Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
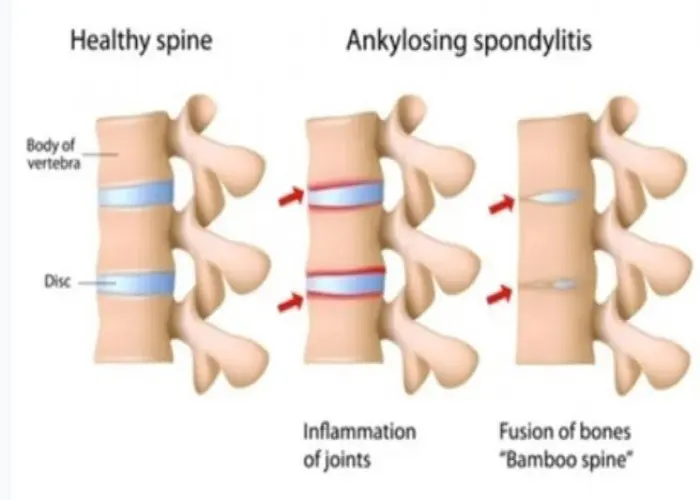
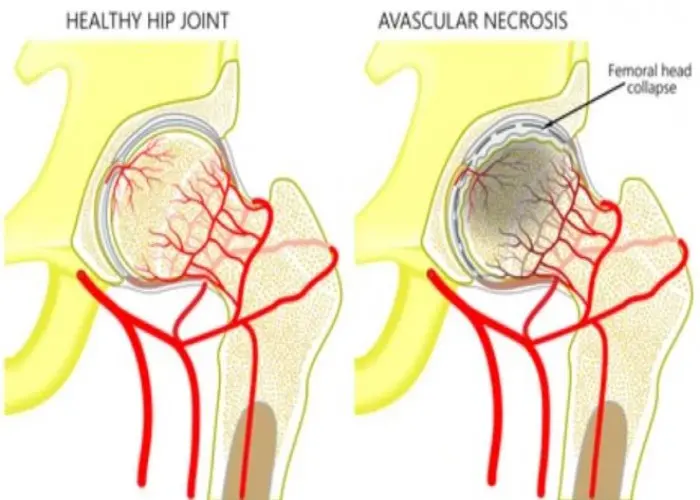
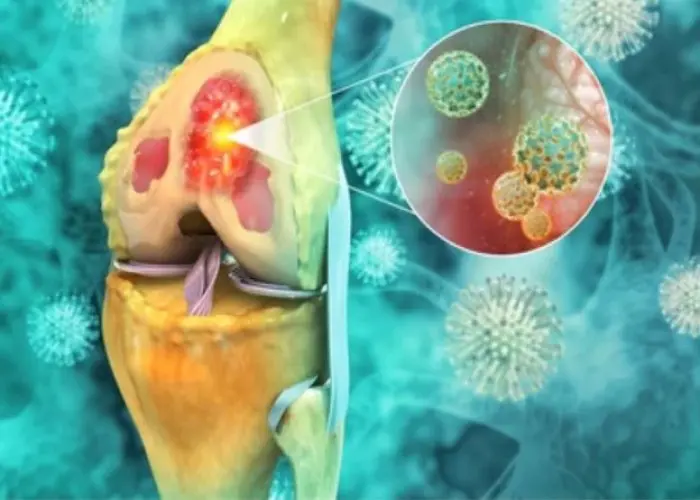
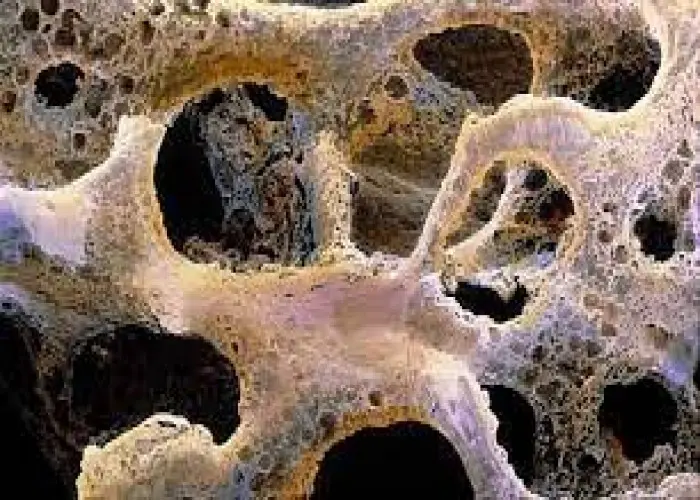
Bones - Diseases
Bones are rigid organs that form the skeletal system of the body, providing support, protection, and movement. The adult human body has 206 bones, which are classified into several categories based on their shape and function.
