Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
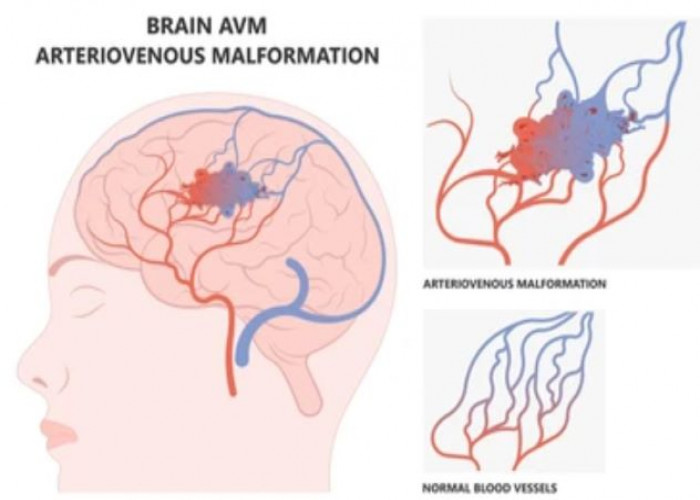
Brain AVM (arteriovenous malformation)

A brain arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain. This condition occurs when the connections between arteries and veins in the brain are not formed properly, and can lead to various complications such as bleeding, seizures, and neurological deficits. Symptoms of a brain AVM can include headache, seizures, weakness or numbness, and vision or speech changes. Treatment for a brain AVM may depend on factors such as the size, location, and severity of the AVM. It can include medication, surgery, embolization, or radiation therapy. Early diagnosis and treatment of a brain AVM is important in order to prevent or minimize potential complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Seizures
- The effects slowly build up and often cause symptoms in early adulthood.
- Brain AVMs can damage brain tissue over time.
- Symptoms may begin at any age but usually emerge between ages 10 and 40.
- Confusion or inability to understand others
- Muscle weakness or numbness in one part of the body
- Headache or pain in one area of the head
- Difficulty speaking
- Numbness
- Muscle weakness
- Headaches
- Once reach middle age, however, brain AVMs tend to remain stable and are less likely to cause symptoms.
Disease Causes
Brain AVM (arteriovenous malformation)
The cause of brain AVM is unknown, but researchers believe most brain AVMs emerge during fetal development.
Normally, your heart sends oxygen-rich blood to your brain through arteries. The arteries slow blood flow by passing it through a series of progressively smaller networks of blood vessels, ending with the smallest blood vessels (capillaries). The capillaries slowly deliver oxygen through their thin, porous walls to the surrounding brain tissue.
The oxygen-depleted blood then passes into small blood vessels and then into larger veins that drain the blood from your brain, returning it to your heart and lungs to get more oxygen.
The arteries and veins in an AVM lack this supporting network of smaller blood vessels and capillaries. Instead, the abnormal connection causes blood to flow quickly and directly from your arteries to your veins, bypassing the surrounding tissues.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
There are several potential treatment options for brain AVM. The main goal of treatment is to prevent hemorrhage, but treatment to control seizures or other neurological complications also may be considered.
Your doctor will determine the most appropriate treatment for your condition, depending on your age, health, and the size and location of the abnormal blood vessels.
Medications also may be used to treat symptoms caused by the AVM, such as headaches or seizures.
Surgery is the most common treatment for brain AVMs. There are three different surgical options for treating AVMs:
- Surgical removal (resection). If the brain AVM has bled or is in an area that can easily be reached, surgical removal of the AVM via conventional brain surgery may be recommended. In this procedure, your neurosurgeon removes part of your skull temporarily to gain access to the AVM.
- With the help of a high-powered microscope, the surgeon seals off the AVM with special clips and carefully removes it from surrounding brain tissue. The surgeon then reattaches the skull bone and closes the incision in your scalp.
- Resection is usually done when the AVM can be removed with little risk of hemorrhage or seizures. AVMs that are in deep brain regions carry a higher risk of complications. In these cases, your doctor may recommend other treatments.
- Endovascular embolization. In this procedure, your doctor inserts a long, thin tube (catheter) into a leg artery and threads it through blood vessels to your brain using X-ray imaging.
- The catheter is positioned in one of the feeding arteries to the AVM, and injects an embolizing agent, such as small particles, a glue-like substance, microcoils or other materials, to block the artery and reduce blood flow into the AVM.
- Endovascular embolization is less invasive than traditional surgery. It may be performed alone, but is frequently used prior to other surgical treatments to make the procedure safer by reducing the size of the AVM or the likelihood of bleeding.
- In some large brain AVMs, endovascular embolization may be used to reduce stroke-like symptoms by redirecting blood back to normal brain tissue.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). This treatment uses precisely focused radiation to destroy the AVM. It is not surgery in the literal sense because there is no incision.
- Instead, SRS directs many highly targeted radiation beams at the AVM to damage the blood vessels and cause scarring. The scarred AVM blood vessels then slowly clot off in one to three years following treatment.
- This treatment is most appropriate for small AVMs that are difficult to remove with conventional surgery and for those that haven't caused a life-threatening hemorrhage.
If you have few or no symptoms or if your AVM is in an area of your brain that's hard to treat, your doctor may prefer to monitor your condition with regular checkups.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Brain AVM (arteriovenous malformation) and Learn More about Diseases
Hamstring injury

Gastrogenous Diarrhoea

Leprosy

Trichotillomania (hair-pulling disorder)

Laryngitis

Bronchiectasis

Carbon monoxide poisoning
Burns
Brain avm, Arteriovenous malformation, AVM medical abbreviation, মস্তিষ্কের এভিএম, আর্টেরিওভেনাস বিকৃতি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.