 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Olfactory epithelium - Diseases
The olfactory epithelium is a specialized tissue located in the upper part of the nasal cavity that is responsible for detecting different smells. It is made up of several different types of cells, including:
- Olfactory receptor cells: These are specialized cells that contain receptors for detecting different smells. When a smell molecule binds to a receptor on an olfactory receptor cell, it sends a signal to the brain to interpret the smell.
- Supporting cells: These cells provide structural support for the olfactory epithelium and help to maintain the proper environment for olfactory receptor cells to function.
- Basal cells: These cells are responsible for regenerating olfactory receptor cells when they are damaged or lost.
The olfactory epithelium is located high up in the nasal cavity and is bathed in a thin layer of mucus. When a person inhales, air carrying different odor molecules enters the nasal cavity and comes into contact with the olfactory epithelium. Olfactory receptor cells in the olfactory epithelium detect these odor molecules and send signals to the brain to interpret them as different smells.
The sense of smell is important for detecting and identifying different substances in the environment, including food, potential dangers, and other people. Disorders of the olfactory epithelium, such as anosmia (loss of sense of smell), can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, affecting their ability to taste food, detect smoke or gas leaks, and even identify other people.

N/A

Artery

Central nervous
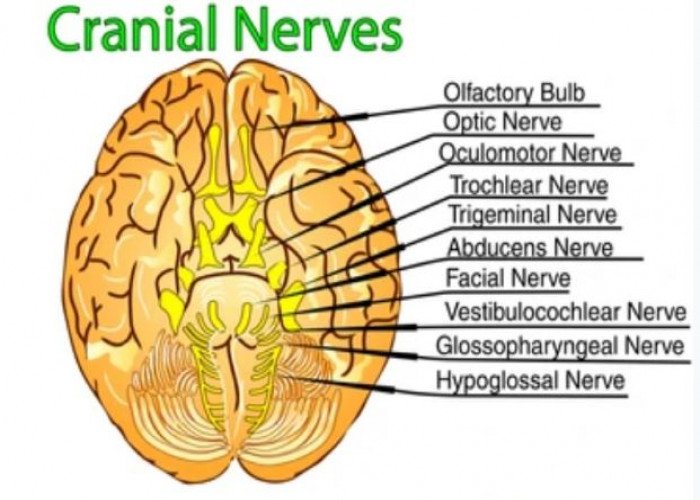
Cranial Nerves

Achilles
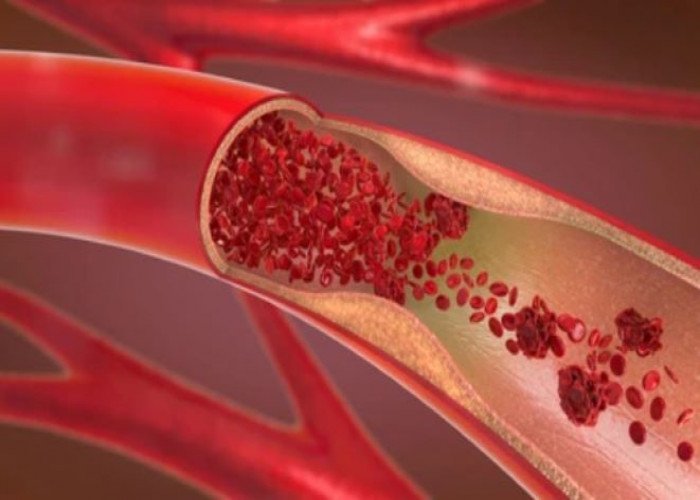
Blood vessel
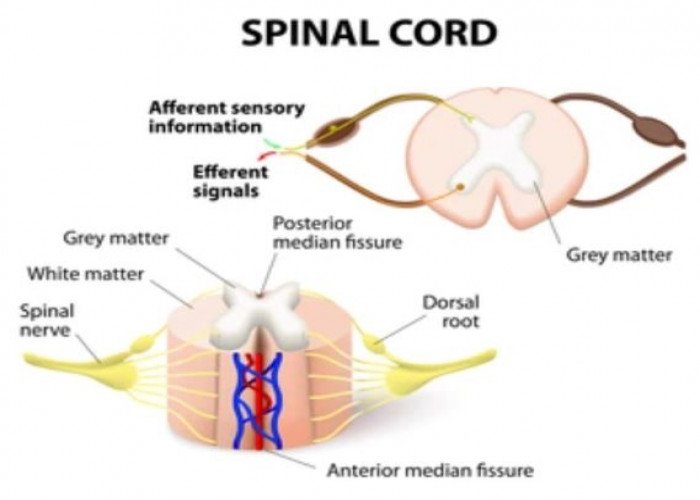
Spinal cord
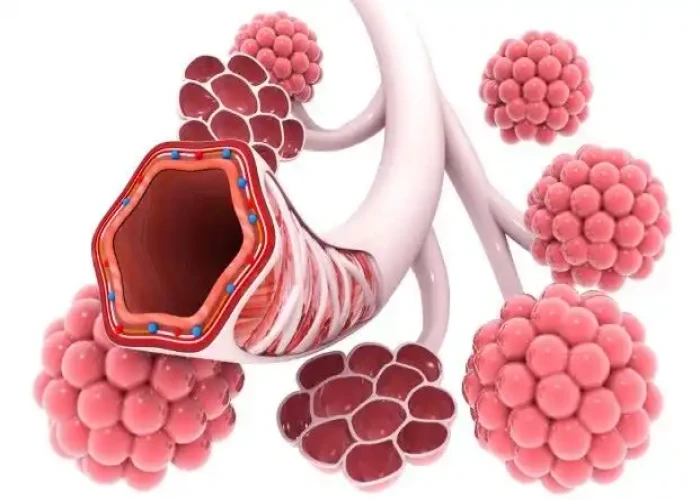
Bronchioles and smaller air passages
Olfactory epithelium, Human olfactory epithelium, অলফ্যাক্টরি এপিথেলিয়াম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.