Bones are made up of a combination of mineralized tissue, such as calcium and phosphorus, and collagen, a type of protein that provides flexibility and strength. The structure of bones varies depending on their location and function, with long bones, such as the femur, having a tubular shape, while flat bones, such as the skull, provide protection for underlying organs.
Bones also play a role in the production of blood cells, as the bone marrow, which is located in the cavities of certain bones, produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
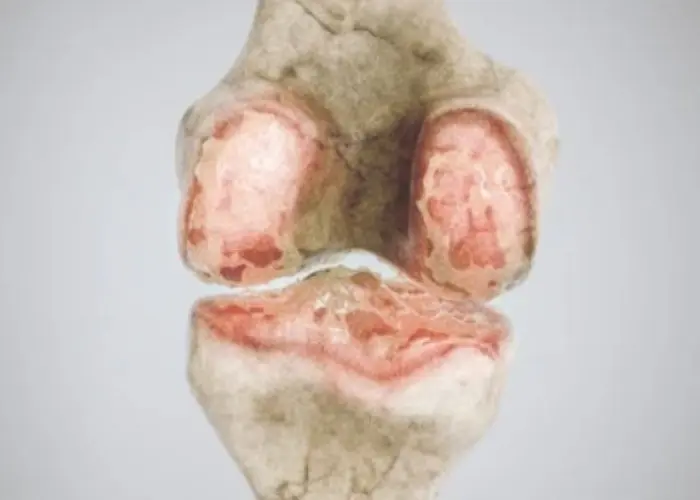
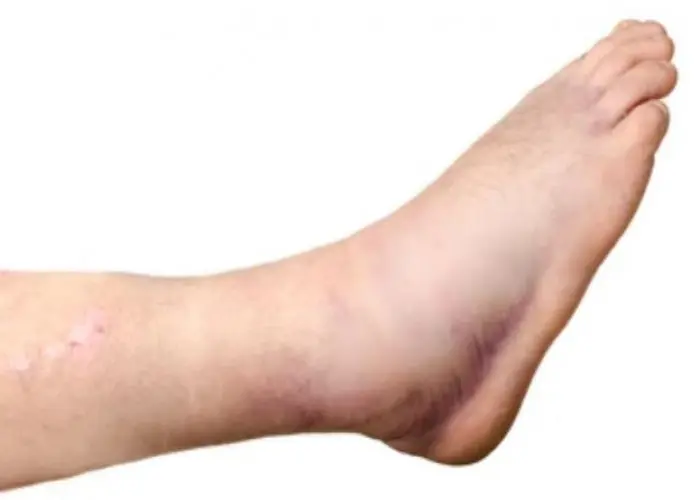
