Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
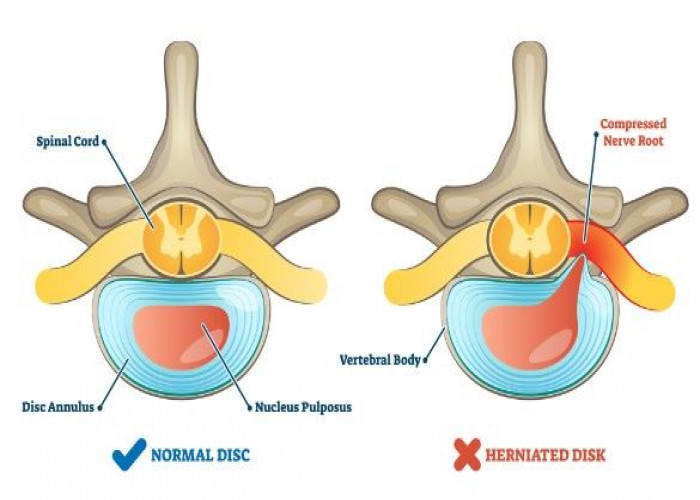
Herniated disk

A herniated disk, also known as a slipped or ruptured disk is a condition that occurs when the soft, jelly-like center of a spinal disk pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior layer. This can irritate or compress nearby nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness in the affected area.
Herniated disks can occur in any part of the spine, but they are most common in the lower back and neck. Common causes of herniated disks include aging, wear, and tear on the spine and injuries or trauma to the back.
Symptoms of a herniated disk can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. In many cases, people with herniated disks may experience pain in the affected area, as well as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the limbs. Some people may also experience muscle spasms or difficulty with coordination and balance.
Treatment for a herniated disk may include rest, physical therapy, pain management, and, in severe cases, surgery. Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition and the individual's specific symptoms and needs. It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of a herniated disk, as early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and prevent complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Leg pain
- Numbness
- Tingling in arms
- Weakness
- Cough
- Sneeze
Disease Causes
Herniated disk
Disk herniation is most often the result of a gradual, aging-related wear and tear called disk degeneration. As people age, the disks become less flexible and more prone to tearing or rupturing with even a minor strain or twist.
Most people can't pinpoint the cause of their herniated disk. Sometimes, using the back muscles instead of the leg and thigh muscles to lift heavy objects can lead to a herniated disk, as can twisting and turning while lifting. Rarely, a traumatic event such as a fall or a blow to the back is the cause.
Disease Prevents
Herniated disk
To help prevent a herniated disk, do the following:
- Exercise. Strengthening the trunk muscles stabilizes and supports the spine.
- Maintain good posture. This reduces pressure on your spine and disks. Keep your back straight and aligned, particularly when sitting for long periods. Lift heavy objects properly, making your legs — not your back — do most of the work.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight puts more pressure on the spine and disks, making them more susceptible to herniation.
- Quit smoking. Avoid the use of any tobacco products.
Disease Treatments
Conservative treatment — mainly modifying activities to avoid movement that causes pain and taking pain medication — relieves symptoms in most people within a few days or weeks.
Medications
- Nonprescription pain medications. If your pain is mild to moderate, your doctor might recommend pain medication available without a prescription, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve).
- Neuropathic drugs. These drugs affect nerve impulses to decrease the pain. They include gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant, Neurontin), pregabalin (Lyrica), duloxetine (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle), or venlafaxine (Effexor XR).
- Muscle relaxers. You might be prescribed these if you have muscle spasms. Sedation and dizziness are common side effects.
- Opioids. Because of the side effects of opioids and the potential for addiction, many doctors hesitate to prescribe them for disk herniation. If other medications don't relieve your pain, your doctor might consider short-term use of opioids, such as codeine or an oxycodone-acetaminophen combination (Percocet, Oxycet). Sedation, nausea, confusion and constipation are possible side effects from these drugs.
- Cortisone injections. If your pain doesn't improve with oral medications, your doctor might recommend a corticosteroid that can be injected into the area around the spinal nerves. Spinal imaging can help guide the needle.
Therapy
Your doctor might suggest physical therapy to help with your pain. Physical therapists can show you positions and exercises designed to minimize the pain of a herniated disk.
Surgery
Few people with herniated disks require surgery. Your doctor might suggest surgery if conservative treatments fail to improve your symptoms after six weeks, especially if you continue to have:
- Poorly controlled pain
- Numbness or weakness
- Difficulty standing or walking
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
In nearly all cases, surgeons can remove just the protruding portion of the disk. Rarely, the entire disk must be removed. In these cases, the vertebrae might need to be fused with a bone graft.
To allow the process of bone fusion, which takes months, metal hardware is placed in the spine to provide spinal stability. Rarely, your surgeon might suggest the implantation of an artificial disk.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Herniated disk and Learn More about Diseases

Chondrosarcoma

Teen depression
Retinal diseases
Gum Boil

Bronchitis

Histoplasmosis

Turner syndrome
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
herniated disk, হারনিয়াটেড ডিস্ক
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.