Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
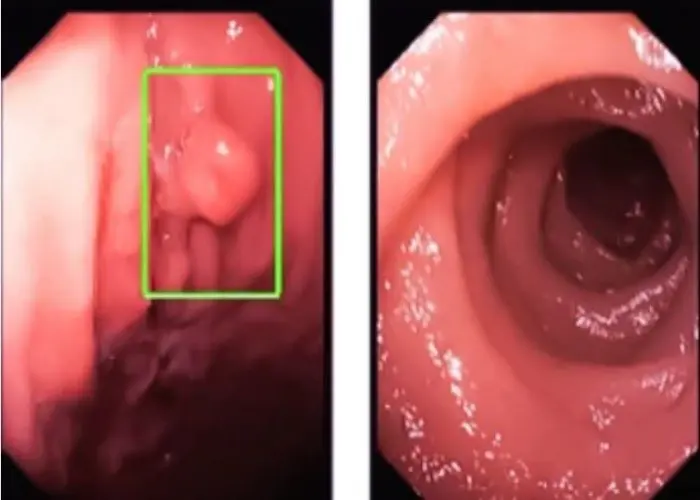
Colon - Diseases
The colon, also known as the large intestine, is part of the digestive system in humans and other animals. It is a long, muscular tube that absorbs water and electrolytes from digested food, forming feces.
The colon is divided into several parts, including the ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon. The colon is also home to a large number of bacteria, which play an important role in digestion and immune system function.
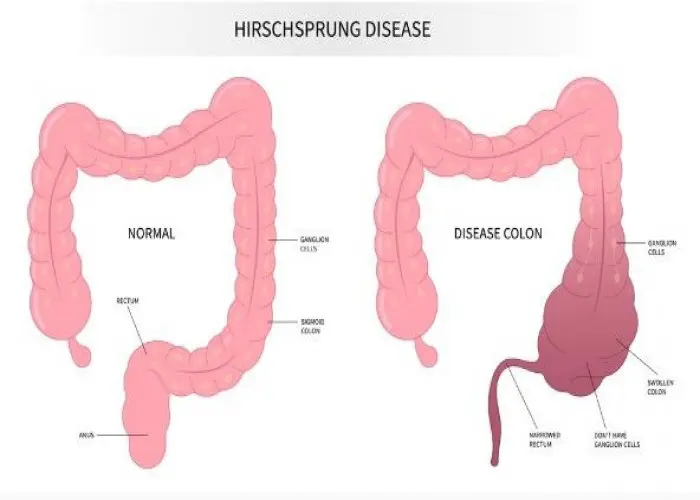
Various conditions can affect the colon, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), colon cancer, and diverticulitis. Treatment options for colon conditions may include medication, dietary changes, surgery, and lifestyle modifications, depending on the underlying problem.
Maintaining good colon health involves engaging in healthy behaviors, such as eating a diet rich in fiber and low in processed foods and red meat, staying hydrated, and exercising regularly. Regular screening for colon cancer is also recommended for individuals at higher risk for the disease.
It is also important to be aware of any changes or abnormalities in bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation, blood in the stool, or abdominal pain, and to seek medical attention if any problems arise. Early detection and treatment of colon conditions can improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
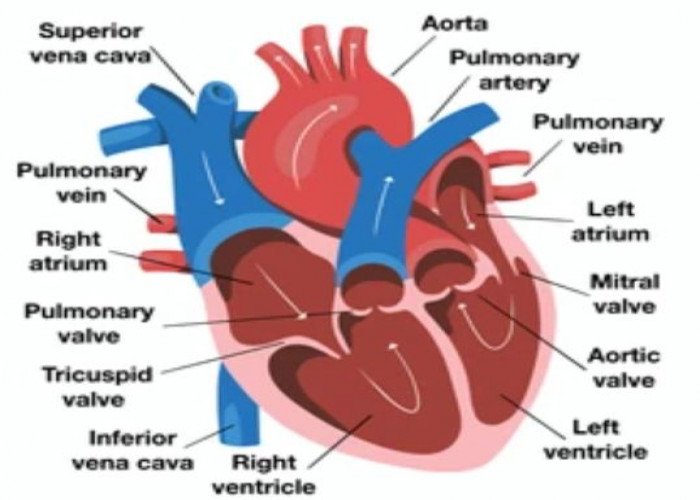
Heart

