 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Spinal Nerves - Diseases
Spinal nerves are a type of nerve that emerges from the spinal cord and extends throughout the body to transmit sensory and motor signals. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves in the human body, each named for the level of the vertebrae they originate from.
Each spinal nerve contains both sensory and motor nerve fibers, and they are classified as either sensory, motor, or mixed nerves depending on their function. Sensory nerves transmit signals from sensory organs or skin to the spinal cord and brain, while motor nerves transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands. Mixed nerves contain both sensory and motor fibers.
The spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord through openings between adjacent vertebrae, known as intervertebral foramina. The spinal nerves are grouped according to their location along the spine into the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions.
Damage to the spinal nerves can result in a variety of symptoms, depending on the location and severity of the injury. Symptoms may include numbness or tingling in the affected area, weakness or paralysis of muscles, or loss of sensation. Treatment for spinal nerve damage may involve medication, physical therapy, or surgery, depending on the cause and extent of the injury.

Skin

N/A
Chest

Liver

Prostate
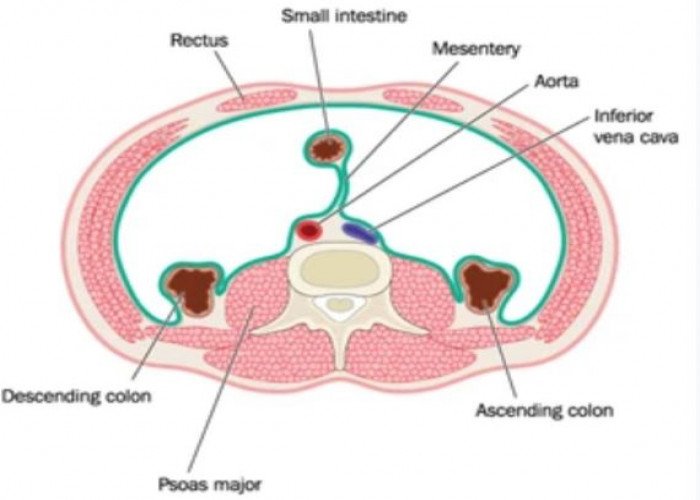
Mesentery

Scalp
Subcutaneous tissue
Spinal Nerves, Accessory nerve, Spinal cord nerves, মেরুদণ্ডের স্নায়ু
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.