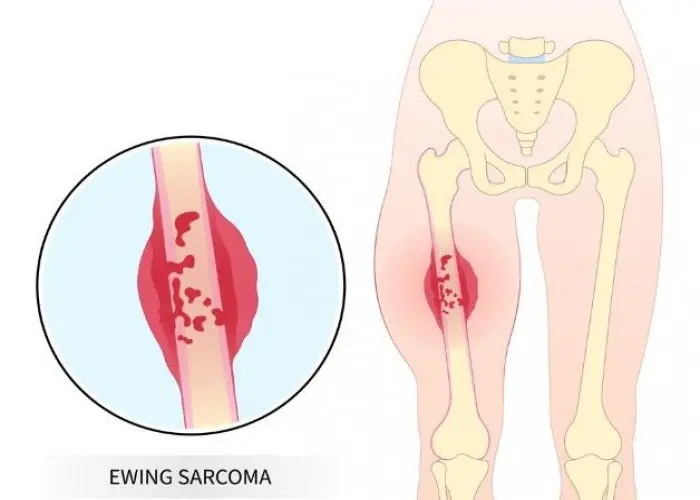
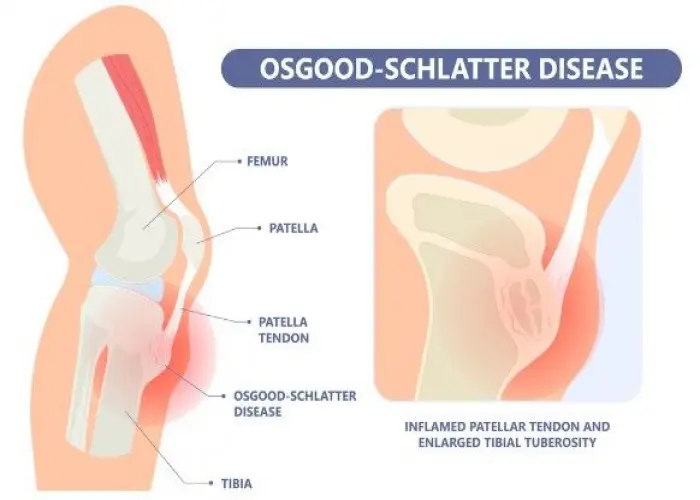
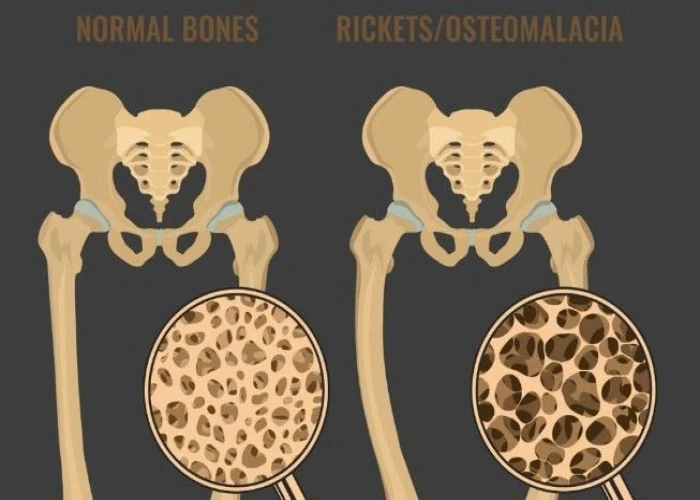
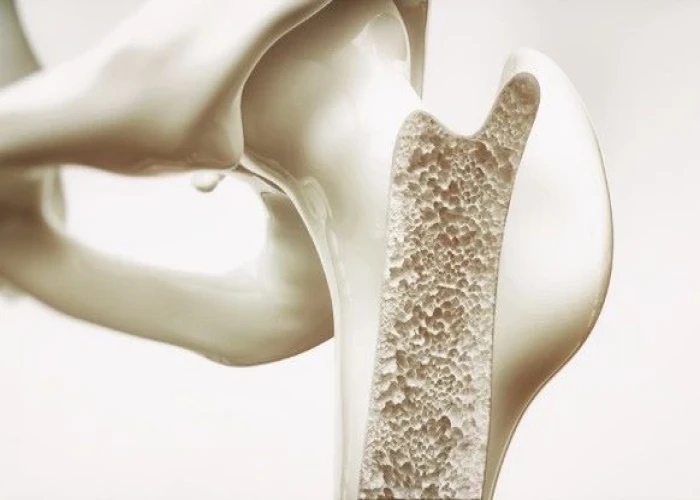
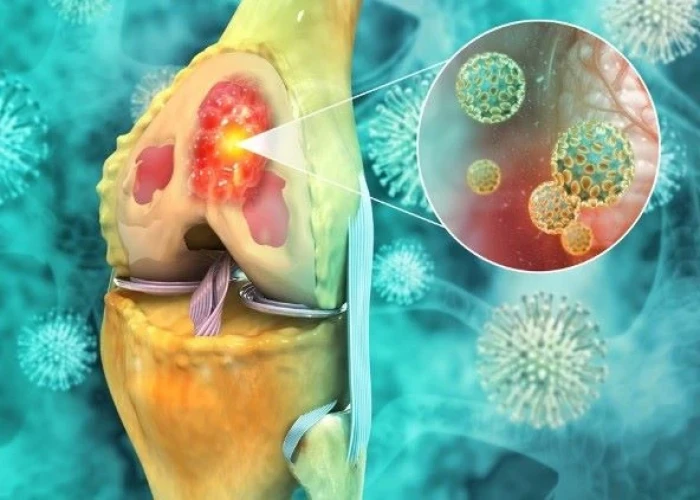
Diseases and conditions that can affect the bones include fractures, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and bone cancer. Treatment for bone disorders may involve medications, physical therapy, surgery, or other specialized therapies, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Proper nutrition and exercise are also important for maintaining bone health and preventing bone loss.
