 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Hypothalamus - Diseases
The hypothalamus is a small but crucial part of the brain located at the base of the brain, just above the brainstem. It is responsible for controlling many vital functions of the body, including the autonomic nervous system, the endocrine system, and the immune system.
The hypothalamus regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep, and wakefulness, as well as the release of hormones from the pituitary gland. It also plays a role in regulating emotions, such as anger, fear, and pleasure.
The hypothalamus communicates with other parts of the brain and the body through the nervous and endocrine systems. It receives information from the senses, such as temperature and light, and sends signals to other parts of the brain and body to initiate appropriate responses.
Various factors can affect hypothalamic function, including injury, disease, and environmental factors. Damage to the hypothalamus can cause disruptions in body temperature regulation, hormone production, and other vital functions.
Treatment for hypothalamic disorders may include medications, hormone replacement therapy, and surgery. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can also help support hypothalamic function.
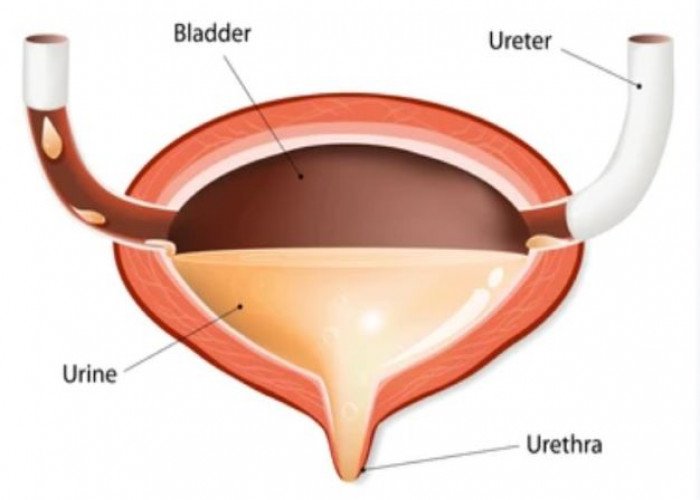
Urethra
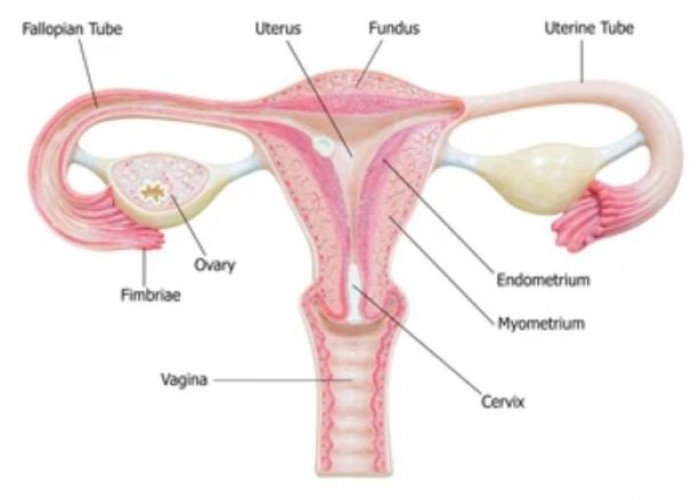
Fallopian tubes

Wrist
Jejunum intestine
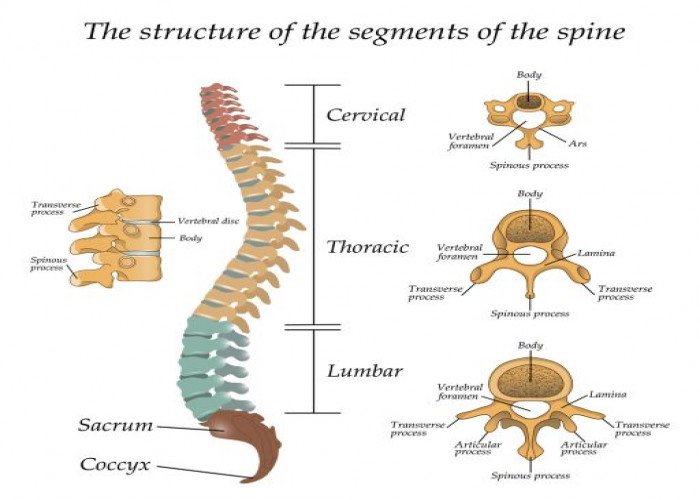
Spine

Spinal Nerves
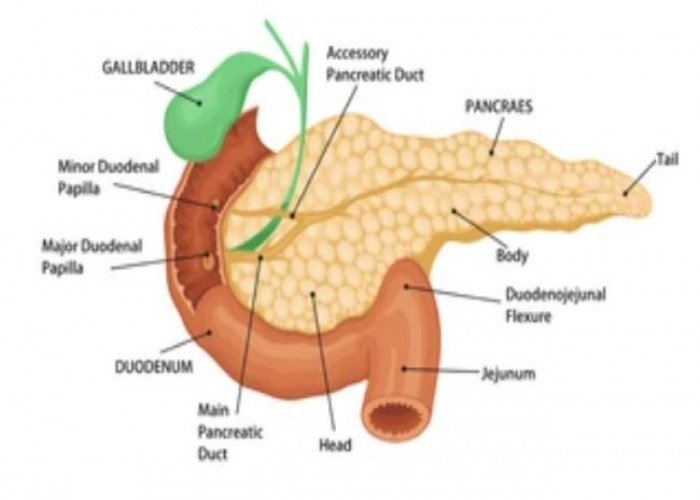
Pancreas
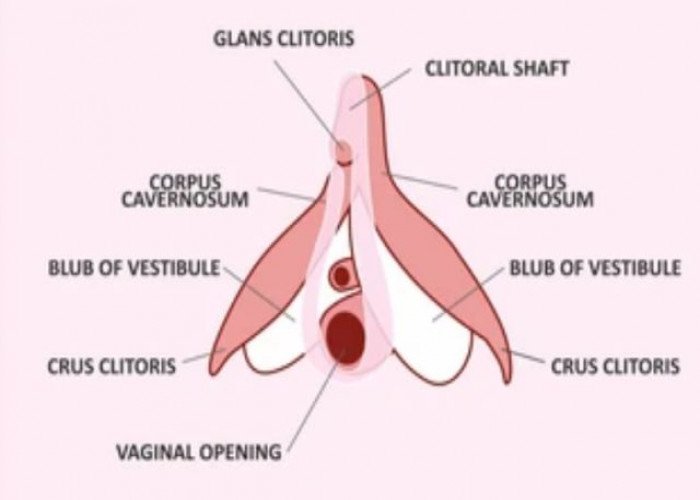
Clitoris
Hypothalamus, Hypothalamus gland, হাইপোথ্যালামাস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.