 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Bleeding from uterus - Homeopathic remedies
Bleeding from the uterus, also known as vaginal bleeding, can occur for a variety of reasons. It can be caused by hormonal changes, pregnancy, medical conditions, or certain medications. The severity of the bleeding can range from light spotting to heavy bleeding.
In women of reproductive age, the most common cause of vaginal bleeding is menstruation. However, abnormal vaginal bleeding can also be a sign of other conditions, such as uterine fibroids, polyps, or endometriosis. In pregnant women, vaginal bleeding can be a sign of a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
Other causes of vaginal bleeding can include infections, such as vaginitis or sexually transmitted infections (STIs), as well as certain medications, such as blood thinners or hormone therapy.
Treatment for vaginal bleeding depends on the underlying cause. In cases of heavy bleeding or bleeding that lasts longer than normal, medical attention may be necessary to rule out serious conditions and to prevent complications such as anemia.
If you experience vaginal bleeding that is heavy, lasts longer than normal, or is accompanied by pain, fever, or other symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.

Heartburn (Acidity)
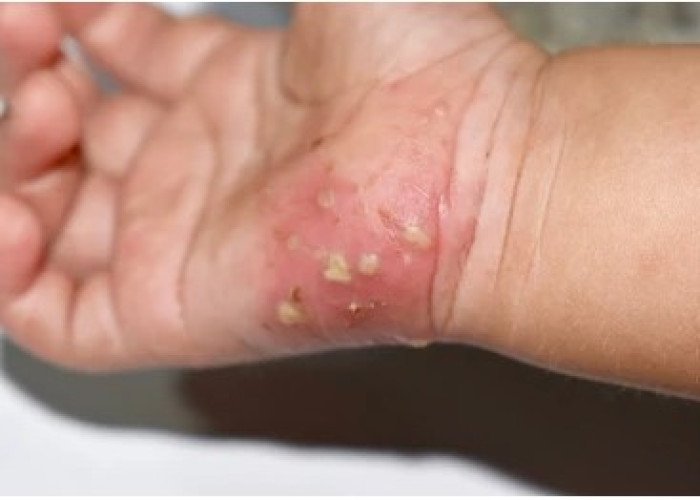
Scabies

Tape worm

Children do not cry
Penis is small in size
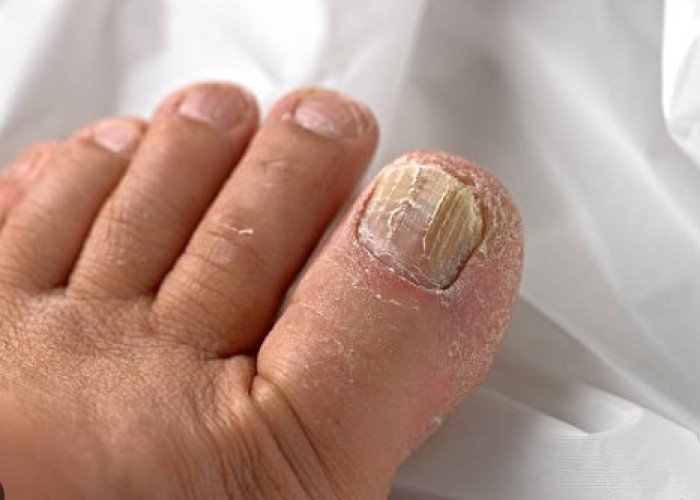
Spoiled nails
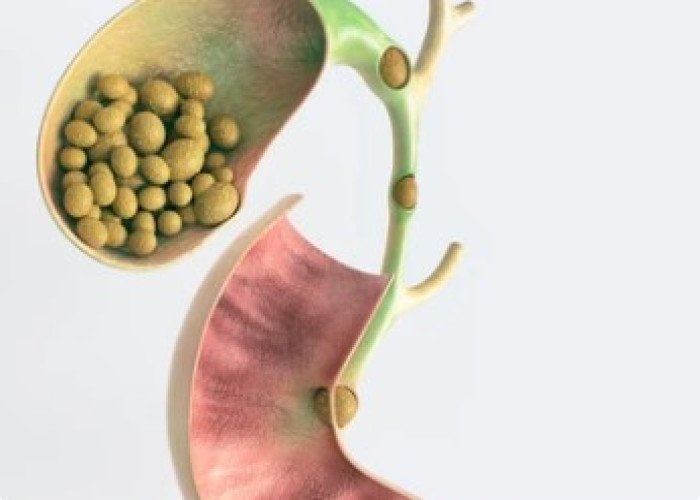
Gallstones
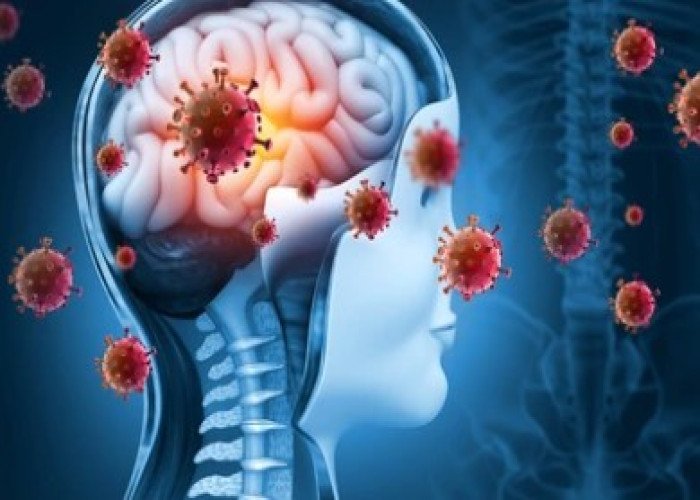
Meningitis
Bleeding from the uterus, জরায়ু হতে রক্তস্রাব
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.