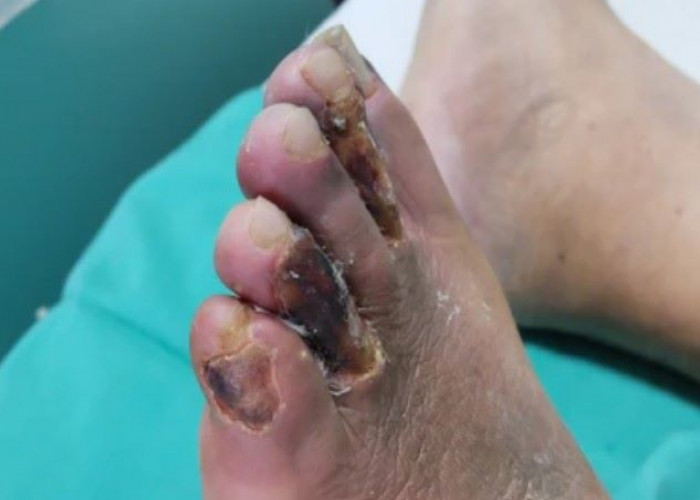
Claudication is a medical term used to describe a condition in which a person experiences pain or discomfort in their legs while walking or exercising due to reduced blood flow to the muscles. The condition is usually caused by peripheral artery disease (PAD), which occurs when there is a buildup of fatty deposits or plaque in the arteries that supply blood to the legs.
The pain or discomfort associated with claudication is typically described as cramping, aching, or burning sensation in the legs, and it often resolves when the person rests. As the disease progresses, the pain may occur at rest, and the skin on the legs may become discolored, shiny, or cool to the touch.
Diagnosis of claudication typically involves a physical examination and various imaging tests, such as a Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography, or magnetic resonance angiography, to assess blood flow and locate the blockages in the arteries.
Treatment for claudication often involves lifestyle modifications, such as exercise programs and quitting smoking, as well as medications to manage risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. In more severe cases, surgical procedures, such as angioplasty or bypass surgery, may be necessary to restore blood flow to the affected arteries.
While claudication can be a chronic and progressive condition, early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications, such as tissue damage and infections.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Muscle pain
- Pain in the calves, thighs, buttocks, hips or feet
- Shoulder pain
- Pain that gets better soon after resting
- Cool skin
- Severe, constant pain that progresses to numbness
- Wounds that don't heal
Disease Causes
Claudication
Claudication is most often a symptom of peripheral artery disease. The peripheral arteries are the large vessels that deliver blood to the legs and arms.
Peripheral artery disease is damage to an artery that restricts the flow of blood in an arm or leg (a limb). When you're at rest, the limited blood flow is generally enough. When you're active, however, the muscles aren't getting enough oxygen and nutrients to work well and remain healthy.
Damage to peripheral arteries is usually caused by atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls. This buildup is called plaque. The plaque can cause the arteries to narrow, blocking blood flow. The plaque can also burst, leading to a blood clot.
Disease Prevents
Claudication
The best way to prevent claudication is to maintain a healthy lifestyle and control certain medical conditions. That means:
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet
- Exercise regularly
- If you have diabetes, keep your blood sugar in good control
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Manage cholesterol and blood pressure
- Quit smoking if you're a smoker
Disease Treatments
The goals of treating claudication and peripheral artery disease are to reduce pain and manage the risk factors that contribute to heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease.
Exercise is an important part of claudication treatment. Exercise reduces pain, increases exercise duration, improves vascular health in the affected limbs, and contributes to weight management and an overall improvement in quality of life.
Recommended walking programs include:
- Walking until you feel moderate pain or as far as you can
- Resting to relieve pain
- Walking again
- Repeating the walk-rest-walk cycle for 30 to 45 minutes
- Walking three or more days a week
Supervised exercise is recommended for beginning the treatment, but long-term exercise at home is important for ongoing management of claudication.
Medications
Your health care provider may prescribe one or more medications to control pain and manage risk factors for cardiovascular disease. For example, medications may be used to manage the following:
- Pain. The drug cilostazol, which improves blood flow, may reduce pain during exercise and help you to walk further.
- High cholesterol. Statins are a drugs that help lower cholesterol, a key factor in the formation of plaques in arteries. Taking statins may improve walking distance.
- High blood pressure. Several different classes of drugs may be prescribed to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart attack or stroke.
- Other cardiovascular risks. Anti-platelet drugs, which help prevent blood clots, may reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke or clots blocking blood flow to limbs. These drugs include aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix) and other classes of drugs.
Talk to your doctor about medications or supplements that you shouldn't take with your prescribed treatment.
Surgery or other procedures
When peripheral artery disease is severe and other treatments don't work, surgery may be required. Options include:
- Angioplasty. This procedure improves blood flow by widening a damaged artery. A health care provider guides a narrow tube through blood vessels to deliver an inflatable balloon that expands the artery. Once the artery is widened, the health care provider may place a small metal or plastic mesh tube (stent) in the artery to keep it open.
- Vascular surgery. During this type of surgery, a surgeon takes a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body to replace the vessel that's causing claudication. This allows blood to flow around the blocked or narrowed artery.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Claudication and Learn More about Diseases
Paget's disease of bone
Pectus excavatum
Tonsillitis
Scrotal masses
Placental abruption
Gastritis

Primary biliary cholangitis

Movement disorders
Claudication, Intermittent claudication, Claudication meaning, ক্লোডিকেশন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.