 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
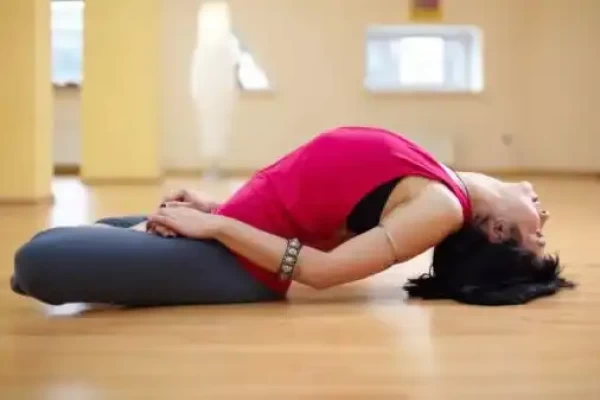
Bile colic - Yoga remedies
Bile colic, also known as a gallbladder attack, is a condition that occurs when there is a sudden, intense pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, often accompanied by nausea or vomiting. It is typically caused by the blockage of the bile duct by gallstones.
Bile is a fluid produced by the liver that helps digest fats in the small intestine. It is stored in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. Bile colic occurs when a gallstone obstructs the flow of bile from the gallbladder into the small intestine, causing a backup of bile and triggering the pain and other symptoms.
Treatment for bile colic typically involves managing the symptoms and addressing the underlying cause. Pain relief medication may be prescribed to manage the pain associated with a gallbladder attack. In some cases, a procedure called a cholecystectomy may be recommended to remove the gallbladder and prevent future attacks.
Preventing bile colic involves maintaining good digestive health, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and staying well-hydrated. If you are experiencing symptoms of bile colic, it is important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They may recommend lifestyle changes or additional therapies to help manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.

Beriberi

Aged

Sinus

Arthritis in the legs
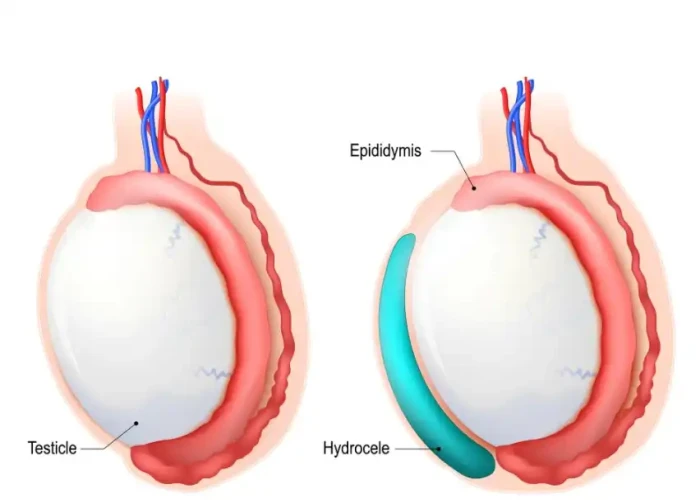
Hydrocele

Memory loss
Laziness

Sick
Bile colic, পিত্তশূল
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.

