 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Arm - Diseases
The arm is the upper limb of the human body, extending from the shoulder to the hand. It is composed of bones, muscles, joints, and other tissues that work together to allow movement and provide support for everyday activities.
The bones of the arm include the humerus in the upper arm, the radius and ulna in the forearm, and the carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges in the hand. The muscles of the arm are responsible for movement and control of the arm and hand. These muscles are attached to the bones via tendons, which allow for movement and stability.
The arm is involved in various activities, such as lifting, pushing, pulling, and grasping. It is also used in fine motor skills, such as writing and playing musical instruments. However, the arm is susceptible to various conditions, such as fractures, dislocations, strains, sprains, and tendonitis. These conditions can cause pain, limited mobility, and other symptoms that can impact daily activities.
Treatment for arm conditions may involve rest, physical therapy, medication, or surgery, depending on the severity and underlying cause of the problem. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and proper nutrition, can help prevent arm injuries and promote overall arm health.

Vulva
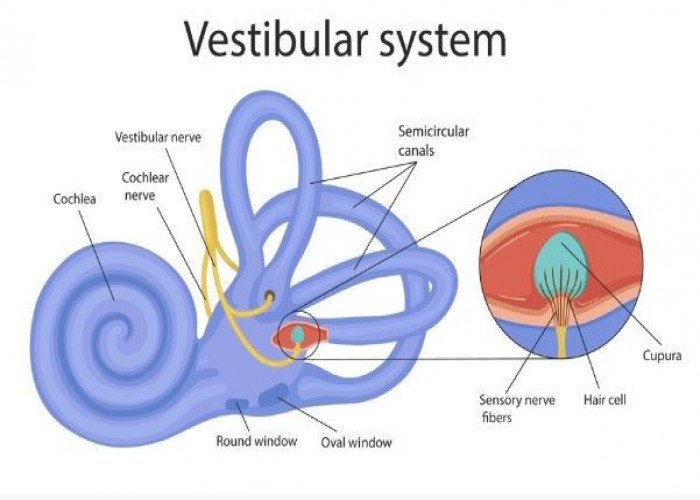
Vestibule of the Inner ear
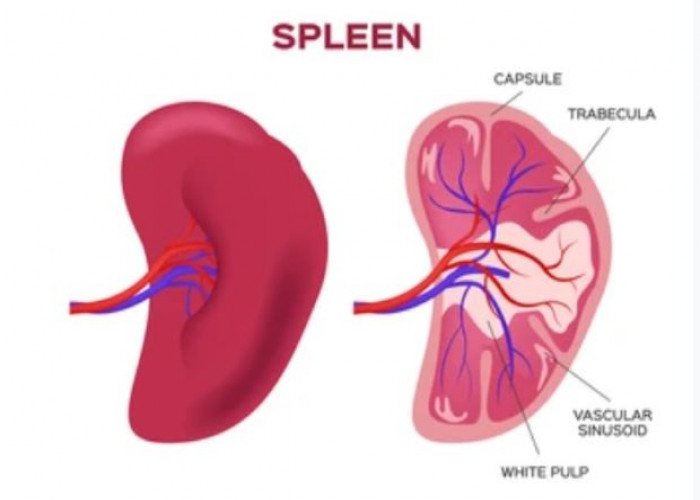
Spleen
Eye

Achilles
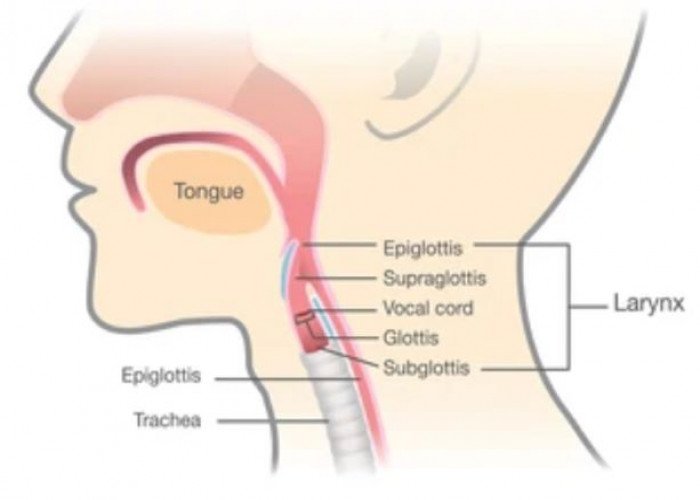
Larynx
Muscles of breathing
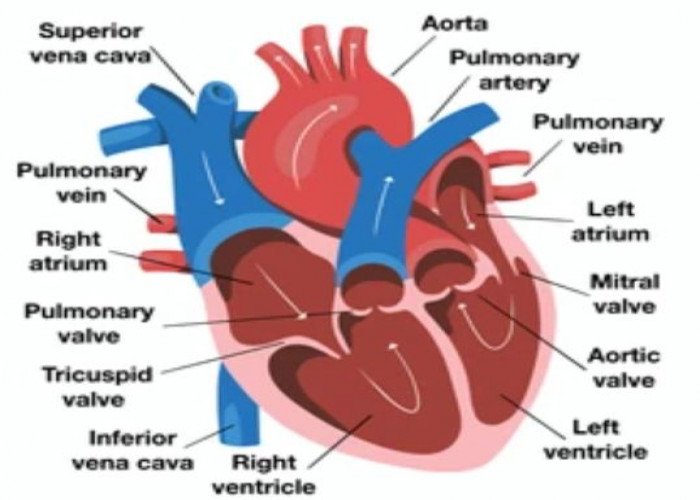
Heart
Arm, Arm architecture, বাহু
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.

