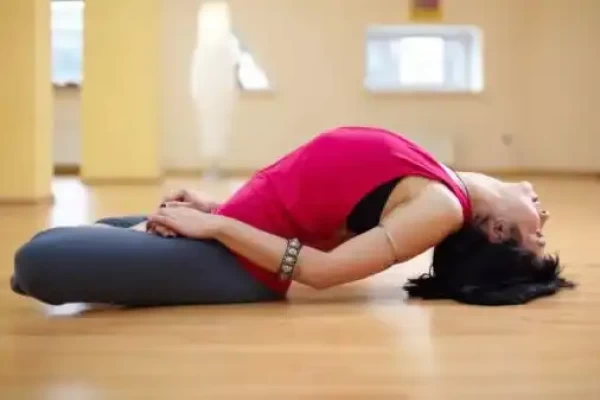
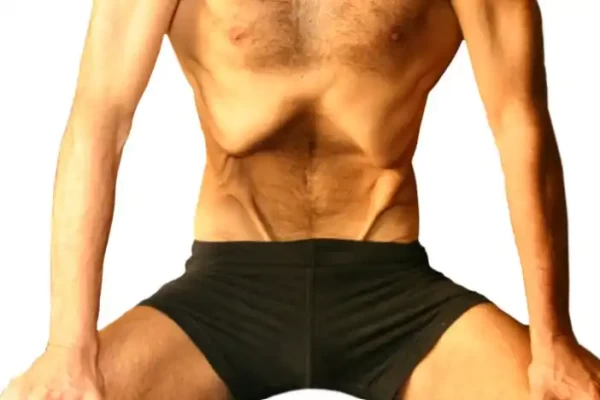
 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Hernia (Intestinal protrusion) - Yoga remedies
A hernia is a condition in which an internal organ or tissue protrudes through a weak point or tear in the muscle or tissue that surrounds it. Hernias can occur in various parts of the body, but they most commonly occur in the abdominal wall, causing an intestinal protrusion.
The most common types of abdominal hernias are inguinal hernias, which occur in the groin area, and umbilical hernias, which occur at the belly button. Other types of hernias include incisional hernias, which occur at the site of a previous surgical incision, and hiatal hernias, which occur in the diaphragm.
Risk factors for developing a hernia include obesity, pregnancy, constipation, chronic coughing or sneezing, and a family history of hernias. Symptoms of a hernia can include a visible bulge or lump, pain or discomfort in the affected area, and a feeling of pressure or heaviness.
Treatment for a hernia typically involves surgery to repair the weakened area and prevent the hernia from recurring. In some cases, a supportive device such as a hernia belt or truss may be used to provide temporary relief of symptoms.
Prevention of a hernia involves maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding activities that strain the abdominal muscles, and treating underlying medical conditions such as constipation or chronic coughing. It's also important to seek prompt medical attention if you experience symptoms of a hernia, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications such as intestinal obstruction or strangulation.
In summary, a hernia is a condition in which an internal organ or tissue protrudes through a weak point or tear in the muscle or tissue that surrounds it. Treatment for a hernia typically involves surgery to repair the weakened area and prevent the hernia from recurring, and prevention involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking prompt medical attention for symptoms.

Workforce reduction

Leukorrhea
Gonorrhea

Hemorrhoids
Liver and spleen problems

Cancer
Chest is weak

One leg is short
Hernia, Intestinal protrusion, হার্ণিয়া, অন্ত্রবৃদ্ধি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.


