 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Ganglion cyst
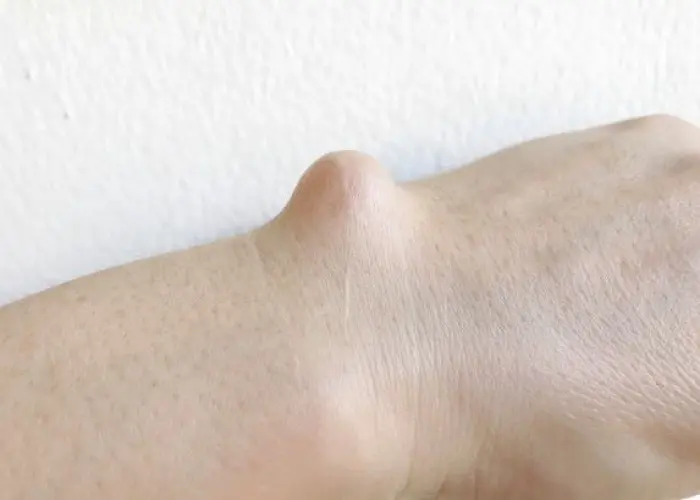
A ganglion cyst is a noncancerous lump or bump that most commonly occurs on the hand or wrist, although it can also appear on the foot, ankle, or knee. Ganglion cysts are typically round or oval in shape and filled with a thick, clear, jelly-like fluid.
The cause of ganglion cysts is not fully understood, but it is believed that they may develop due to a weakness in the joint capsule or tendon sheath, allowing the joint tissue to bulge out and form a cyst. They are more common in women and are most frequently found in people between the ages of 20 and 40.
Most ganglion cysts are painless and do not require treatment. In some cases, they may be associated with mild pain or discomfort, especially if they are in a location that interferes with joint movement. Treatment options may include draining the fluid with a needle or, less commonly, surgical removal. However, even with treatment, ganglion cysts may recur.
It's important to note that while ganglion cysts are usually harmless, any new lump or bump should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to ensure that it is not a sign of a more serious underlying condition.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Ankle problems
- Ganglion cysts usually are painless.
- Cyst presses on nerve even if the cyst is too small to form a noticeable lump it can cause pain, tingling, numbness or muscle weakness.
- Swollen lump or skin nodules
Disease Causes
Ganglion cyst
No one knows exactly what causes a ganglion cyst to develop. It grows out of a joint or the lining of a tendon, looking like a tiny water balloon on a stalk, and seems to occur when the tissue that surrounds a joint or a tendon bulges out of place. Inside the cyst is a thick lubricating fluid similar to that found in joints or around tendons.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Ganglion cysts are often painless, requiring no treatment. Your doctor may suggest a watch-and-wait approach. If the cyst is causing pain or interfering with joint movement, your doctor may recommend:
- Immobilization. Because activity can cause the ganglion cyst to get larger, it may help to temporarily immobilize the area with a brace or splint. As the cyst shrinks, it may release the pressure on your nerves, relieving pain. Avoid long-term use of a brace or splint, which can cause the nearby muscles to weaken.
- Aspiration. In this procedure, your doctor uses a needle to drain the fluid from the cyst. The cyst may recur.
- Surgery. This may be an option if other approaches haven't worked. During this procedure, the doctor removes the cyst and the stalk that attaches it to the joint or tendon. Rarely, the surgery can injure the surrounding nerves, blood vessels or tendons. And the cyst can recur, even after surgery.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Ganglion cyst and Learn More about Diseases
Strep throat
Myofascial pain syndrome
Gastritis
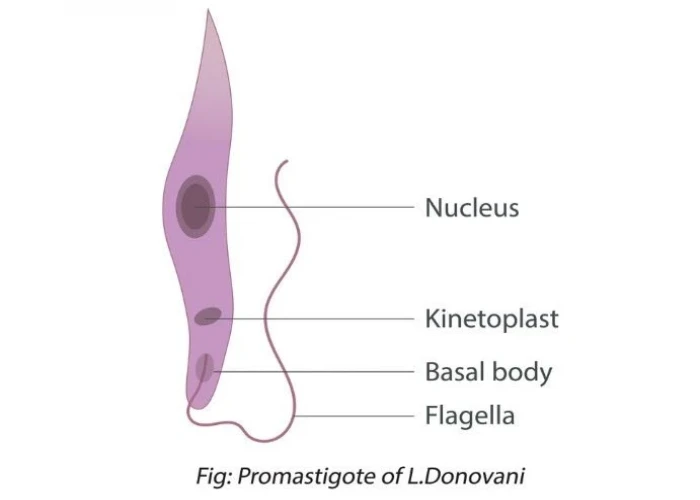
Kala Azar

Retention of Urine
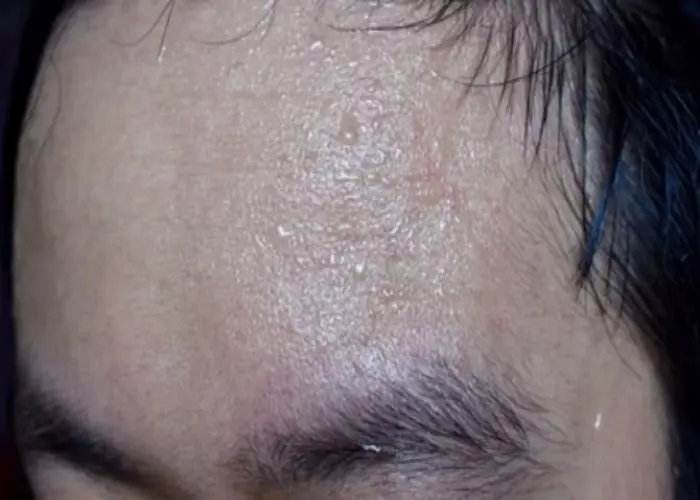
Anhidrosis

Sprained ankle

Schizoid personality disorder
ganglion cyst, গ্যাংলিয়ন সিস্ট
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
