Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Broken arm
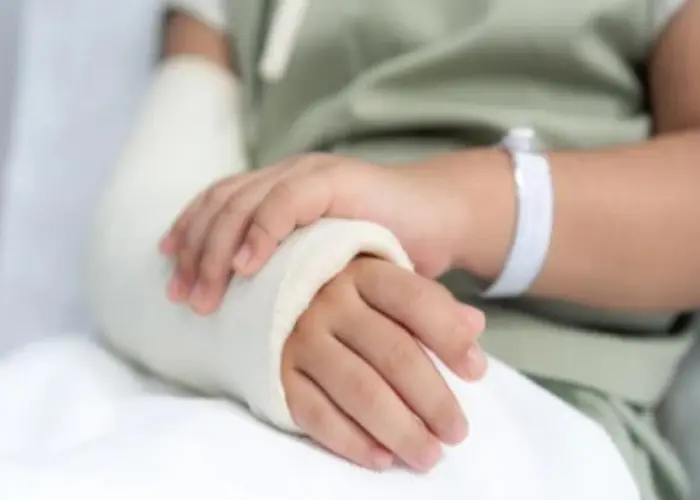
A broken arm is a medical condition where one or more of the bones in the arm is fractured or broken. It typically causes pain, swelling, and a limited range of motion. Treatment may involve immobilizing the arm with a cast or splint, pain management, and sometimes surgery. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a broken arm.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Arm or Hand pain
- Swollen arms or hands
- Severe pain, which might increase with movement
- Broken arm
- Broken bones or sprains
Disease Causes
Broken arm
Common causes for a broken arm include:
- Falls. Falling onto an outstretched hand or elbow is the most common cause of a broken arm.
- Sports injuries. Direct blows and injuries on the field or court cause all types of arm fractures.
- Significant trauma. Any of your arm bones can break during a car accident, bike accident or other direct trauma.
- Child abuse. In children, a broken arm might be the result of child abuse.
Disease Prevents
Broken arm
Although it's impossible to prevent an accident, these tips might offer some protection against bone breakage.
- Eat for bone strength. Eat a healthy diet that includes calcium-rich foods, such as milk, yogurt and cheese, and vitamin D, which helps your body absorb calcium. You can get vitamin D from fatty fish, such as salmon; from fortified foods, such as milk and orange juice; and from sun exposure.
- Exercise for bone strength. Weight-bearing physical activity and exercises that improve balance and posture can strengthen bones and reduce the chance of a fracture. The more active and fit you are as you age, the less likely you are to fall and break a bone.
- Prevent falls. To prevent falling, wear sensible shoes. Remove home hazards that can cause you to trip, such as area rugs. Make sure your living space is well lit. Install grab bars in your bathroom and handrails on your stairways, if necessary.
- Use protective gear. Wear wrist guards for high-risk activities, such as in-line skating, snowboarding, rugby and football.
- Don't smoke. Smoking can increase your risk of a broken arm by reducing bone mass. It also hampers healing of fractures.
Disease Treatments
Treatment of a broken arm depends on the type of break. The time needed for healing depends on a variety of factors, including severity of the injury; other conditions, such as diabetes; your age; nutrition; and tobacco and alcohol use.
Fractures are classified into one or more of the following categories:
- Open (compound) fracture. The broken bone pierces the skin, a serious condition that requires immediate, aggressive treatment to decrease the risk of infection.
- Closed fracture. The skin remains unbroken.
- Displaced fracture. The bone fragments on each side of the break aren't aligned. Surgery might be required to realign the fragments.
- Comminuted fracture. The bone is broken into pieces, so it might require surgery.
- Greenstick fracture. The bone cracks but doesn't break all the way — like what happens when you bend a green stick of wood. Most broken bones in children are greenstick fractures because children's bones are softer and more flexible than are those of adults.
- Buckle (torus) fracture. One side of the bone is compressed, which causes the other side to bend (buckle). This type of fracture is also more common in children.
Setting the bone
If you have a displaced fracture, your doctor might need to move the pieces back into position (reduction). Depending on the amount of pain and swelling you have, you might need a muscle relaxant, a sedative or even a general anesthetic before this procedure.
Immobilization
Restricting movement of a broken bone, which requires a splint, sling, brace or cast, is critical to healing. Before applying a cast, your doctor will likely wait until the swelling goes down, usually five to seven days after injury. In the meantime, you'll likely wear a splint.
Your doctor might ask you to return for X-rays during the healing process to make sure the bones haven't shifted.
Medications
To reduce pain and inflammation, your doctor might recommend an over-the-counter pain reliever. If your pain is severe, you may need a prescription medication that contains a narcotic for a few days.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help with pain but might also hamper bone healing, especially if used long term. Ask your doctor if you can take them for pain relief.
If you have an open fracture, in which you have a wound or break in the skin near the wound site, you'll likely be given an antibiotic to prevent infection that could reach the bone.
Therapy
Rehabilitation begins soon after initial treatment. In most cases, it's important, if possible, to begin some motion to minimize stiffness in your arm, hand and shoulder while you're wearing your cast or sling.
After your cast or sling is removed, your doctor might recommend additional rehabilitation exercises or physical therapy to restore muscle strength, joint motion and flexibility.
Surgery
Surgery is required to stabilize some fractures. If the fracture didn't break the skin, your doctor might wait to do surgery until the swelling has gone down. Keeping your arm from moving and elevating it will decrease swelling.
Fixation devices — such as wires, plates, nails or screws — might be needed to hold your bones in place during healing. Complications are rare, but can include infection and lack of bone healing.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Broken arm and Learn More about Diseases
Mesenteric ischemia

Delirium
Angina

Heart murmurs

Neck pain
Fibrous dysplasia
Colon cancer

Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Broken arm, Fractured arm, Forearm fracture, ভাঙা বাহু
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.