Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Spine - Diseases
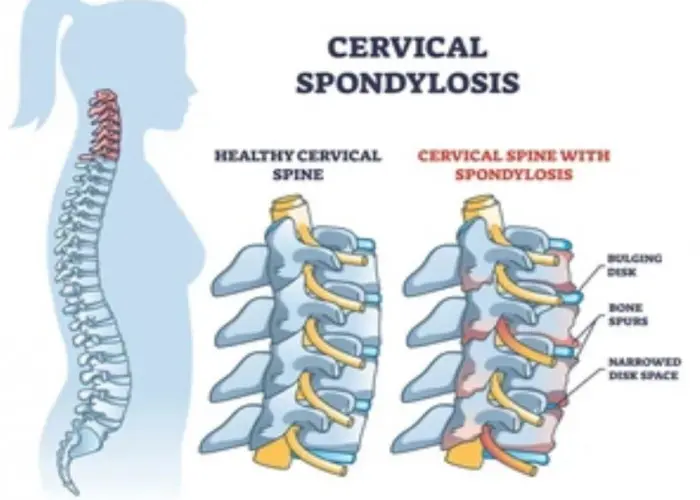
The spine, also known as the vertebral column or backbone, is a flexible and sturdy column of bones that extends from the skull to the pelvis in humans and other vertebrates. The spine is made up of 33 individual vertebrae that are stacked on top of each other and are separated by intervertebral discs.
The spine has four main regions, each with a unique curvature: the cervical spine (neck region), thoracic spine (upper back region), lumbar spine (lower back region), and sacral spine (pelvic region). The spine serves several important functions, including providing support and stability for the body, protecting the spinal cord and nerve roots, and allowing for movement and flexibility.
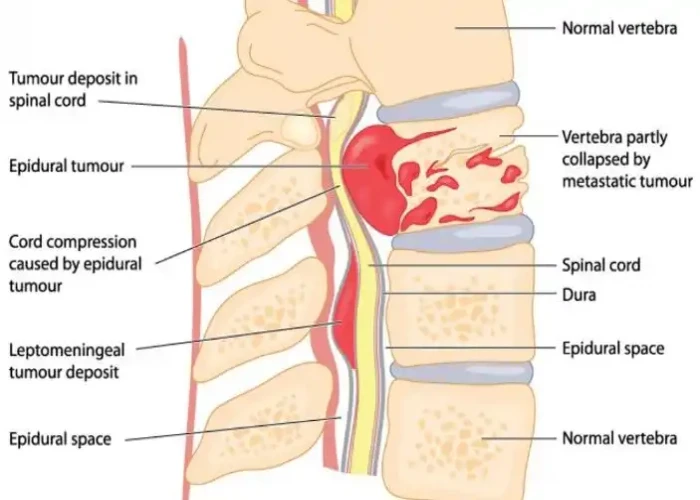
The spinal cord runs through the center of the spine and is surrounded and protected by the vertebrae. The spinal cord is a vital part of the central nervous system, transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
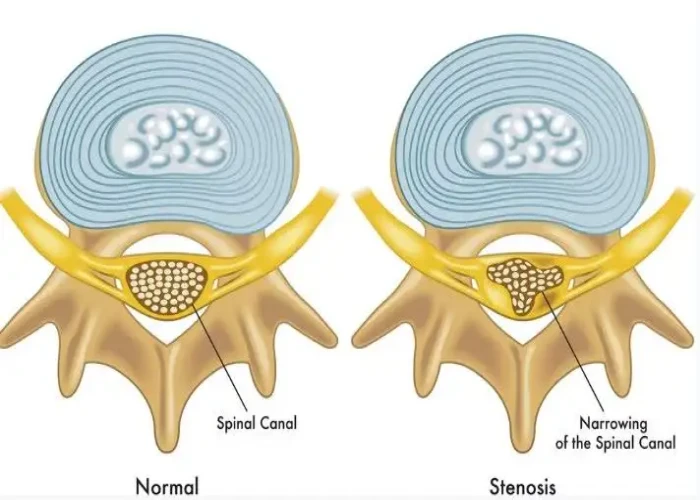
Various conditions and injuries can affect the spine, including spinal fractures, herniated discs, scoliosis, spinal stenosis, and spinal cord injuries. Treatment options for these conditions may include medication, physical therapy, surgery, or a combination of approaches, depending on the severity of the problem.

Taste buds Tongue
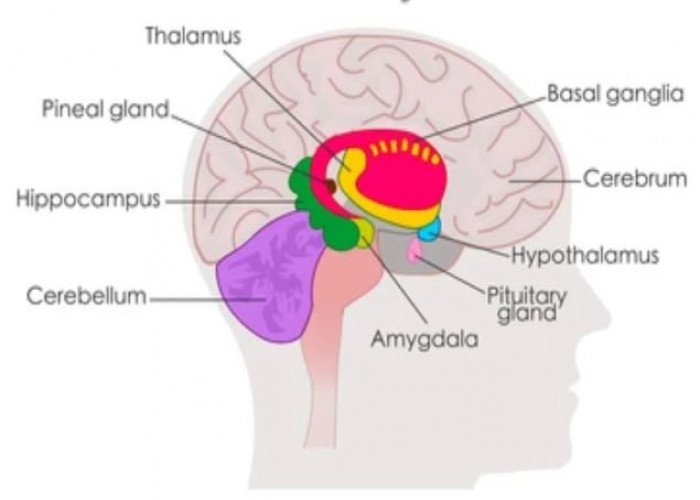
Hypothalamus
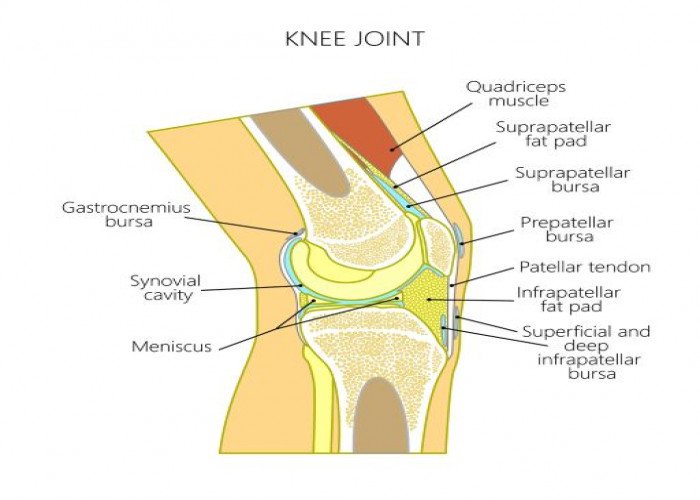
Knee
Colon

Testes

Pharynx

Wrist

N/A
Spine, Spinal cord, Scoliosis, মেরুদণ্ড
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.