Mental
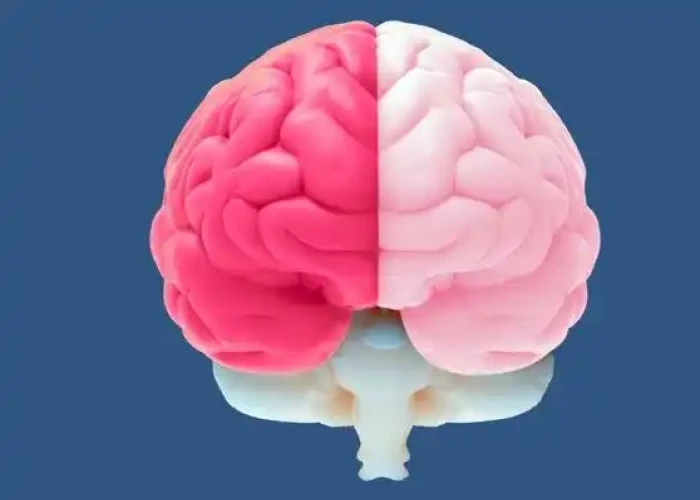
Cerebral hemispheres Brain
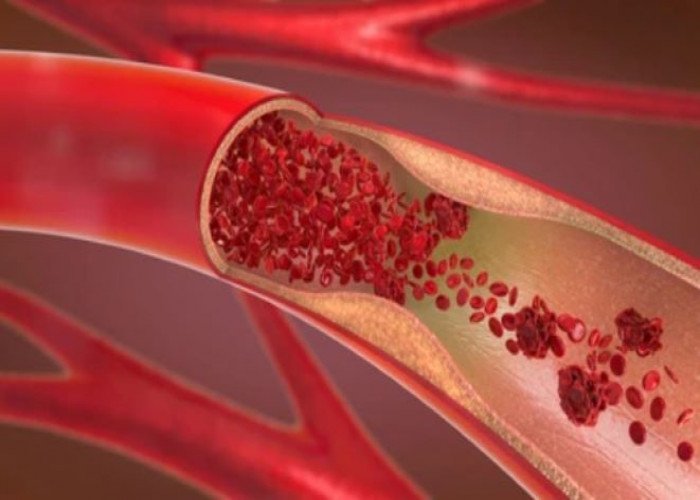
Blood vessel
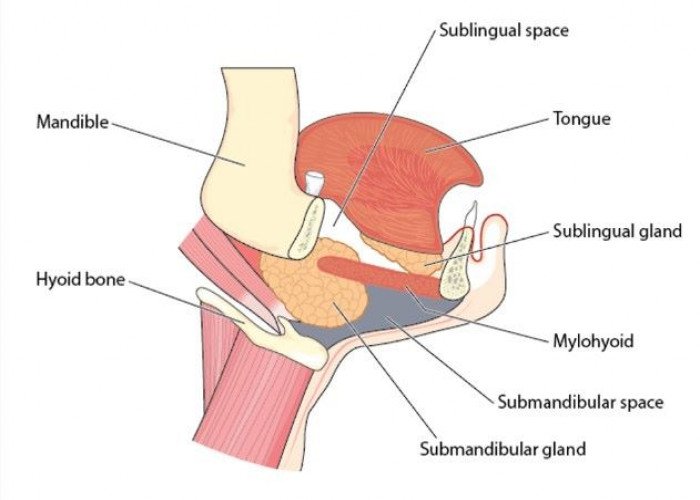
Sublingual glands

Pharynx
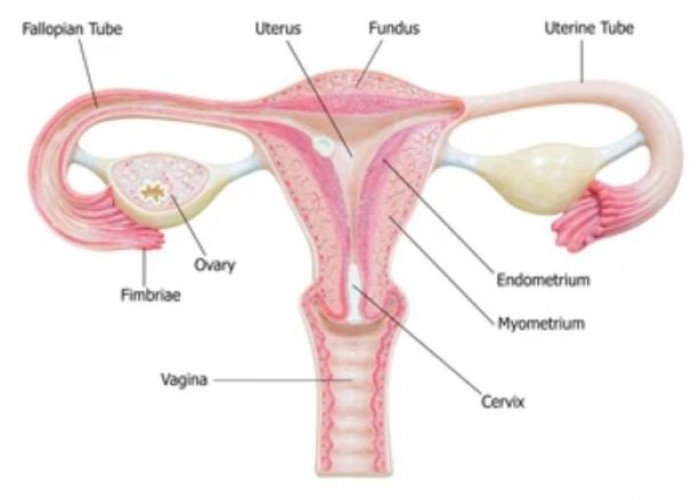
Fallopian tubes

Hip
Colon, Colon cleanse, Sigmoid colon, কোলন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.