Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Congenital myopathies
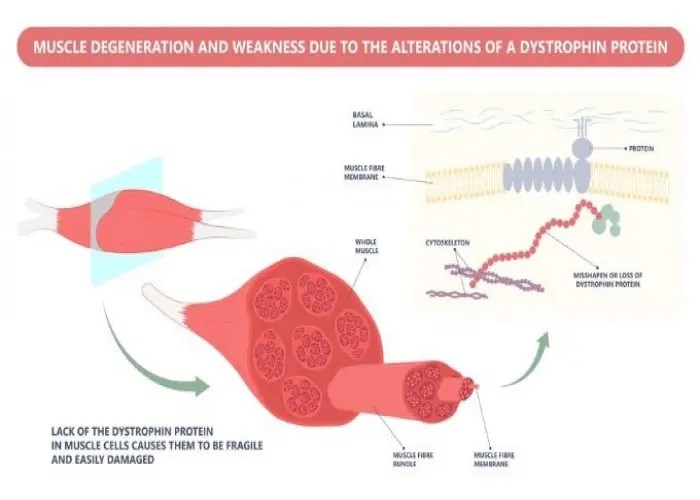
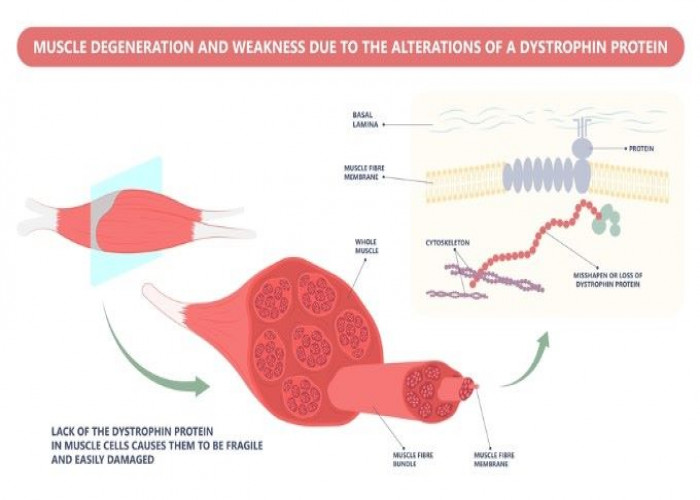
Congenital myopathies (CM) are a group of genetic muscle disorders that are present at birth or manifest in early infancy. These disorders are caused by mutations in genes that affect the development, structure, and function of the muscles, resulting in a range of muscle weakness and/or muscle wasting.
There are many different types of CM, each with its own set of symptoms and genetic causes. Some of the most common types of CM include:
- Central core disease: This type of CM is characterized by muscle weakness and wasting that typically starts in infancy or early childhood. It is caused by mutations in the RYR1 gene, which is involved in the regulation of calcium release in muscle cells.
- Nemaline myopathy: This is a type of CM that is characterized by muscle weakness and wasting, particularly in the muscles of the face, neck, and limbs. It is caused by mutations in the genes that produce proteins called nebulin, troponin, and tropomyosin, which are important for muscle contraction.
- Centronuclear myopathy: This type of CM is characterized by muscle weakness and wasting, particularly in the muscles of the face, neck, and limbs. It is caused by mutations in the genes that produce proteins that help regulate the movement of muscle fibers.
Diagnosis of CM may involve a combination of physical exams, medical history, and genetic testing. Treatment for CM typically focuses on managing symptoms, which may involve physical therapy to help maintain muscle strength and function, mobility aids such as wheelchairs or braces, and respiratory support for individuals with breathing difficulties.
While there is currently no cure for CM, advances in genetic testing and treatment have improved outcomes for people with the condition, allowing them to better manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Weak muscle tone (hypotonia)
- Muscle weakness
- Weakness
- Facial weakness or numbness
- Drooping eyelid or pupil narrowing
- Muscle cramps
Disease Causes
Congenital myopathies
Congenital myopathies are caused by one or more genetic abnormalities in genes that control muscle development.
Disease Prevents
Congenital myopathies
There's no way to prevent congenital myopathies. If you're at high risk of having a child with a congenital myopathy, you may want to consult a genetic counselor before becoming pregnant.
A genetic counselor can help you understand your chances of having a child with a congenital myopathy. He or she can also explain the prenatal tests that are available and help explain the pros and cons of testing.
Disease Treatments
Congenital myopathies can't be cured, but doctors can help you manage the condition and symptoms. Treatment may include several options.
- Genetic counseling. Genetic counselors may help you understand the genetics of the condition.
- Medications. Medications may help treat symptoms of some myopathies. For example, the drug albuterol (Proair HFA, Ventolin HFA, others) may be helpful in some congenital myopathies.
- Nutritional and respiratory support. Nutritional or respiratory support may be needed as the condition progresses.
- Orthopedic treatments. Orthopedic support devices or other treatments, such as surgery to correct or improve scoliosis or contractures, may be helpful.
- Physical, occupational or speech therapy. Physical, occupational or speech therapy may help manage symptoms. Low-impact aerobic exercise, such as walking and swimming, can help maintain strength, mobility and general health. Some types of strengthening exercises also might be helpful.
- Respiratory therapy. Some patients need respiratory support or respiratory treatments.
In addition to these treatments, some people with congenital myopathies may benefit from an evaluation from an endocrinologist. An endocrinologist can monitor bone health, as bone diseases such as osteopenia and osteoporosis may develop in some people with congenital myopathies.
It's also important to take precautions to prevent respiratory infections. Annual influenza vaccinations and regular pneumonia vaccinations are recommended. Try to avoid contact with anyone who has an obvious respiratory infection.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Congenital myopathies and Learn More about Diseases

Mastitis

Malignant hyperthermia

Bunions
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)

Leprosy

Toxic hepatitis

Premature ejaculation

Congenital myopathies
Congenital myopathies, Nemaline myopathy, জন্মগত মায়োপ্যাথি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.