Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Genetic - Diseases
Genetics is the study of genes and their role in inheritance and variation of traits in living organisms. Genes are segments of DNA that contain the instructions for the development and function of cells, tissues, and organs.
In humans, each cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, which carry the genetic information that determines a person's traits, such as eye color, hair color, and height. Genes are inherited from parents, and the combination of genes from both parents determines an individual's unique characteristics.
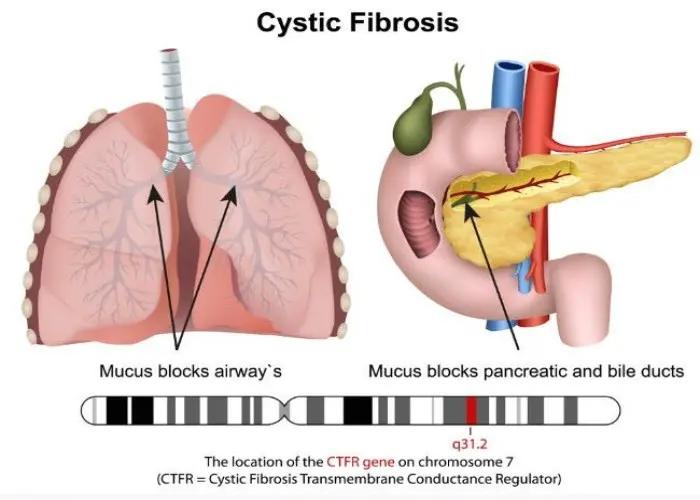
Genetic research has led to many important discoveries, including the identification of genes responsible for certain diseases, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington's disease. Genetic testing can be used to identify carriers of certain genetic mutations, which can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and reproductive options.
Advances in genetic engineering and gene therapy have also led to the development of new treatments for genetic disorders. For example, gene therapy involves the insertion of healthy genes into cells to replace or repair defective genes that cause disease.
However, genetic research also raises ethical concerns, particularly around the use of genetic information for discrimination or eugenics. It is important to balance the potential benefits of genetic research with ethical considerations and respect for individual rights and privacy.
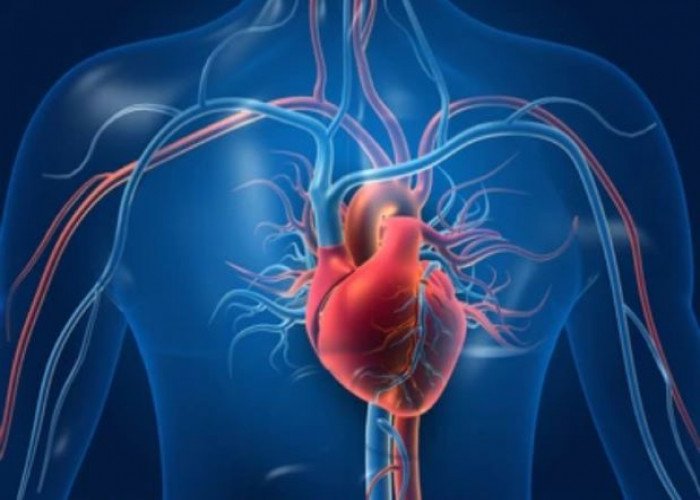
Veins
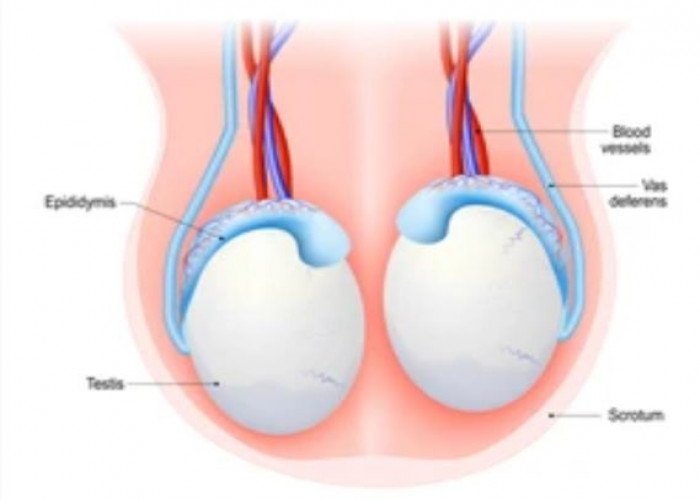
Testicle

