 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Memory - Diseases
Memory refers to the ability to encode, store, and retrieve information in the brain. It is the process by which the brain creates and retains a record of past experiences, knowledge, and skills.
Memory can be categorized into several types, including sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory is the brief retention of sensory information, such as visual or auditory information, and lasts for only a few seconds. Short-term memory, also known as working memory, is the temporary retention of information that is actively being used and lasts for a few seconds to a minute. Long-term memory is the more permanent retention of information, which can last from hours to a lifetime.
Memory can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as age, stress, sleep, and nutrition. Certain medical conditions, medications, and injuries can also affect memory.
Memory loss can occur due to normal aging or as a result of certain medical conditions, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, or traumatic brain injury. Treatment for memory loss may involve medication, therapy, lifestyle changes, and cognitive rehabilitation.
To improve memory, it is important to engage in activities that stimulate the brain, such as learning new things, practicing mindfulness, and staying physically active. Getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and reducing stress can also help support memory function.
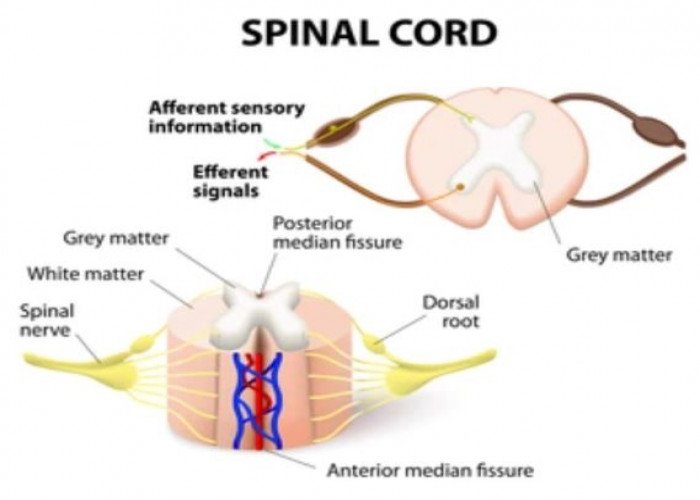
Spinal cord
Muscles of breathing

Foot

Lip
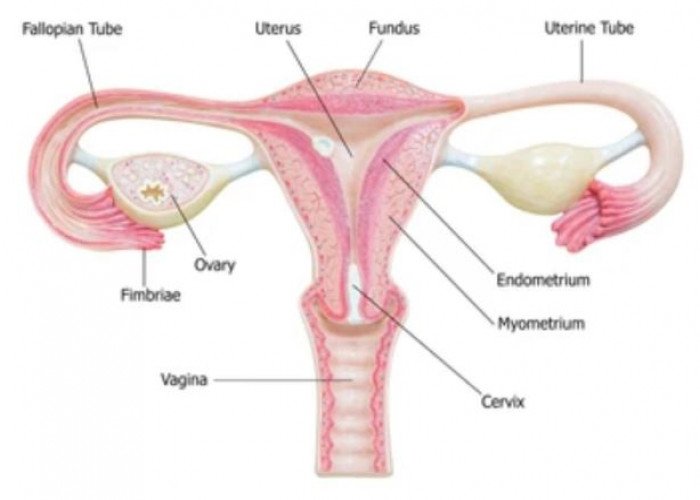
Ovaries

Vagina

Bile ducts

Pharynx
Memory, Short term memory, Photographic memory, স্মৃতি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.