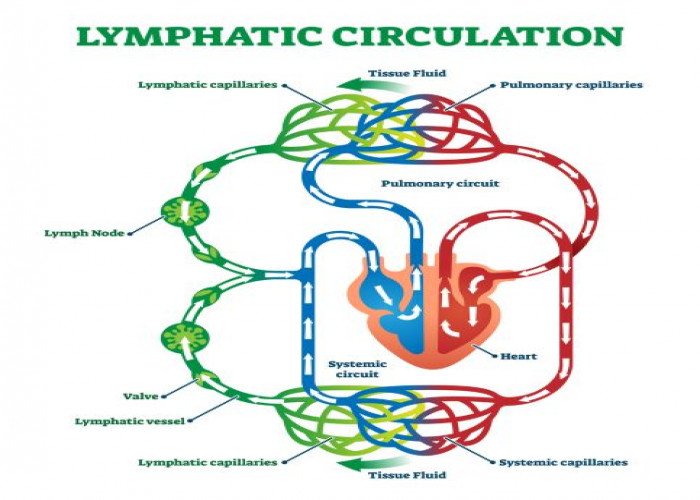
Lymphatic vessel
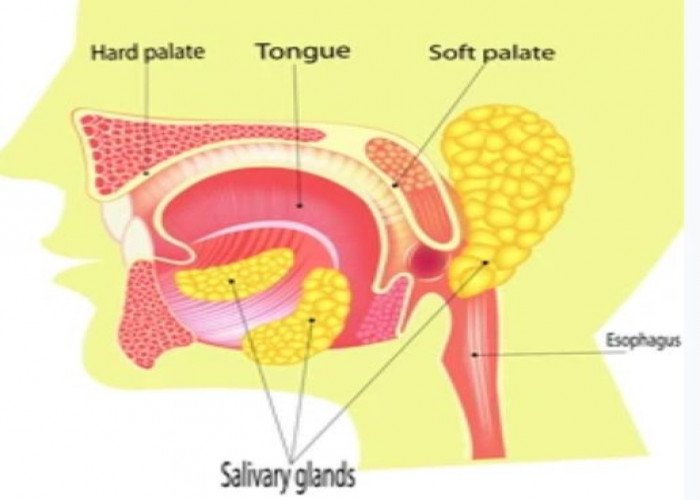
Salivary glands
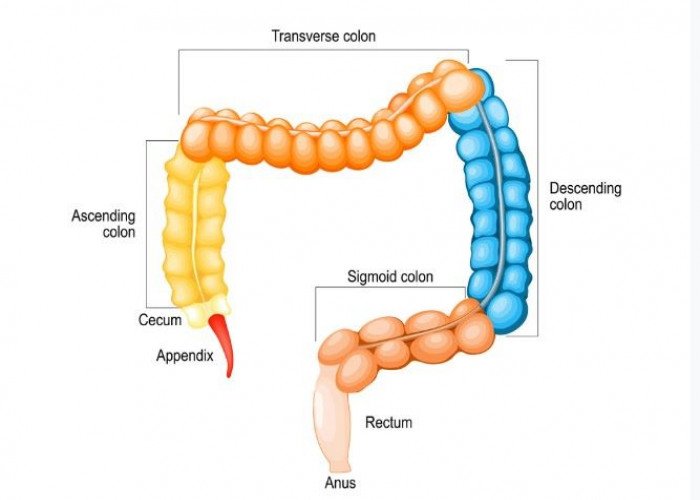
Sigmoid colon intestine
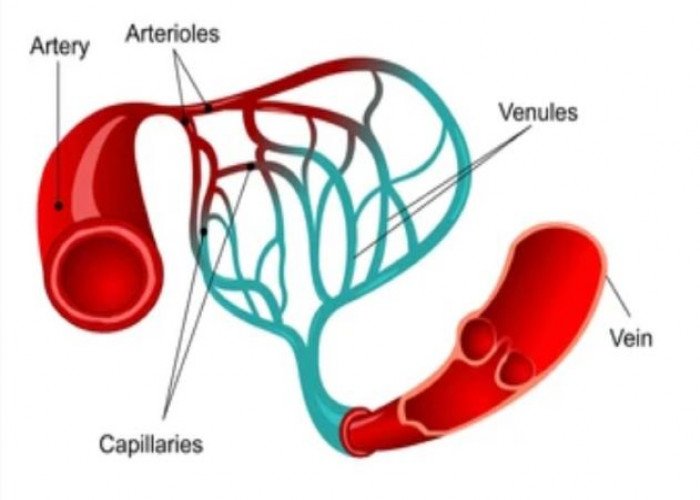
Capillaries
