 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Semicircular canals Inner ear - Diseases
The semicircular canals are a part of the inner ear that plays a critical role in the body's sense of balance and spatial orientation. There are three semicircular canals in each ear, and they are positioned at right angles to each other.
The semicircular canals are filled with a fluid called endolymph and are lined with tiny hair-like structures called cilia. When the head moves, the fluid in the semicircular canals moves as well, which causes the cilia to bend. The movement of the cilia sends signals to the brain that help the body maintain its balance and coordinate its movements.
The semicircular canals work in conjunction with other parts of the inner ear, such as the utricle and saccule, to provide the brain with information about the body's position in space. Collectively, these structures are known as the vestibular system, and they are essential for maintaining balance and preventing falls. Dysfunction of the semicircular canals or other parts of the vestibular system can lead to vertigo, dizziness, and other balance disorders.

Esophagus
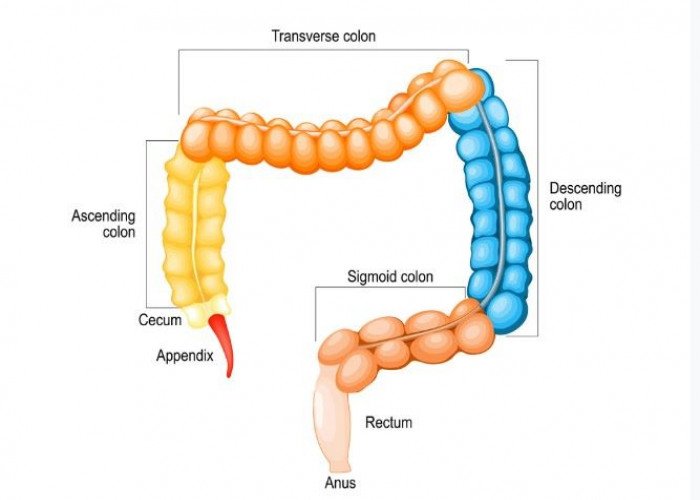
Sigmoid colon intestine

Hip

Lip

Nails
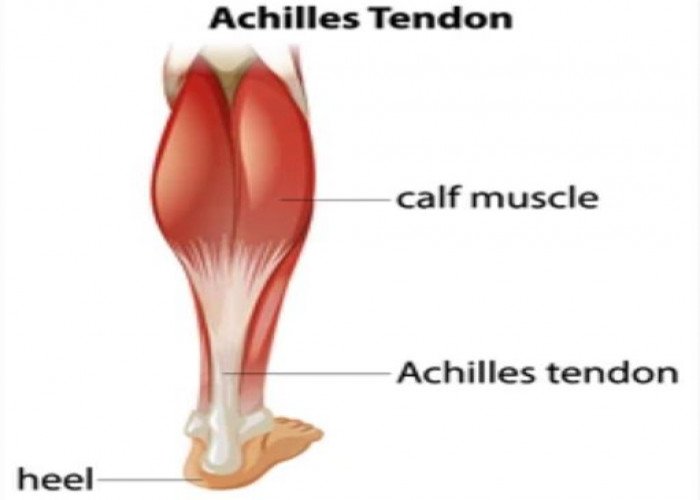
Tendons
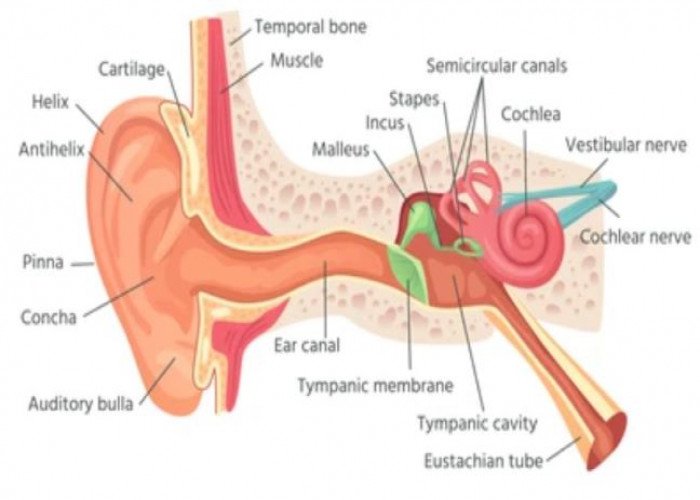
Eardrum
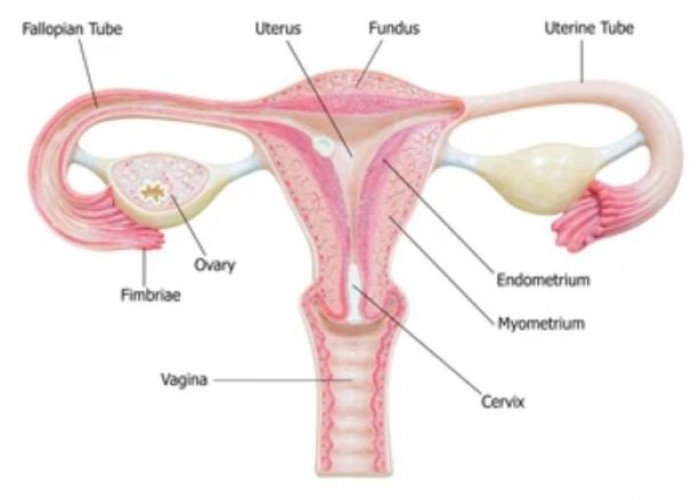
Fallopian tubes
Semicircular canals Inner ear, Inner ear semicircular canals balance, অভ্যন্তরীণ কানের অর্ধবৃত্তাকার চ্যানেল
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.