 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Sublingual glands - Diseases
The sublingual glands are a pair of small salivary glands located beneath the tongue. They are one of several pairs of salivary glands in the mouth and produce about 5% of the total saliva in the mouth.
The sublingual glands secrete a thin, watery fluid that contains enzymes, electrolytes, and mucus. The enzymes in the saliva help to break down carbohydrates and fats in the food, while the mucus helps to lubricate the mouth and throat.
The sublingual glands are innervated by the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) and the glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX), which provide both motor and sensory functions. Stimulation of these nerves can increase the production and flow of saliva from the sublingual glands.
Several conditions can affect the sublingual glands, including infections, inflammation, and tumors. If the sublingual glands become inflamed or infected, it can cause pain and swelling in the mouth and difficulty in eating and swallowing. Treatment for sublingual gland disorders may involve medication, antibiotics, or in some cases, surgical removal of the affected gland.
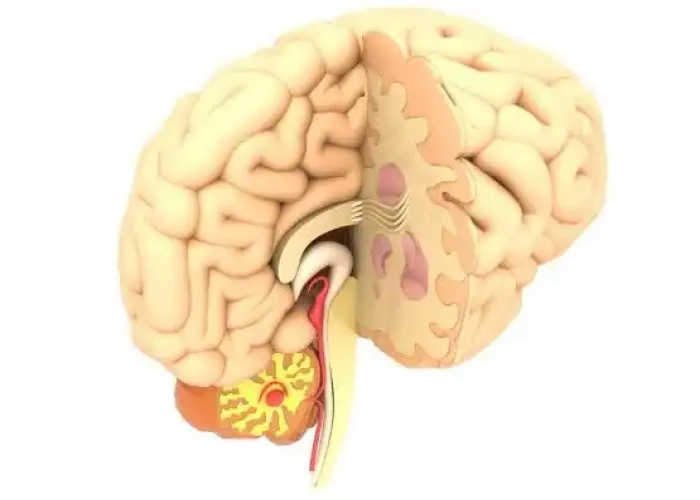
Midbrain Brainstem
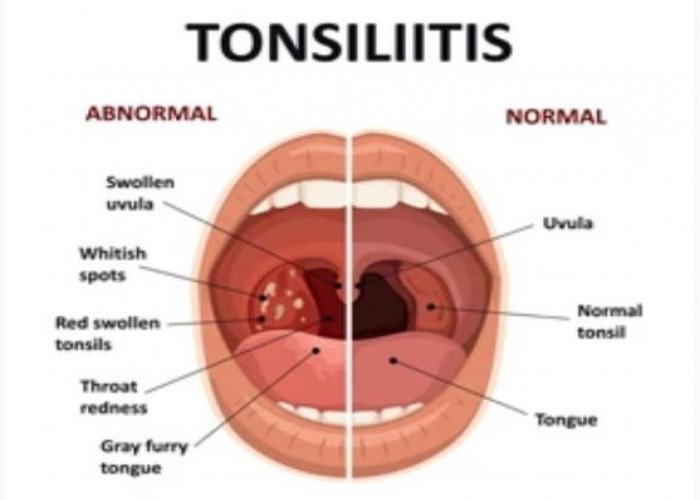
Tonsils
Lymph node
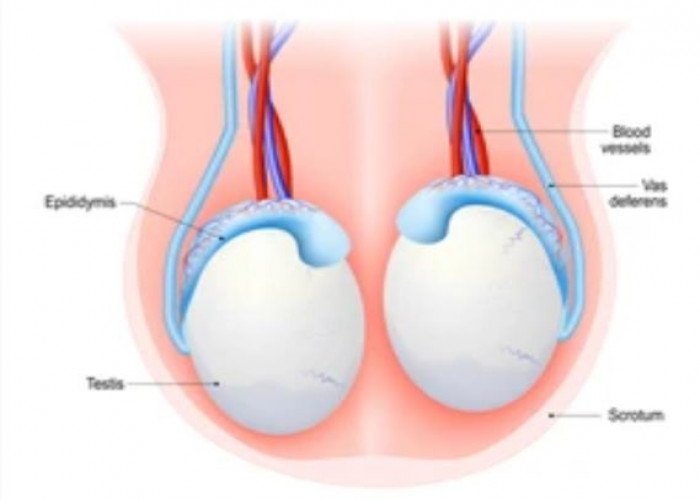
Testicle

Back
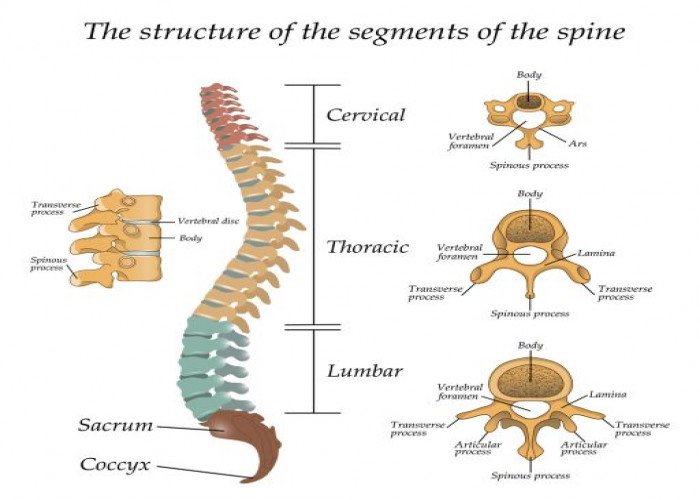
Spine
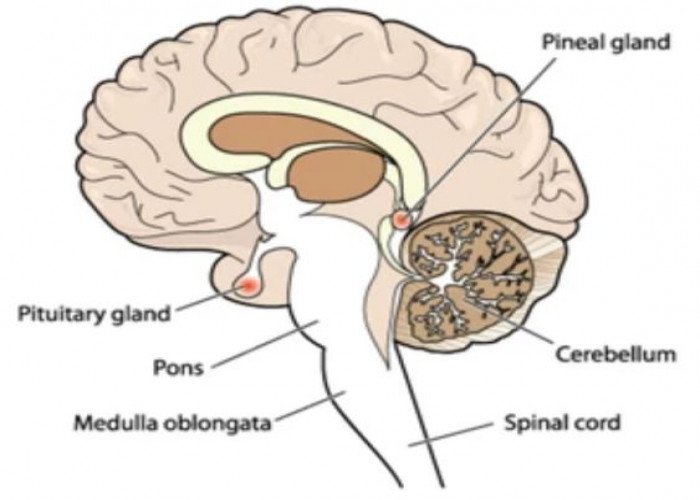
Pituitary gland
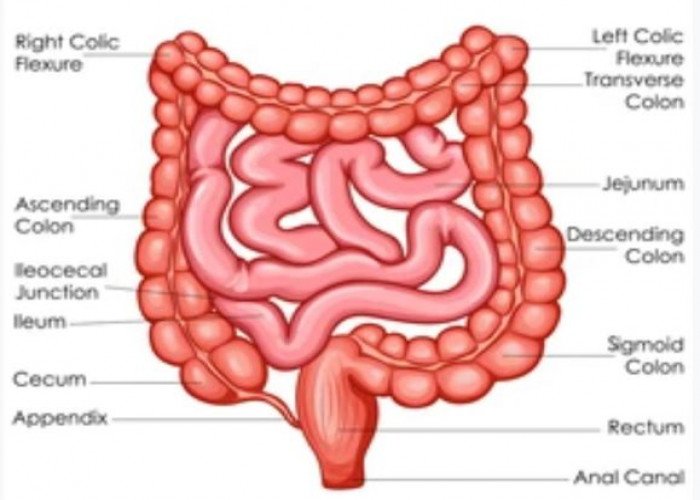
Intestine
Sublingual glands, Sublingual salivary gland, সাবলিঙ্গুয়াল গ্রন্থি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.