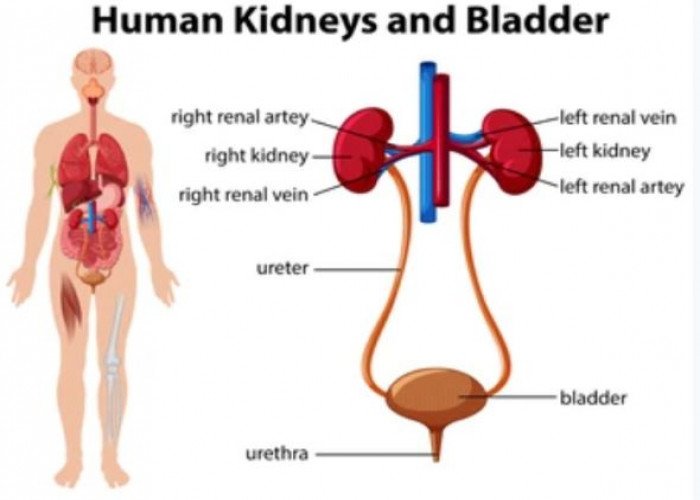
Kidneys
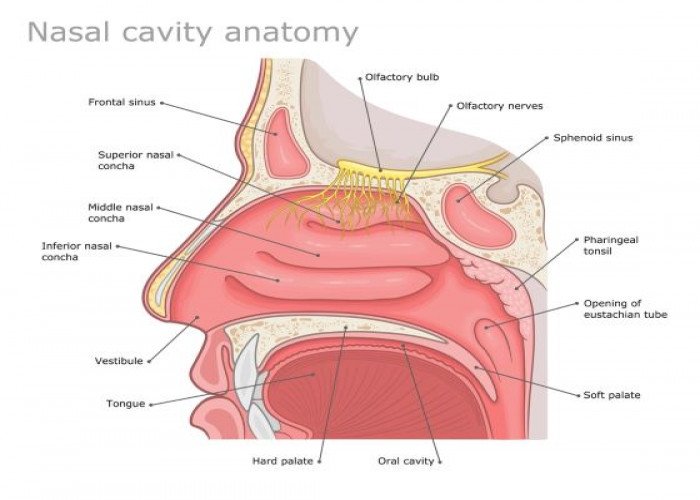
Nasal cavity
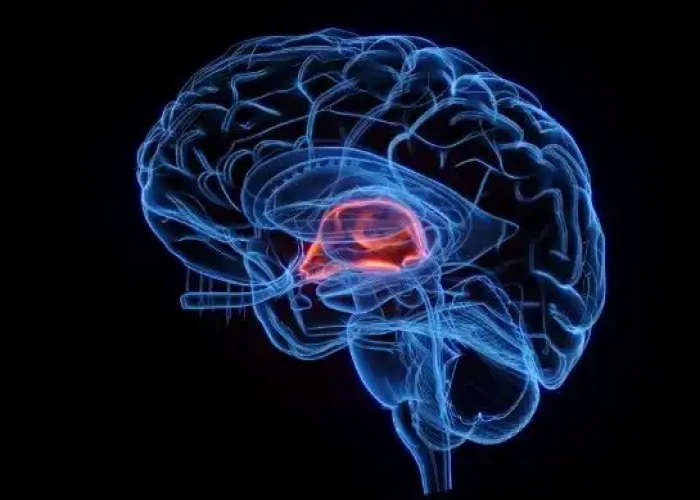
Choroid plexus Ventricular system

Blood
Bones, Emily deschanel, হাড়
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.