Hip
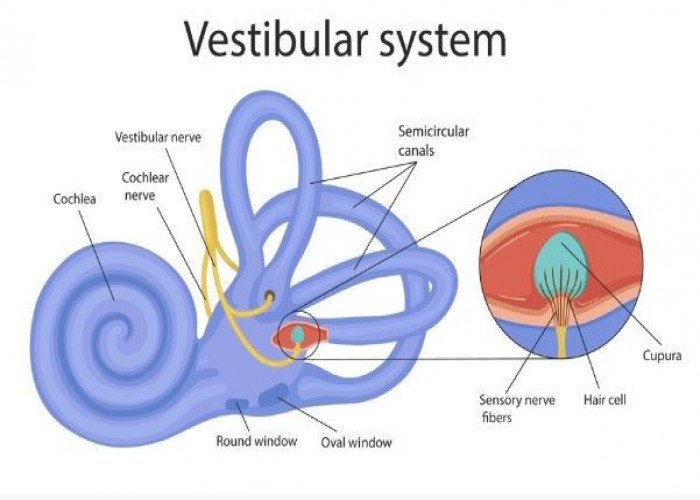
Vestibule of the Inner ear

Spinal Nerves
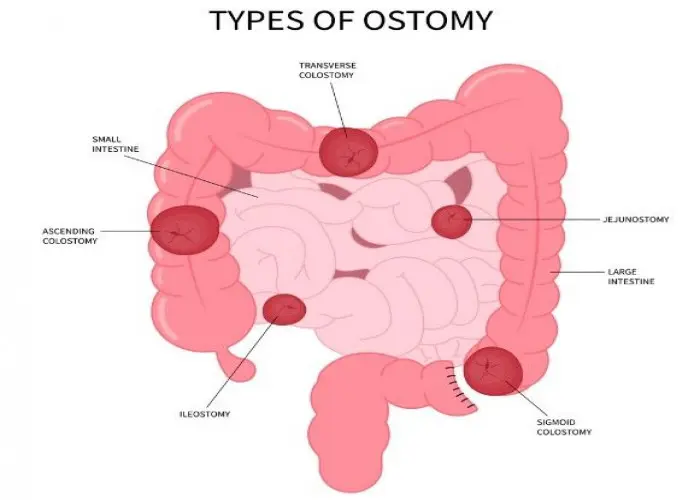
Transverse colon intestine

Vocal cords

Bladder
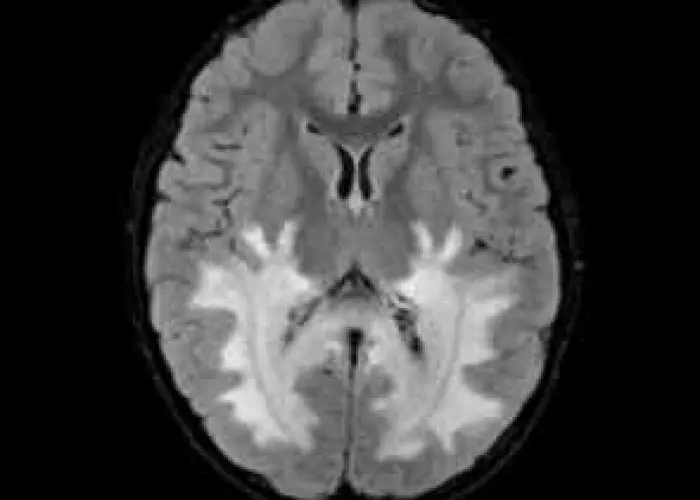
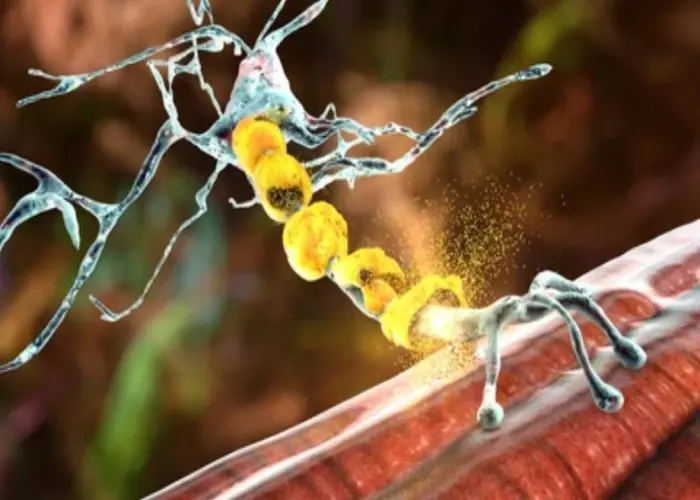
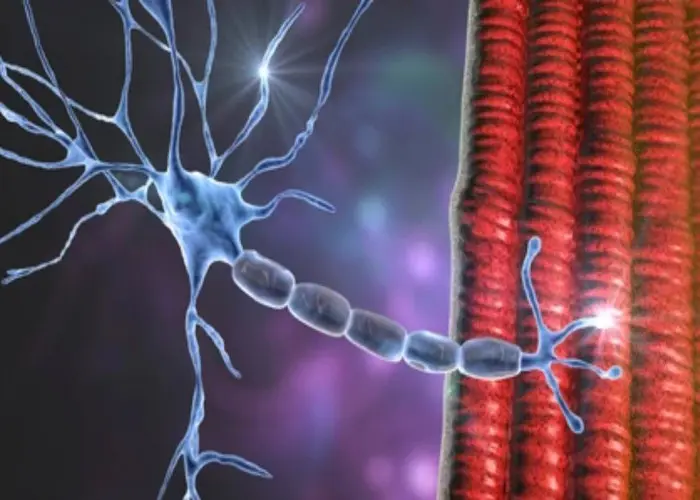
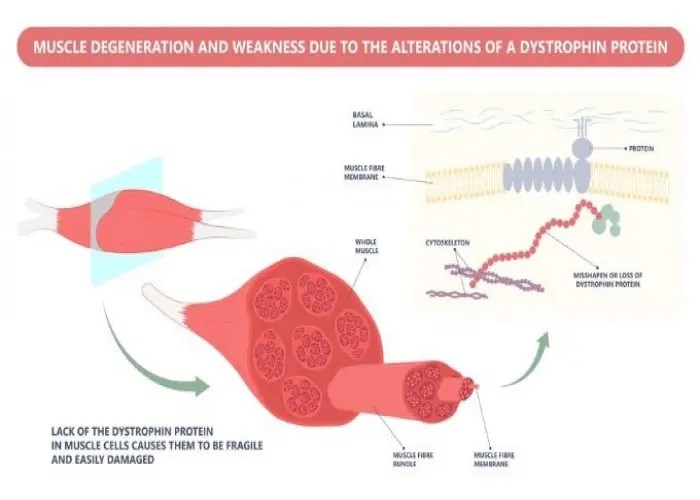
Genetic, Gene, Chromosomal, জেনেটিক
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.